
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
7th Edition
ISBN: 8220102804487
Author: BEER
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 1.2, Problem 17P
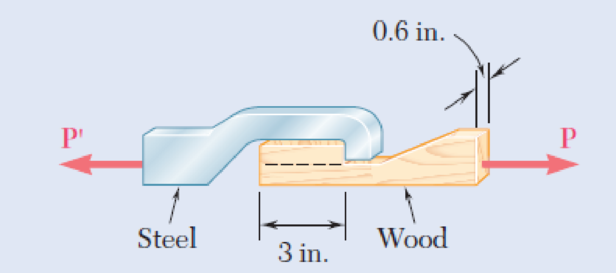
When the force P reached 1600 lb, the wooden specimen shown failed in shear along the surface indicated by the dashed line. Determine the average shearing stress along that surface at the time of failure.
Fig. P1.17
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
1.26 part B thanks
1.16 Two wooden planks, each 12 mm thick and 225 mm wide, are
joined by the dry mortise joint shown. Knowing that the wood
used shears off along its grain when the average shearing stress
reaches 8 MPa, determine the magnitude P of the axial load that
will cause the joint to fail.
16 mm
16 mm
25 mm
50 mm
Pl
P'
50 mm
25 mm
295 mm
Fig. P1.16
.29 Two wooden members of uniform rectangular cross section
are joined by the simple glued scarf splice shown. Knowing that
P= 11 kN, determine the normal and shearing stresses in the
glued splice.
150 mm
15
75 mm
Fig. P1.29 and P1.30
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 1.2 - Two solid cylindrical rods AB and BC are welded...Ch. 1.2 - Two solid cylindrical rods AB and BC are welded...Ch. 1.2 - Two solid cylindrical rods AB and BC are welded...Ch. 1.2 - Two solid cylindrical rods AB and BC are welded...Ch. 1.2 - A strain gage located at C on the surface of bone...Ch. 1.2 - Two brass rods AB and BC, each of uniform...Ch. 1.2 - Each of the four vertical links has an 8 36-mm...Ch. 1.2 - Link AC has a uniform rectangular cross section 18...Ch. 1.2 - Three forces, each of magnitude P = 4 kN, are...Ch. 1.2 - Link BD consists of a single bar 1 in. wide and 12...
Ch. 1.2 - For the Pratt bridge truss and loading shown,...Ch. 1.2 - The frame shown consists of four wooden members,...Ch. 1.2 - An aircraft tow bar is positioned by means of a...Ch. 1.2 - Two hydraulic cylinders are used to control the...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the diameter of the largest circular...Ch. 1.2 - Two wooden planks, each 12 in. thick and 9 in....Ch. 1.2 - When the force P reached 1600 lb, the wooden...Ch. 1.2 - A load P is applied to a steel rod supported as...Ch. 1.2 - The axial force in the column supporting the...Ch. 1.2 - Three wooden planks are fastened together by a...Ch. 1.2 - A 40-kN axial load is applied to a short wooden...Ch. 1.2 - An axial load P is supported by a short W8 40...Ch. 1.2 - Link AB, of width b = 2 in. and thickness t=14...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the largest load P that can be applied...Ch. 1.2 - Knowing that = 40 and P = 9 kN, determine (a) the...Ch. 1.2 - The hydraulic cylinder CF, which partially...Ch. 1.2 - For the assembly and loading of Prob. 1.7,...Ch. 1.2 - Two identical linkage-and-hydraulic-cylinder...Ch. 1.5 - Two wooden members of uniform rectangular cross...Ch. 1.5 - Two wooden members of uniform rectangular cross...Ch. 1.5 - The 1.4-kip load P is supported by two wooden...Ch. 1.5 - Two wooden members of uniform cross section are...Ch. 1.5 - A centric load P is applied to the granite block...Ch. 1.5 - A 240-kip load P is applied to the granite block...Ch. 1.5 - A steel pipe of 400-mm outer diameter is...Ch. 1.5 - A steel pipe of 400-mm outer diameter is...Ch. 1.5 - A steel loop ABCD of length 5 ft and of 38-in....Ch. 1.5 - Link BC is 6 mm thick, has a width w = 25 mm, and...Ch. 1.5 - Link BC is 6 mm thick and is made of a steel with...Ch. 1.5 - Members AB and BC of the truss shown are made of...Ch. 1.5 - Members AB and BC of the truss shown are made of...Ch. 1.5 - Link AB is to be made of a steel for which the...Ch. 1.5 - Two wooden members are joined by plywood splice...Ch. 1.5 - For the joint and loading of Prob. 1.43, determine...Ch. 1.5 - Three 34-in.-diameter steel bolts are to be used...Ch. 1.5 - Three steel bolts are to be used to attach the...Ch. 1.5 - A load P is supported as shown by a steel pin that...Ch. 1.5 - A load P is supported as shown by a steel pin that...Ch. 1.5 - A steel plate 14 in. thick is embedded in a...