
College Physics (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780321902788
Author: Hugh D. Young, Philip W. Adams, Raymond Joseph Chastain
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 59GP
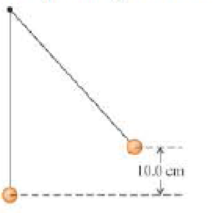
In Figure 11.38 the upper ball is released from rest, collides with the stationary lower ball, and sticks to it. The strings are both 50.0 cm long. The upper ball has mass 2.00 kg, and it is initially 10.0 cm higher than the lower ball, which has mass 3.00 kg. Find the frequency and maximum
Figure 11.38
Problem 59.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
In Fig. the upper ball is released from rest, collides with the stationary lower ball, and sticks to it. The strings are both 50.0 cm long. The upper ball has mass 2.00 kg, and it is initially 10.0 cm higher than the lower ball, which has mass 3.00 kg. Find the frequency and maximum angular displacement of the motion after the collision.
A 5 kg block is suspended from the ceiling by a 1.5 m long rope and is at rest. A 25 g
projectile is fired horizontally at the block with a velocity of 50 m/s, and sticks inside the
block. The block then moves as a simple pendulum in simple harmonic motion. How far
above the block's equilibrium position does it go?
A 480-gg block on a frictionless surface is attached to a rather limp spring of constant k=8.7N/mk=8.7N/m. A second block rests on the first, and the whole system executes simple harmonic motion with a period of 1.2 ss . When the amplitude of the motion is increased to 35 cmcm, the upper block just begins to slip.
What is the coefficient of static friction between the blocks?
Chapter 11 Solutions
College Physics (10th Edition)
Ch. 11 - Think of several examples in everyday life of...Ch. 11 - The analysis of simple harmonic motion in this...Ch. 11 - In any periodic motion, unavoidable friction...Ch. 11 - At what point in the motion of a simple pendulum...Ch. 11 - Which could you use as a timekeeping device in an...Ch. 11 - What happens to the original energy as a damped...Ch. 11 - Distinguish clearly between the angular frequency...Ch. 11 - It is easy to get mixed up and think that the...Ch. 11 - If a metal wire has its length doubled and its...Ch. 11 - Would you expect a rubber band to have a larger or...
Ch. 11 - In designing structures in an earthquake-prone...Ch. 11 - A springmass system is undergoing simple harmonic...Ch. 11 - Suppose you increase the amplitude of oscillation...Ch. 11 - An object of mass M suspended by a spring vibrates...Ch. 11 - When two wires of identical dimensions are used to...Ch. 11 - A mass on a spring oscillates with a period T. If...Ch. 11 - A pendulum oscillates with a period T. If both the...Ch. 11 - When a 100 kg mass is hung from a cable made of a...Ch. 11 - An object with mass M suspended by a spring...Ch. 11 - A pendulum on earth swings with angular frequency...Ch. 11 - A mass oscillates with simple harmonic motion of...Ch. 11 - A thin, light wire 75.0 cm long having a circular...Ch. 11 - A petite young woman distributes her 500 N weight...Ch. 11 - Two circular rods, one steel and the other copper,...Ch. 11 - A 5.0 kg mass is hung by a vertical steel wire...Ch. 11 - Biceps muscle. A relaxed biceps muscle requires a...Ch. 11 - Stress on a mountaineers rope. A nylon rope used...Ch. 11 - A steel wire 2.00 m long with circular cross...Ch. 11 - Achilles tendon. The Achilles tendon, which...Ch. 11 - Human hair. According to one set of measurements,...Ch. 11 - The effect of jogging on the knees. High-impact...Ch. 11 - A small aluminum sphere is placed in a vacuum...Ch. 11 - In the Challenger Deep of the Marianas Trench, the...Ch. 11 - Effect of diving on blood. It is reasonable to...Ch. 11 - Shear forces are applied to a rectangular solid....Ch. 11 - Compression of human bone. The bulk modulus for...Ch. 11 - In Figure 11.30, suppose the object is a square...Ch. 11 - Figure 11.31 Problem 17. 