
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Hydrogen that can be exchanged with deuterium in a solution of
Concept Introduction:
Tautomerism is the ability of a molecule to exist in more than one chemical form. Tautomers are formed by the migration of a hydrogen atom, accompanied by the switching of a single and neighboring double bond.
The only difference in keto-enol tautomer is the location of hydrogen and double bond.

(b)
Interpretation:
Hydrogen that can be exchanged with deuterium in a solution of
Concept Introduction:
Tautomerism is the ability of a molecule to exist in more than one chemical form. Tautomers are formed by the migration of a hydrogen atom, accompanied by the switching of a single and neighboring double bond.
The only difference in keto-enol tautomer is the location of hydrogen and double bond.

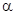 -carbon is the carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon.
-carbon is the carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon.
(c)
Interpretation:
Hydrogen that can be exchanged with deuterium in a solution of
Concept Introduction:
Tautomerism is the ability of a molecule to exist in more than one chemical form. Tautomers are formed by the migration of a hydrogen atom, accompanied by the switching of a single and neighboring double bond.
The only difference in keto-enol tautomers is the location of hydrogen and double bond.

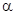 -carbon is the carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon.
-carbon is the carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry (3rd Edition)
- Give detailed Solution with explanation needed..arrow_forwardWhat two components are needed to prepare para red by azo coupling?arrow_forwardCompounds A, B, and C are isomers of xylene (dimethylbenzene). When each of these isomers undergoes a single nitration, compound A produces just one product, B produces a mixture of two products, and C produces a mixture ofthree products. Identify which of compounds A, B, and C is the ortho isomer, which is the meta isomer, and which is the para isomer.arrow_forward
- Which group elements show maximum catalytic activity for hydrogenationreactions?arrow_forwardWhich of the following compounds can be prepared by radical halogenation with minimum complication due to the formation o isomeric by-products? CI Br Br Br CIarrow_forwardWhat is the best choice of solvent for the formation of phenylmagnesium bromide by the reaction of bromobenzene with magnesium? Explain whyarrow_forward
- The reaction of CH3CH2NH3+ Cl− with aqueous sodium hydroxide will give an organic product of?arrow_forwardWhat is the oxidation number of P in H3PO3 (OR H3 P O3)?arrow_forward[Rh(PPh3)3Cl] is a precatalyst that can be activated by dissociation of a phosphine ligand to form an active catalyst, B, which is used in the hydrogenation of alkenes. The active catalyst can then undergo oxidative addition in the presence of H2 to form complex C. Propene coordinates to C to form complex D, which then undergoes a 1,2- insertion step to form E. Reductive elimination of propane from E regenerates the active catalyst B. Draw complexes B – E and hence provide a full catalytic cycle, including the activation step, for the hydrogenation of propenearrow_forward
- Describe the species that would result from the subsequent transfer of the proton from the metal to one of the Cp rings of ferrocene. Give the formal oxidation state of the metal centre and the valence electron countarrow_forwardOzonolysis of one mole of the compound shown is expected to produce how many moles of CO, upon completion of the reaction?arrow_forwardPCl5 reacts with finely divided silver on heating and a white silver salt is obtained, which dissolves on adding excess aqueous NH3 solution. Write the reactions involved to explain what happensarrow_forward
 Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
