
Concept explainers
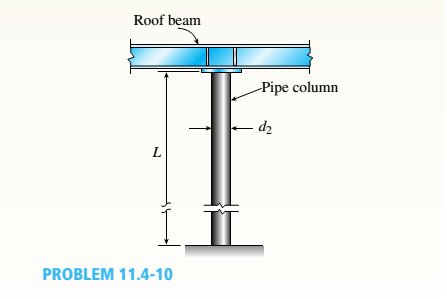
The roof beams of a warehouse are supported by pipe columns (see figure) having an outer diameter d2= 100 mm and inner diameter d2, = 90mm. The columns have a length L = 4.0 m, modulus E = 210 GPa, and fixed supports at the base.
Calculate the critical load Pcrof one of the columns using the following assumptions: (a) the upper end is pinned and the beam prevents horizontal displacement; (b) the upper end is fixed against rotation and the beam prevents horizontal displacement; (c) the upper end is pinned, but the beam is free to move horizontally; and (d) the upper end is fixed against rotation, but the beam is free to move horizontally.
i.
The critical load when the upper end is pinned and the beam prevents horizontal displacement.
Answer to Problem 11.4.10P
The critical load when the upper end is pinned and the beam prevents horizontal displacement is 447 kN
Explanation of Solution
Given:
E=210 GPa
L= 4 m
d1= 90 mm
d2= 100 mm
Concept Used:
Moment of interia of the column, I =π(d04−di4)64The critical load of the column, Pcr=π2EILeffective2Where,I= moment of inertiaE=modulus of elasticity
Calculation:
Moment of interia of the column, I =π(d04−di4)64I =π(1004−904)64I =1688×103 mm4The critical load of the column, Pcr=π2EILeffective2For pinned−pinned end codition Leffective=0.699LPcr=π2×210×103×1688×103(0.699×4000)2Pcr=447 kN
Conclusion:
The critical load for the pinned-pinned condition is 447 kN
ii.
The critical load when the upper end is fixed for rotation and the beam prevents horizontal displacement.
Answer to Problem 11.4.10P
The critical load when the upper end is fixed for rotation and the beam prevents horizontal displacement is 875 kN
Explanation of Solution
Given:
E=210 GPa
L= 4 m
d1= 90 mm
d2= 100 mm
Concept Used:
Moment of interia of the column, I =π(d04−di4)64The critical load of the column, Pcr=π2EILeffective2Where,I= moment of inertiaE=modulus of elasticity
Calculation:
Moment of interia of the column, I =π(d04−di4)64I =π(1004−904)64I =1688×103 mm4The critical load of the column, Pcr=π2EILeffective2For fixed−free end codition Leffective=L2Pcr=π2×210×103×1688×103×4(4000)2Pcr=875 kN
Conclusion:
The critical load when the upper end is fixed for rotation and the beam prevents horizontal displacement is 875 kN
iii.
The critical load when the upper end is pinned but beam free to move horizontally.
Answer to Problem 11.4.10P
The critical load when the upper end is pinned but beam free to move horizontally is 54.7 kN
Explanation of Solution
Given:
E=210 GPa
L= 4 m
d1= 90 mm
d2= 100 mm
Concept Used:
Moment of interia of the column, I =π(d04−di4)64The critical load of the column, Pcr=π2EILeffective2Where,I= moment of inertiaE=modulus of elasticity
Calculation:
Moment of interia of the column, I =π(d04−di4)64I =π(1004−904)64I =1688×103 mm4The critical load of the column, Pcr=π2EILeffective2For fixed−pinned end codition Leffective=2LPcr=π2×210×103×1688×103(2×4000)2Pcr=54.7 kN
Conclusion:
The critical load when the upper end is pinned but beam free to move horizontally is 54.7 kN .
iv.
The critical load when the upper end is fixed under rotation but the beam is free to move horizontally.
Answer to Problem 11.4.10P
The critical load when the upper end is fixed under rotation but the beam is free to move horizontally is 219 kN
Explanation of Solution
Given:
E=210 GPa
L= 4 m
d1= 90 mm
d2= 100 mm
Concept Used:
Moment of interia of the column, I =π(d04−di4)64The critical load of the column, Pcr=π2EILeffective2Where,I= moment of inertiaE=modulus of elasticity
Calculation:
Moment of interia of the column, I =π(d04−di4)64I =π(1004−904)64I =1688×103 mm4The critical load of the column, Pcr=π2EI4×Leffective2For pinned−pinned end codition Leffective=L2Pcr=π2×210×103×1688×103(4000)2Pcr=219 kN
Conclusion:
The critical load when the upper end is fixed under rotation but the beam is free to move horizontally is 219 kN.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
- room to be maintained with a dry-bulb temperature of 72ºF and 30% relative humidity. The room has a sensible heat factor of 0.8 and a total hourly heating load of 200,000 Btu. A flow rate of 1000 cfm of outdoor air (at 20% relative humidity and a dry-bulb temperature of 40ºF) is used. In order to maintain adequate comfort, the supply air to the room is set to a dry-bulb temperature of 120ºF. To humidify the air, steam with a specific enthalpy of 1150 Btu per pound is utilized.Determine the wet bulb temperature, specific enthalpy, and volumetric flow rate of the supply air to the room. Evaluate the increase in dry-bulb temperature as the air is sensibly heated, and the mass flow rate (in lb/hr) of steam required during the latent heating of the air. Calculate the heat added to the room during sensible heating (i.e., excluding humidification).arrow_forwardPlease can you help with the attached question? Many thanksarrow_forwardWhich of the following sequences converge and which diverge? 20) an = 21) a = n! 106 1/(Inn) 3n+1 " 22) a = 3n-1 1/n x" 23) a = , x>0 2n+1 3" x 6" 24) an 25) a, = tanh(n) = 2" xn! n² 1 26) a = sin 2n-1 n 27) a = tan(n) 1 28) a = 1 3 ++ (Inn) 200 2" 29) an n 30) =n-√√n²-n 1"1 31) a == dx nixarrow_forward
- Which of the following sequences converge and which diverge? n+1 6) a = 1- 2n (-1)+1 7) a = 2n-1 2n 8) an = n+1 1 9) a = sin + 2 n sin n 10) a = n 11) an = 12) a = 13) an 14) an 15) an 16) an n 2" In(n+1) = 81/n n n =(1+7)" = = 10n 3 n 1/n 17) an = In n 1/n n' 18) a =√4"narrow_forwardQu 3 Nickel (Ni) single crystal turbine blades burn less fuel at higher temperatures because blades are grown on [110] closed packed direction. Nickel (Ni) at 20°C is FCC, and has an atomic radius, R, of 0.125 nm. Draw a reduced-sphere unit cell for this crystal and draw and label the vector [I 10], starting from the origin (0, 0, 0). a) Calculate the length of the vector [| 10] in nanometers. Express your answer in nanometers to one significant figure. b) Calculate the linear density of Nickel in the [| 1 0] direction in [atom/nm]. Express your answer in atoms/nm to one significant figure. show all work problemsarrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forward
- handwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forwardRequired information An eccentric force P is applied as shown to a steel bar of 25 × 90-mm cross section. The strains at A and B have been measured and found to be εΑ = +490 μ εB=-70 μ Know that E = 200 GPa. 25 mm 30 mm 90 mm 45 mm B Determine the distance d. The distance dis 15 mm mm.arrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forward
- handwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forward! Required information Assume that the couple shown acts in a vertical plane. Take M = 25 kip.in. r = 0.75 in. A B 4.8 in. M 1.2 in. [1.2 in. Determine the stress at point B. The stress at point B is ksi.arrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