17. A cube of brass has a...Ch. 11 - A steel wire has the following properties: Length...Ch. 11 - A steel cable with cross-sectional area of 3.00...Ch. 11 - Weight lifting. The legs of a weight lifter must...Ch. 11 - (a) Music. When a person sings, his or her vocal...Ch. 11 - Find the period, frequency, and angular frequency...Ch. 11 - If an object on a horizontal frictionless surface...Ch. 11 - The graph shown in Figure 11.32 closely...Ch. 11 - The wings of the blue-throated hummingbird, which...Ch. 11 - A 0.500 kg glider on an air track is attached to...Ch. 11 - A toy is undergoing SHM on the end of a horizontal...Ch. 11 - A 2.00 kg frictionless block is attached to an...Ch. 11 - A 2.00 kg frictionless block is attached to an...Ch. 11 - You are watching an object that is moving in SHM....Ch. 11 - A mass is oscillating with amplitude A at the end...Ch. 11 - (a) If a vibrating system has total energy E0,...Ch. 11 - A 2.40 kg ball is attached to an unknown spring...Ch. 11 - A concrete block is hung from an ideal spring that...Ch. 11 - One end of a stretched ideal spring is attached to...Ch. 11 - A mass of 0.20 kg on the end of a spring...Ch. 11 - A harmonic oscillator is made by using a 0.600 kg...Ch. 11 - Weighing astronauts. In order to study the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 39PCh. 11 - An object of unknown mass is attached to an ideal...Ch. 11 - A science museum has asked you to design a simple...Ch. 11 - A simple pendulum in a science museum entry hall...Ch. 11 - Youve made a simple pendulum with a length of 1.55...Ch. 11 - A pendulum consisting of a 0.5 kg mass tied to a...Ch. 11 - A pendulum on Mars. A certain simple pendulum has...Ch. 11 - In the laboratory, a student studies a pendulum by...Ch. 11 - (a) If a pendulum has period T and you double its...Ch. 11 - A 1.35 kg object is attached to a horizontal...Ch. 11 - A 2.50 kg rock is attached at the end of a thin,...Ch. 11 - A mass is vibrating at the end of a spring of...Ch. 11 - What is the maximum kinetic energy of the...Ch. 11 - A small cylindrical brass bar of length 1 cm and...Ch. 11 - An astronaut uses a simple pendulum to measure the...Ch. 11 - An astronaut notices that a pendulum that took...Ch. 11 - An object suspended from a spring vibrates with...Ch. 11 - A pendulum is formed by taking a 2 kg mass and...Ch. 11 - An apple weighs 1.00 N. When you hang it from the...Ch. 11 - A block with mass M rests on a frictionless...Ch. 11 - In Figure 11.38 the upper ball is released from...Ch. 11 - A 15.0 kg mass fastened to the end of a steel wire...Ch. 11 - You hang a floodlamp from the end of a vertical...Ch. 11 - Tendon-stretching exercises. As part of an...Ch. 11 - A 100 kg mass suspended from a wire whose...Ch. 11 - A brass rod with a length of 1.40 m and a...Ch. 11 - Crude oil with a bulk modulus of 2.35 GPa is...Ch. 11 - Seeing surfaces at the nanoscale. One technique...Ch. 11 - What is the mechanical energy of the vibration...Ch. 11 - By what percentage does the frequency of...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
31. (II) Your grandfather clock's pendulum has a length of 0.9930 m. If the clock runs slow and loses 21 s per ...
Physics: Principles with Applications
1.31 For the vectors and in Fig. E1.24, use the method of components to find the magnitude and direction of (...
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
Rectangular coordinates of a point are given by (2,y) and its polar coordinates are given by (r,/6) . Find y y ...
University Physics Volume 1
Give the metric symbol, or abbreviation, for each prefix.
