
Concept explainers
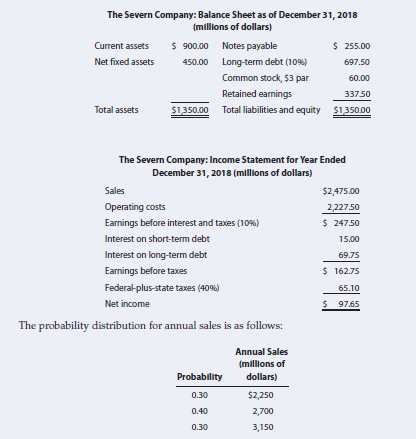
The Severn Company plans to raise a net amount of
$270 million to finance new equipment in early 2019. Two alternatives are being considered:
Common stock may be sold to net $60 per share, or bonds yielding 12% may be issued.
The
follows:
Assuming that EBIT equals 10% of sales, calculate earnings per share (EPS) under the debt
financing and the stock financing alternatives at each possible sales level. Then calculate
expected EPS and σEPS under both debt and stock financing alternatives. Also calculate the
debt-to-capital ratio and the times-interest-earned (TIE) ratio at the expected sales level
under each alternative. The old debt will remain outstanding. Which financing method do
you recommend? (Hint: Notes payable should be included in both the numerator and the
denominator of the debt-to-capital ratio.)
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 7 steps with 15 images

- For the year ended 2020, Frilo Company has $1,250,000 of debt with an annual interest rate of 8.8%, $2,000,000 of preferred stock with an annual preferred dividend rate of 10.5%, $3,500,000 of common stock (total book value), and 250,000 common shares outstanding. In 2021, the company plans to raise $500,000 external capital to fund a new project through a term loan with an interest rate of 9.3%. The new loan's sinking fund provision requires the loan to be fully amortized over the next 5 years, commencing in 2022. The company expects that the existing debt and preferred stock will not be retired until the year 2026; hence, they will remain in the same amount in 2021. If the project goes as planned, the company expects $1,200,000 of EBIT in 2021. The company's tax rate is 40%. What will the expected earnings per share under the new debt alternative be? (Hint: Perform EBIT-EPS Analysis in the long-term financing decisions.) Group of answer choices $1.58 $1.66 $1.55 $1.51…arrow_forwardAuto Motors Plc is a listed automotive company financed by a mixture of debt and equity. The company’s finance department is about to undertake its annual revision of the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) for use in all of the company’s investment appraisals for the forthcoming year. The following information on the company’s long-term financing was available as at 31 May 2023. £m 220 million ordinary shares of 25 pence each 55 Share premium 23 Revaluation reserve 26 Retained earnings 33 12% loan stock (2025) 100 The loan stock interest for the year has just been paid. Interest on this loan will be paid on 31 May 2024 and 2025. On 31st of May 2025,…arrow_forwardToefungus Ltd. issued $8,000,000 face value bonds, with an interest rate of 4.0 %, on July 1, 2020. The bonds mature in seven years time, on July 1, 2027 and pay interest semi-annually on July 1 and January 1. The company’s financial advisors have indicated that the yield the market is expecting to receive on their investment is 3.5 %. Toefungus Ltd. has a December 31 year end for financial and tax reporting and uses straight line amortization for allocating premium or discount. Required: a. Calculate the issue price for the bond. Show all steps and calculations. b. Prepare all journal entries required to account for bond transactions during the first full year the bond is outstanding. c. Clearly disclose all information related to this bond that would appear in the Company’s 2020 year-end financial statements.arrow_forward
- The balance sheet at December 31, 2024, for Nevada Harvester Corporation includes the liabilities listed below: a. 7% bonds with a face amount of $46 million were issued for $46 million on October 31, 2015. The bonds mature on October 31, 2035. Bondholders have the option of calling (demanding payment on) the bonds on October 31, 2025, at a redemption price of $46 million. Market conditions are such that the call is not expected to be exercised. b. Management intended to refinance $6.6 million of its 14% notes that mature in May 2025. In early March, prior to the actual issuance of the 2024 financial statements, Nevada Harvester negotiated a line of credit with a commercial bank for up to $4.6 million any time during 2025. Any borrowings will mature two years from the date of borrowing. c. Noncallable 6% bonds with a face amount of $14.5 million were issued for $14.5 million on September 30, 2005. The bonds mature on September 30, 2025. Sufficient cash is expected to be available to…arrow_forwardOn December 31, 2018, Marsh Company held Xenon Company bonds in its portfolio of available-for-sale securities. The bonds have a par value of $14,000, carry a 10% annual interest rate, mature in 2025, and had originally been purchased at par. The market value of the bonds at December 31, 2018 was $12,000. The December 31, 2018, balance sheet showed the following: Marsh Company Partial Balance Sheet December 31, 2018 1 Assets 2 Investment in Available-for-Sale Securities $14,000.00 3 Less: Allowance for Change in Fair Value of Investment (2,000.00) 4 $12,000.00 5 Shareholders’ Equity: 6 Unrealized Holding Gain/Loss $(2,000.00) On January 1, 2019, Marsh acquired bonds of Yellow Company with a par value of $16,000 for $16,200. The Yellow Company bonds carry an annual interest rate of 12% and mature on December 31, 2023. Additionally, Marsh acquired Zebra Company bonds with a face value of 19,000 for…arrow_forwardOn March 1, 2024, Baddour, Incorporated, issued 10% bonds, dated January 1, with a face amount of $160 million. The bonds were priced at $142.00 million (plus accrued interest) to yield 12%. The price if issued on January 1 would have been $139.25 million. Interest is paid semiannually on June 30 and December 31. Baddour’s fiscal year ends September 30. Required: 1. to 3. What would be the amount(s) related to the bonds Baddour would report in its balance sheet, income statement and statement of cash flows for the year ended September 30, 2024?arrow_forward
- On January 1, 2021, Ithaca Corp. purchases Cortland Inc. bonds that have a face value of $210,000. The Cortland bonds have a stated interest rate of 10%. Interest is paid semiannually on June 30 and December 31, and the bonds mature in 10 years. For bonds of similar risk and maturity, the market yield on particular dates is as follows: (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.): January 1, 2021 11.0 % June 30, 2021 12.0 % Required:1. Calculate the price Ithaca would have paid for the Cortland bonds on January 1, 2021 (ignoring brokerage fees), and prepare a journal entry to record the purchase.2. Prepare all appropriate journal entries related to the bond investment during 2021, assuming Ithaca accounts for the bonds as a held-to-maturity investment. Ithaca calculates interest revenue at the effective interest rate as of the date it purchased the bonds.3. Prepare all appropriate…arrow_forwardOn January 1, 2020, Blossom Ltd. issued 820 5-year, 11% convertible bonds at par of $1,000, with interest payable each December 31. Each bond is convertible into 100 common shares, and the current fair value of each common share is $6. Similar straight bonds carry an interest rate of 13%. Calculate the PV of the debt component by itself. Calculate using any of the following methods: (1) factor tables, (2) a financial calculator, or (3) Excel function PV. QUESTION: 1) PV of the debt component 2) How should Blossom record the issuance if it follows IFRS? Use the amount you arrived at in part (a) using a financial calculator or Excel. Date Account Titles and Explanation January 1 enter an account title enter an account title January 1 enter an account title Date Account Titles and Explanation enter an account title Debit 3) How should Blossom record the issuance if it follows ASPE? enter an account title enter a debit amount enter a credit amount Credit enter a debit amount enter a credit…arrow_forward[The following information applies to the questions displayed below] On January 1, 2021, Wild Rapids Water Park issues $40.0 million of 8% bonds to finance expansion. The bonds are due in 15 years, with interest payable semiannually on June 30 and December 31 each year. Required: 1-a. If the market rate is 7%, calculate the issue price (PV of $1. PV of $1, FVA of $1, and PVA of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided. Do not round interest rate factors. Enter your answers in dollars not in millions. Round "Market interest rate" to 1 decimal place. Round your final answers to the nearest whole dollar.) Bond Characteristics Amount Face amount 40,000,000 Interest payment Periods to maturity Market interest rate Issue price 1-b. The bonds will issue at OA Discount OA Premium O Face amountarrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





