
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the reaction in Equation 12-17 is as follows, but the curved arrows have been omitted. The mechanism by drawing in the curved arrows is to be completed. Also, the name of each elementary step below the appropriate reaction arrow is to be written.
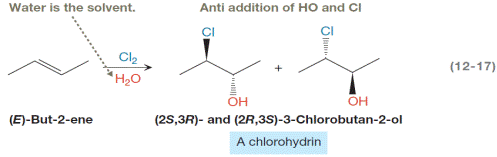
Concept introduction:
A chlorohydrin is produced when an
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
- this is an organic chemistry question please answer accordindly!! please post the solution draw the figures and post, answer the question in a very simple and straight forward manner thanks!!!!! please answer EACH part till the end and dont just provide wordy explanations wherever asked for structures or diagrams, please draw them on a paper and post clearly!! answer the full question with all details EACH PART CLEARLY please thanks!! im reposting this kindly solve all parts and draw it not just word explanations!!arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Select to Edit Arrows H H Select to Add Arrows > H CFCI: Select to Edit Arrows H Select to Edit Arrowsarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
