
Concept explainers
The chapter sections to review are shown in parentheses at the end of each problem.
12.87 Match the diagrams with the following: (12.1)
a. a polar solute and a polar solvent
b. a nonpolar solute and a polar solvent
c. a nonpolar solute and a nonpolar solvent
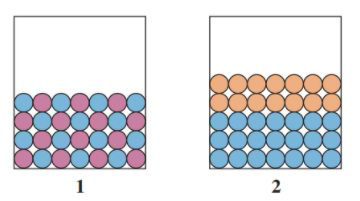 c
c
Interpretation:
The problem shows two diagrams with different type of solute-solvents.
Concept introduction:
- Like dissolves like is typically true between species
- Polar-polar solvents will always mix as well as Nonpolar-nonpolar solvents
- Nonpolar-Polar mixture will never mix, will form two phases.
To Match:The diagrams which shows the best option.
Answer to Problem 87UTC
Solution:
- 1
- 2
- 1
Explanation of Solution
There are different type of interaction between polar-polar, nonpolar-nonpolar and nonpolar-polar species. Therefore, one must ensure that the solute and solvent are well defined.
The solute is always in smaller amount than the solvent. Image (1) states an uniform mixture of species, whereas image (2) shows two phase, no mixture.
For any given mixture, there must be then either a polar-polar or a nonpolar-nonpolar solute/solvent system.
Image (2) shows the only combination possible, a nonpolar-polar mixture.
Always ensure to identify the solute, solvent and the type of interaction between them.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Basic Chemistry
- Write A if the compound is soluble/miscible in water and B if not 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.arrow_forward11. What is the molarity of the mixture of two solution, first solution 4 M and 10 liter and second solution 2 M and 40 liter? (2 Points) 1.2 M 2.4 M 4.8 M 9.2 Marrow_forward9.56 Calculate the final concentration of each of the following: a. 1.0 L of a 4.0 M HNO, solution is added to water so that the final volume is 8.0 L. b. Water is added to 0.25 L of a 6.0 M NaF solution to make 2.0 L of a diluted NaF solution. c. A 50.0-mL sample of an 8.0% (m/v) KBr solution is diluted with water so that the final volume is 200.0 mL. d. A 5.0-mL sample of a 50.0% (m/v) acetic acid (HC,H,O2) solution is added to water to give a final volume of 25 mL.arrow_forward
- 4. 3.2 g of non-volatile, nonelectrolyte solute is dissolved in 70 g of water. The resulting vapor pressure is 26.75 mmHg. If the vapor pressure of pure solvent in the condition is 28.95 mmHg and the density of the solution is 0.98 g/ml, find the following for the solution: a. osmotic pressure at 40°C b. boiling point of solution c. freezing point of solutionarrow_forward(14.6) Which of the following aqueous solution has the highest boiling point? O 1.00 M NaCl O 1.00 M Ca(NO3)2 O 1.00 M C6H1206 O 1.00 M NaNO3arrow_forwardMatch the following aqueous solutions with the appropriate letter from the column on the right. 1. 2. 3. 4. 0.130 m 0.165 m 0.150 m 0.360 m Mn(CH3COO)2 KOH MgSO4 Glucose (nonelectrolyte) A. Highest boiling point Second highest boiling point C. Third highest boiling point D. Lowest boiling point B.arrow_forward
- anchPad G Google O Hudl O Football Pics BIM - 1st Art 1- 2nd A WoHistory 4th AAlg2-5th A English - 6th Chem 4. 6. 7 8. 9. 10 What is the molarity of a solution containing 15.0 g of sodium hydroxide dissolved in 1.00 L of solution? Molar mass of NaOH is 40.0 grams/mole. SHOW YOUR WORK 8 10 Show Your Work 0.500 M moles 0.400 M M= 0.200 M Liter 0.374 M What is the total number of moles of NaCl(s) needed to make 1.5 liters of a 2.0 M NaCl solution? SHOW YOUR WORK 9. 10 Show Your Work 1.3 mol 5 2,269 MAY 12arrow_forward11.2 If 56.1 grams of NaCl are dissolved in 44.0 mL of Sulfuric acid, H2SO4 Sulfuric acid has a density of 1.84 grams per mL. How do I calculate the g concentration measures of: a) Weight/weight percent b) Molarityarrow_forward4.8arrow_forward
- 9.44 For each of the following solutions, calculate the: a. grams of 2.0% (m/m) NaCl solution that contains 7.50 g of NaCl b. milliliters of 25% (m/v) NaF solution that contains 4.0 g of NaF c. milliliters of 8.0% (v/v) ethanol solution that contains 20.0 mL of ethanolarrow_forward9.69 Are the following solutions isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic compared with a red blood cell? a. distilled H,O c. 0.9% (m/v) NaCl b. 1% (m/v) glucose d. 15% (m/v) glucosearrow_forwardPage 5. Calculate the molarity for each of the following solutions. (6 points) a. Dissolving 45.1 moles of KCl into 1005 ml of solution. b. Dissolving 45.1 grams of KCa into 115 mL of solution.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