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the factor of safety for the cable...Ch. 1.5 - Link AC is made of a steel with a 65-ksi ultimate...Ch. 1.5 - Solve Prob. 1.51, assuming that the structure has...Ch. 1.5 - Each of the two vertical links CF connecting the...Ch. 1.5 - Solve Prob. 1.53, assuming that the pins at C and...Ch. 1.5 - In the structure shown, an 8-mm-diameter pin is...Ch. 1.5 - In an alternative design for the structure of...Ch. 1.5 - Prob. 57PCh. 1.5 - The Load and Resistance Factor Design method is to...Ch. 1 - In the marine crane shown, link CD is known to...Ch. 1 - Two horizontal 5-kip forces are applied to pin B...Ch. 1 - For the assembly and loading of Prob. 1.60,...Ch. 1 - Two steel plates are to be held together by means...Ch. 1 - A couple M of magnitude 1500 N m is applied to...Ch. 1 - Knowing that link DE is 18 in. thick and 1 in....Ch. 1 - A 58-in.-diameter steel rod AB is fitted to a...Ch. 1 - In the steel structure shown, a 6-mm-diameter pin...Ch. 1 - Prob. 67RPCh. 1 - A force P is applied as shown to a steel...Ch. 1 - The two portions of member AB are glued together...Ch. 1 - The two portions of member AB are glued together...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 125 mm 75 mm 1,32 Two wooden members of uniform cross section are joined by the simple scarf splice shown. Knowing that the maximum allowable tensile stress in the glued splice is 500 kPa, determine (a) the largest load P that can be safely supported, (b) the corresponding shearing stress in the splice. 60" P' P1.32arrow_forward1. A circular piece of wood, 90mm in diameter, is used as a compression block. Determine the axial force F that can be safely applied to the block if the compressive stress in wood is limited to 20MPA and the shearing stress parallel to the grain is limited to 5MPA. The grain makes an angle of 15° with the vertical.arrow_forward1.3 (A). Define the terms shear stress and shear strain, illustrating your answer by means of a simple sketch. (Two circular bars.) one of brass and the other of steel, are to be loaded by a shear load of 30 kN. Determine(the necessary diametet of the bars (a) in single shear, (b) in double shear, if the shear stress in the two materials must not exceed 50 MN/m and 100 MN/m respectively. Ans: [27.6, 19.5, 19.5, 13.8mm.]arrow_forward
- 1,45 Three 18 mm diameter steel bolts are to be used to attach the steel plate shown to a wooden beam. Knowing that the plate will support a 1100 AN load and that the ultimate shearing stress for the steel used is 360 MPa, determine the factor of safety for this design. Fig. P1.45 and P1.46arrow_forwardDraw and label the diagram correctly.Show the complete solution and write it legiblyarrow_forwardDraw and label the diagram correctly.Show the complete solutionarrow_forward
- 1.35 A steel pipe of 400-mm outer diameter is fabricated from 10-mm- thick plate by welding along a helix that forms an angle of 20° with a plane perpendicular to the axis of the pipe. Knowing that a 300-kN axial force P is applied to the pipe, determine the nor- mal and shearing stresses in directions respectively normal and tangential to the weld. 10 mm Weld -20° Fig. P1.35 and P1.36arrow_forwardcan you draw the 2 Free body diagram where the shearing force is acting on the plate and the rod respectively. I do not understand why the shearing area is pi*t*darrow_forwardA rectangular block of a material with a modulus of rigidity G= 90 ksi is bonded to two rigid horizontal plates. The lower plate is fixed, while the upper plate is subjected to a horizontal force P . Knowing that the upper plate moves through 0.04 in. under the action of the force, determine (a) the average shearing strain in the material and (b) the force Pexerted on the upper plate.arrow_forward
- Only 1.35 plzarrow_forwardPart 1 please, refer to the image.... PART 2 Determine the shear force acting at each of the following locations: (a) x = 2m (b) x = 6m (c) x = 9m (d) x = 12m Answer: (a) V= ________________kN (b) V= ________________kN (c) V= ________________kN (d) V= ________________kN PART 3 Determine the bending moment acting at each of the following locations: (a) x=4m (b) x = 8 m (c) x = 10 m When entering your answers, use the bending moment sign convention. Answers: (a) M= ________________kN-m (b) M= ________________kN-m (c) M= ________________kN-marrow_forwardA chain block is hanged on a pin which is supported by plates on both side as shown. If the maximum safe load capacity is 3000 lb, determine (a) the shearing stress on the shaft having a diameter of 1.75 in. (b) and the thickness of the plates if the bearing stress on the plates is 20% greater than the shearing stress.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Understanding Failure Theories (Tresca, von Mises etc...); Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xkbQnBAOFEg;License: Standard youtube license