
Concept explainers
The three-dimensional motion of a particle is defined by the position
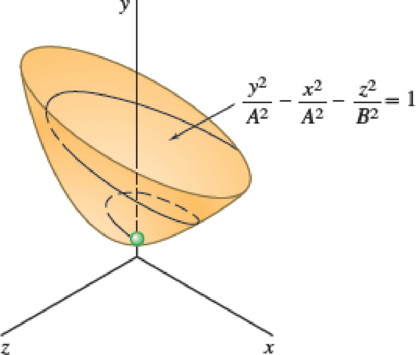
Fig. P11.96
(a)
The magnitude of the velocity (v) and acceleration (a) when time is 0 sec.
Answer to Problem 11.96P
The magnitude of the velocity (v) and acceleration (a) when time is 0 sec are
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The three dimensional motion of a particle is defined by the position vector is
The curve described by the particle lies on the hyperboloid is
The value of A and B are 3 and 1 respectively.
Calculation:
Write the three dimensional motion of a particle position vector equation.
Here, x is
Consider x:
Consider y:
Consider z:
Calculate the
Substitute
Check whether the position vector equation satisfied the curve equation or not.
Substitute
Hence, the equation is satisfied.
Rewrite the Equation (1).
Substitute 3 for A and 1 for B in Equation (1).
Write the expression for velocity using the relation:
Substitute
Calculate velocity vector
Substitute 0 for t in Equation (5).
Here,
Calculate the magnitude of velocity (v) using the relation:
Substitute
Write the expression for acceleration vector using the relation:
Substitute
Substitute 0 sec for t.
Here,
Calculate the magnitude
Substitute 0 is
Therefore, the magnitude of the velocity (v) and acceleration (a) when time is 0 sec are
(b)
The smallest nonzero value of t for which the position vector and the velocity are perpendicular to each other.
Answer to Problem 11.96P
The smallest nonzero value of t for which the position vector and the velocity are perpendicular to each other is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The three dimensional motion of a particle is defined by the position vector is
The curve described by the particle lies on the hyperboloid is
The value of A and B are 3 and 1 respectively.
Calculation:
Write the equation if the position vector and velocity vector are perpendicular:
Substitute
Using trial and error method the smallest root is (t) is 4.38 sec.
Therefore, the smallest nonzero value of t for which the position vector and the velocity are perpendicular to each other is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYN.(LL)-W/ACCESS
- Consider a single crystal of silver oriented such that a tensile stress is applied along a [112] direction. If slip occurs on a (011) plane and in a [111] direction and is initiated at an applied tensile stress of 15.9 MPa, compute the critical resolved shear stress.arrow_forwardA hypothetical component must not fail when a tensile stress of 15.25 MPa is applied. Determine the maximum allowable internal crack length if the surface energy of the component is 1.50 J/m2. Assume a modulus of elasticity of 350 GPa.arrow_forwardFresh air at 21.1 C in which partial pressure of water vapor is 0.018 atmosphere is blown at the rate of 214 m3/h first through a preheater and then adiabatically saturated in spray chambers to 100% saturation and again reheated this reheated air has humidity of 0.024 kg water vapor per kg dry air. It is assumed that the fresh air and the air leaving the re-heater have the same percentage humidity. Determine:- a- The temperature of preheater, spray-chamber and re-heater b- Heat requirement for preheating and re-heating 11:39 مarrow_forward
- Example(3): 0.15 kg/s steam at atmospheric pressure and superheated to 400 K is bled into an air stream at 320 K and 20 per cent relative humidity. What is the temperature, enthalpy, and relative humidity of the mixed stream if the air is flowing at 5 kg/ s? How much steam would be required to provide an exit temperature of 330 K and what would be the humidity of this mixture? 11:39 مarrow_forwardThe answer to the problem is 31.3rad/s. Please show me how to get the final answerarrow_forwardThe answer to the problem is 1.00 m/s^2. Please show me how to get the final answerarrow_forward
- The answer to the problem is 0.30. Please show me how to get the final answerarrow_forwardThe answer to the problem is 1.96 m/s. Please show me how to get the final answerarrow_forwardA cylindrical tank of diameter D is currently filled with water to a height h, as shown in the figure to the right. Water enters the tank through the pipe at (1) with a cross-sectional area A₁ and a uniform velocity V₁. The height of water in the tank is increasing at a constant rate of 5 mm/s. Given the parameters below, find the volumetric flow rate in the pipe at (2), V2, in cm³/s, and classify it as an inflow or outflow. D = 20 cm h = 0.5 m A₁ = 1 cm² V₁ = 0.1 m/s h 1 V₁ D Pwater = 1,000 kg/m³ V2 2arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