13. mega
Applied Physics (11th Edition)
(II) You buy a 75-W lightbulb in Europe, where electricity is delivered to homes at 240 V. If you use the light...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
3. A football coach sits on a sled while two of his players build their strength by dragging the sled across ...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider an undamped linear oscillator with a natural frequency ω0 = 0.5 rad/s and the step function a = 1 m/s2. Calculate and sketch the response function for an impulse forcing function acting for a time τ = 2π/ω0. Give a physical interpretation of the results.arrow_forwardQ2: A cylindrical plastic bottle of negligible mass is filled with 310 mL of water and left floating in a pond with still water. If pressed downward slightly and released, it starts performing simple harmonic motion at angular frequency. If the radius of the bottle is 2.5 cm then w is close to (density of water = 10 kg/m) (a) 2.50 rad s (b) 3.75 rad s (c) 5.00 rad s (d) 1.25 rad sarrow_forwardA rifle bullet with mass m = 0.030 kg traveling with a velocity v = 300.0 m/s buries itself in a 2.00-kg pendulum hanging on a string of length L = 2.50 m. What is the height h at the highest pointwhere the pendulum and bullet travel?arrow_forward
- A 0.0421 kg bullet is five horizontally into a 2.77 kg wooden block attached to one end of a mass list, horizontal spring (k=897 N/m). The other end of the spring is fixed in place, in the spring is unrestrained initially. The block rest on a horizontal, frictionless surface. The bullet strikes to block perpendicularly and quickly comes to a halt within it. As a result of this completely inelastic collision, the spring is compressed along its axis and causes the block/bullet to oscill with an amplitude of 0.180 m. What is the speed of the bullet?arrow_forwardPlease solve this problem. Thank you so much!arrow_forwardA 1.0-kg block (m1) is attached to the end of a 2.5-m string to form a pendulum. This pendulum is released from rest with an angle θ = 60° to the vertical as shown in the figure. At the lowest point in its swing when it is moving horizontally, the block collides elastically with another block of mass m2 = 2.0-kg initially at rest on a horizontal surface which is frictionless except for a length of 1.5 m, where the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.25 (see the figure below). After the collision the second block move towards the spring of force constant k = 10000 N/m which is fixed at one end of the surface (see the figure below). Answer the following questions. (a) Calculate the velocity of m1 just before the collision. (b) Calculate the velocities of m1 and m2 just after the collision. (c) Calculate the maximum height to which m1 rises after the collision. (d) Calculate the maximum compression, xc, of the spring.arrow_forward
- The figure shows block 1 of mass 0.195 kg sliding to the right over a frictionless elevated surface at a speed of 7.20 m/s. The block undergoes an elastic collision with stationary block 2, which is attached to a spring of spring constant 1287 N/m. (Assume that the spring does not affect the collision.) After the collision, block 2 oscillates in SHM with a period of 0.145 s, and block 1 slides off the opposite end of the elevated surface, landing a distance d from the base of that surface after falling height h = 6.80 m. What is the value of d?arrow_forwardThe figure shows block 1 of mass 0.155 kg sliding to the right over a frictionless elevated surface at a speed of 7.65 m/s. The block undergoes an elastic collision with stationary block 2, which is attached to a spring of spring constant 1298 N/m. (Assume that the spring does not affect the collision.) After the collision, block 2 oscillates in SHM with a period of 0.140 s, and block 1 slides off the opposite end of the elevated surface, landing a distance d from the base of that surface after falling height h = 4.60 m. What is the value of d?arrow_forwardA spring is hung from the ceiling. A 0.588-kg block is then attached to the free end of the spring. When released from rest, the block drops 0.101 m before momentarily coming to rest, after which it moves back upward. (a) VWhat is the spring constant of the spring? (b) Find the angular frequency of the block's vibrations. (a) Number i 57.09 Units N/m (b) Number i 97.0989 Units rad/sarrow_forward
- The figure depicts the displacement of an oscillator x[m], as a function of time t[s] 3 2 1 0 -1 -2 0 0.5 Mass of the oscillator is 1.2 kg. What is the oscillator's amplitude (with more than 2 significant digits)? A = 1 What is the oscillator's angular velocity (with more than 2 significant digits)? rad Kinetic energy at time 1.25 (with more than 2 significant digits)? Ex= Oscillator's total energy (with more than 2 significant digits)? Erot 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 Write the equation for oscillator's position in the following format: z = Asin (wt +)? Insert the answer as follows: x = (A)*sin((omega)'t + (phi)), where (A), (omega).(phi) are replaced with numerical values of amplitude, angular velocity and smallest positive phase angle rounded to one decimal after the decimal separator. 4arrow_forwardA homogeneous rectangular disc with length 2b, height b and mass m, slides on two small lugs A and B along a horizontal plane. Just before the corner D of the disc hits the wall that slopes 45 degrees, the disc has a speed of v. The lugs at A and B and the corner D are in contact with the ground and the wall, respectively, during the entire shock process, and after the shock the disc is at rest. All shock impulses are perpendicular to the contact surfaces (frictionless contacts). Calculate the shock impulses at A, B and D. (m, g, v,, b are known quantities) 2b D g b yA m Aarrow_forwardThere is a pendulum on a very long, light, string. The bob is made entirely of play-do and weighs 19.90 kg. It sits motionless directly below its point of support. A 100 g bullet is fired at the bob and strikes it with a velocity of 200 m/s. Although the bob is badly deformed, it remains one piece with the bullet embedded deep within it. The bob/bullet swing attaining a maximum height of h. Calculate h.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION (Physics Animation); Author: EarthPen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XjkUcJkGd3Y;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY