
Concept explainers
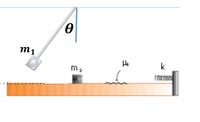
A 1.0-kg block (m1) is attached to the end of a 2.5-m string to form a pendulum. This pendulum is released from rest with an angle θ = 60° to the vertical as shown in the figure. At the lowest point in its swing when it is moving horizontally, the block collides elastically with another block of mass m2 = 2.0-kg initially at rest on a horizontal surface which is frictionless except for a length of 1.5 m, where the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.25 (see the figure below). After the collision the second block move towards the spring of force constant k = 10000 N/m which is fixed at one end of the surface (see the figure below). Answer the following questions.
(a) Calculate the velocity of m1 just before the collision.
(b) Calculate the velocities of m1 and m2 just after the collision.
(c) Calculate the maximum height to which m1 rises after the collision.
(d) Calculate the maximum compression, xc, of the spring.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

- A pendulum has a 10 kg bob on a string that is 2 m long. It is raised so that it forms an angle of 90 degrees with it's resting position. (It is horizontal, parallel with the ground). [I can't find a decent picture of this on the internet so ask me if you can't picture this. ] O-196 J O-20J 20 J O 196Jarrow_forwardA spring with a spring constant of 369 N/m is initially compressed by a distance of 0.064 m from its equilibrium position. A mass of 0.031 kg is then held against the compressed spring and released from rest while upon a horizontal, frictionless surface. Assuming that the spring then pushes the mass across the surface, with speed does the mass leave the spring? Assume proper SI Units.arrow_forwardA spring with a spring constant of 349 N/m is initially compressed by a distance of 0.072 m from its equilibrium position. A mass of 0.056 kg is then held against the compressed spring and released from rest while upon a horizontal, frictionless surface. Assuming that the spring then pushes the mass across the surface, with speed does the mass leave the spring? Assume proper SI Units.arrow_forward
- A 0.2-kg pendulum bob A hangs from a 0.75 m cord attached to a fixed pivot. It is released from rest at point 1 when the cord is horizontal and without slack, and swings down to strike 0.2-kg bob B at point 2. The coefficient of restitution between the two bobs is e = 0.7. Neglect the size of the bobs and the mass of the cords. 0.75 m 1 For parts b-f below, consider bob A at the instant the cord is vertical, when it has reached point 2, and immediately before the collision: a) ) What is the tension in the cord of the stationary bob B? b) ( Draw a clear and complete free body diagram of bob A. с) ( Find the speed of bob A. d) Find the tangential acceleration of bob A. e) Find the normal acceleration of bob A. f) Find the tension in the cord of bob A. g) Find the speed of bob A immediately after the collision.arrow_forwardSuppose that a simple pendulum consists of a small 67 g bob at the end of a cord of negligible mass. If the angle between the cord and the vertical is given by 0 = (0.063 rad) cos[(9.0 rad/s) t + ø], what are (a) the pendulum's length and (b) its maximum kinetic energy? (a) Number i 0.00000499 Units (b) Number i 0.000000269 Units ☐arrow_forwardA 5.00-g bullet moving with an initial speed of vi = 390 m/s is fired into and passes through a 1.00-kg block as shown in the figure below. The block, initially at rest on a frictionless, horizontal surface, is connected to a spring with force constant 860 N/m. The block moves d = 5.60 cm to the right after impact before being brought to rest by the spring a) Find the speed at which the bullet emerges from the block.=----m/s b) Find the amount of initial kinetic energy of the bullet that is converted into internal energy in bullet–block system during the collision. =-------Jarrow_forward
- A 0.454-kg block is attached to a horizontal spring that is at its equilibrium length, and whose force constant is 23.0 N/m. The block rests on a frictionless surface. A 5.90×10−2-kg wad of putty is thrown horizontally at the block, hitting it with a speed of 8.96 m/s and sticking.How far does the putty-block system compress the spring?arrow_forwardA 2.00-kg pendulum ball is attached to a light-uniform cable of length 1.20 m that is hanging from the ceiling at an angle of 50.00 to the vertical. When the pendulum ball is released from the rest position, it swings to the very bottom of the motion where it collides head-on with a 1.40-kg block that is initially at rest on a level surface. lí the pendulum ball recoils at 1.50 m/s, what is the speed of the block after the collision? e = 50° 1.2 m 2.0 kg 1.4 kg a. 5.98 m/s b. 3.88 m/s c. 6.29 m/s d. 4.75 m/s e. 3.03 m/sarrow_forwardIs the kinetic energy conserved in the collision? If not, then what percentage of energy is lost in the collision between the steel ball and the pendulum? (See equation) what happens to remaining energy?arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





