
Concept explainers
(a) Interpretation:
Assuming the solution containing the 5
Concept introduction:
Pyruvate produced in glycolysis of glucose is oxidised to carbon dioxide and water through a sequence of complicated reaction cycle, popularly named as Krebs cycle. Citric acid and some other tricarboxylic acids occur in the intermediate steps of this reaction sequence, hence the name citric acid cycle and tricarboxylic acid cycle are also given. It is through this cycle of reactions that all food stuff and nutrients are completely oxidised in the cell. All food stuff including carbohydrate must be converted to pyruvate or some other intermediate products for theiroxidation to carbon dioxide and water.
Pictorial representation:
The citric acid cycle with all the reagent and enzymes and metabolic enzymes can be shown as follows:
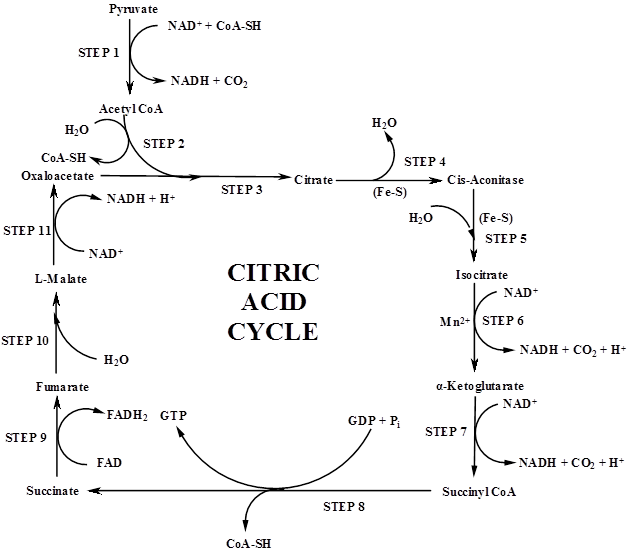
Figure: Citric acid cycle
(b) Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Pyruvate produced in glycolysis of glucose is oxidised to carbon dioxide and water through a sequence of complicated reaction cycle, popularly named as Krebs cycle. Citric acid and some other tricarboxylic acids occur in the intermediate steps of this reaction sequence; hence the name citric acid cycle and tricarboxylic acid cycle are also given. It is through this cycle of reactions that all food stuff and nutrients are completely oxidised in the cell. All food stuff including carbohydrate must be converted to pyruvate or some other intermediate products for theiroxidation to carbon dioxide and water.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





