
Bundle: General Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version, 11th + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781337128391
Author: Darrell Ebbing, Steven D. Gammon
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 11.109QP
Decide which substance in each of the following pairs has the lower melting point. Explain how you made each choice.
- a potassium chloride, KCl; or calcium oxide, CaO
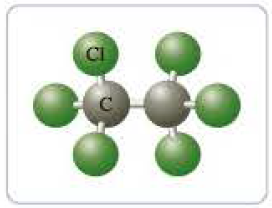
- b carbon tetrachloride,
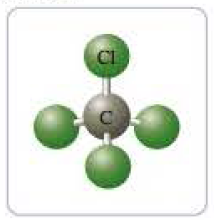
or hexachloroethane,
- c zinc, Zn; or chromium, Cr
- d acetic acid, CH3COOH; or ethyl chloride, C2H5Cl
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Which compound has the highest melting point: NaCl, CH 4, or H 2SO 4?
There are three sets of sketches below, showing the same pure molecular compound (ammonia, molecular formula NH,) at three different temperatures. The
sketches are drawn as if a sample of ammonia were under a microscope so powerful that individual atoms could be seen. Only one sketch in each set is correct.
Use the slider to choose the correct sketch in each set. You may need the following information:
melting point of NH3: – 77.7 °C
boiling point of NH3: – 33.3 °C
00
A
(Choose one) (Choose one) (Choose one)
do
4
5
4
5.
21. °C
- 60. °C
- 89. °C
Tra
JAN
..
W
14
...
MacBook Air
DII
DD
80
000
000
F11
F7
F8
F9
F10
F1
F4
F5
F6
F2
F3
Arrange the following substances in order of increasing total
intermolecular forces between their molecules.
○ | < 1 < |||
OI< | < |
○ | < | < 1
O # < 1< ||
O | < | < 1
Ol< | < |
I
OH
11
111
OH
Chapter 11 Solutions
Bundle: General Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version, 11th + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
Ch. 11.2 - The heat of vaporization of ammonia is 23.4...Ch. 11.2 - Shown here is a representation of a closed...Ch. 11.2 - Prob. 11.2ECh. 11.2 - Selenium tetrafluoride, SeF4, is a colorless...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 11.4ECh. 11.3 - When camping at high altitude, you need to pay...Ch. 11.5 - Consider two liquids, labeled A and B, that are...Ch. 11.5 - List the different intermolecular forces you would...Ch. 11.5 - Arrange the following hydrocarbons in order of...Ch. 11.5 - At the same temperature, methyl chloride, CH3Cl,...
Ch. 11.5 - A common misconception is that the following...Ch. 11.6 - Prob. 11.8ECh. 11.6 - Prob. 11.9ECh. 11.7 - Figure 11.35 shows solid dots (atoms) forming a...Ch. 11.8 - Shown here is a representation of a unit cell for...Ch. 11.9 - Lithium metal has a body-centered cubic structure...Ch. 11.9 - Potassium metal has a body-centered cubic...Ch. 11 - List the different phase transitions that are...Ch. 11 - Describe how you could purify iodine by...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.3QPCh. 11 - Explain why 15 g of steam at 100C melts more ice...Ch. 11 - Why is the heat of fusion of a substance smaller...Ch. 11 - Explain why evaporation leads to cooling of the...Ch. 11 - Describe the behavior of a liquid and its vapor in...Ch. 11 - Gases that cannot be liquefied at room temperature...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.9QPCh. 11 - Why does the vapor pressure of a liquid depend on...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.11QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.12QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.13QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.14QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.15QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.16QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.17QPCh. 11 - What is the coordination number of Cs in CsCl? of...Ch. 11 - Explain in words how Avogadros number could be...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.20QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.21QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.22QPCh. 11 - Under the right conditions, hydrogen gas, H2, can...Ch. 11 - An element crystallizes with a simple cubic...Ch. 11 - Intermolecular Forces The following picture...Ch. 11 - Heat and Molecular Behavior Part 1: a Is it...Ch. 11 - Shown here is a curve of the distribution of...Ch. 11 - Consider a substance X with a Hvap = 20.3 kJ/mol...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.29QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.30QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.31QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.32QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.33QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.34QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.35QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.36QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.37QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.38QPCh. 11 - Use Figure 11.7 to estimate the boiling point of...Ch. 11 - Use Figure 11.7 to estimate the boiling point of...Ch. 11 - An electric heater coil provided heat to a 15.5-g...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.42QPCh. 11 - Isopropyl alcohol, CH3CHOHCH3, is used in rubbing...Ch. 11 - Liquid butane, C4H10, is stored in cylinders to be...Ch. 11 - Water at 0C was placed in a dish inside a vessel...Ch. 11 - A quantity of ice at 0.0C was added to 33.6 g of...Ch. 11 - A quantity of ice at 0C is added to 64.3 g of...Ch. 11 - Steam at 100C was passed into a flask containing...Ch. 11 - Chloroform, CHCl3, a volatile liquid, was once...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.50QPCh. 11 - White phosphorus, P4, is normally a white, waxy...Ch. 11 - Carbon disulfide, CS2 is a volatile, flammable...