
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is to be identified as
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 14.11P
The given molecule is nonaromatic.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given molecule is
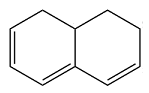
In the given compound, six carbon atoms are
Because of the
Therefore, this molecule is nonaromatic.
The presence of four
(b)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is to be identified as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic.
Concept introduction:
Huckel’s rule for aromaticity states that if a species is planar and possesses a
Answer to Problem 14.11P
The given molecule is aromatic.
Explanation of Solution
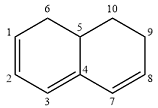
Structure of the given molecule is
In this molecule, six carbon atoms are
Therefore, the given molecule is aromatic.
The presence of six
(c)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is to be identified as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic.
Concept introduction:
Huckel’s rule for aromaticity states that if a species is planar and possesses a
Answer to Problem 14.11P
The given molecule is nonaromatic.
Explanation of Solution
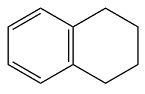
Structure of the given molecule is
In the given compound, four carbon atoms are
Therefore, the given molecule is nonaromatic.
The presence of one
(d)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is to be identified as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic.
Concept introduction:
Huckel’s rule for aromaticity states that if a species is planar and possesses a
Answer to Problem 14.11P
The given molecule is nonaromatic.
Explanation of Solution
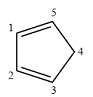
Structure of the given molecule is
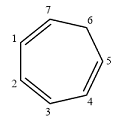
In the given compound, six carbon atoms are
Therefore, the given molecule is nonaromatic.
The presence of one
(e)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is to be identified as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic.
Concept introduction:
Huckel’s rule for aromaticity states that if a species is planar and possesses a
Answer to Problem 14.11P
The given molecule is nonaromatic.
Explanation of Solution
Structure of the given molecule is
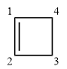
In the given compound, two carbon atoms are
Therefore, the given molecule is nonaromatic.
The presence of two
(f)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is to be identified as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic.
Concept introduction:
Huckel’s rule for aromaticity states that if a species is planar and possesses a
Answer to Problem 14.11P
The given molecule is nonaromatic.
Explanation of Solution
Structure of the given molecule is
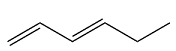
The molecule is not a cyclic system.
Therefore, the given molecule is nonaromatic.
Non-cyclic form of the given molecule indicates that the molecule is nonaromatic.
(g)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is to be identified as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic.
Concept introduction:
Huckel’s rule for aromaticity states that if a species is planar and possesses a
Answer to Problem 14.11P
The given molecule is aromatic.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given molecule is
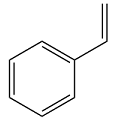
The molecule has a cyclic part with alternating single and double bonds. This means all ring atoms are
Therefore, this molecule is aromatic.
The presence of six
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- (12) Which one of the following statements about fluo- rometry is FALSE? a) Fluorescence is better detected at 90 from the exci- tation direction. b) Fluorescence is typically shifted to longer wave- length from the excitation wavelength. c) For most fluorescent compounds, radiation is pro- duced by a transitionarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