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.53QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.54QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.55QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.56QPCh. 11 - Which of the following substances can be liquefied...Ch. 11 - A tank of gas at 21C has a pressure of 1.0 atm....Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.59QPCh. 11 - Krypton, Kr, has a triple point at 169C and 133...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.61QPCh. 11 - The heats of vaporization of liquid O2, liquid Ne,...Ch. 11 - For each of the following substances, list the...Ch. 11 - Which of the following compounds would you expect...Ch. 11 - Arrange the following substances in order of...Ch. 11 - Arrange the following substances in order of...Ch. 11 - Methane, CH4, reacts with chlorine, Cl2, to...Ch. 11 - The halogens form a series of compounds with each...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.69QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.70QPCh. 11 - List the following substances in order of...Ch. 11 - Arrange the following compounds in order of...Ch. 11 - Classify each of the following by the type of...Ch. 11 - Classify each of the following by the type of...Ch. 11 - Classify each of the following solid elements as...Ch. 11 - Which of the following do you expect to be...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.77QPCh. 11 - Arrange the following substances in order of...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.79QPCh. 11 - On the basis of the description given, classify...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.81QPCh. 11 - Associate each of the solids BN, P4S3, Pb, and...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.83QPCh. 11 - How many atoms are there in a body-centered cubic...Ch. 11 - Metallic iron has a body-centered cubic lattice...Ch. 11 - Nickel has a face-centered unit cell with all...Ch. 11 - Copper metal has a face-centered cubic structure...Ch. 11 - Barium metal has a body-centered cubic lattice...Ch. 11 - Gold has cubic crystals whose unit cell has an...Ch. 11 - Chromium forms cubic crystals whose unit cell has...Ch. 11 - Assume X has a body-centered cubic lattice with...Ch. 11 - Lead has a face-centered cubic lattice with all...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.93QPCh. 11 - Metallic barium has a body-centered cubic...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.95QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.96QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.97QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.98QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.99QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.100QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.101QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.102QPCh. 11 - Describe the formation of hydrogen bonds in...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.104QPCh. 11 - Ethylene glycol (CH2OHCH2OH) is a slightly viscous...Ch. 11 - Pentylamine, CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2NH2, is a liquid that...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.107QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.108QPCh. 11 - Decide which substance in each of the following...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.110QPCh. 11 - Iridium metal, Ir, crystallizes in a face-centered...Ch. 11 - The edge length of the unit cell of tantalum...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.113QPCh. 11 - Rubidium metal has a body-centered cubic structure...Ch. 11 - Calculate the percent of volume that is actually...Ch. 11 - Calculate the percent of volume that is actually...Ch. 11 - For the hydrogen halides and the noble gases, we...Ch. 11 - For the carbon and nitrogen family hydrides, we...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.119QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.120QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.121QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.122QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.123QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.124QPCh. 11 - A geckos toes have been shown to stick to walls...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.126QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.127QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.128QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.129QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.130QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.131QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.132QPCh. 11 - In an experiment, 20.00 L of dry nitrogen gas, N2,...Ch. 11 - On a particular summer day, the temperature is...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.135QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.136QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.137QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.138QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.139QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.140QPCh. 11 - Rhenium forms a series of solid oxides: Re2O7...Ch. 11 - Shown below is the cubic unit cell of an ionic...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.143QPCh. 11 - Strontium crystallizes as a face-centered cubic...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.145QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.146QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.147QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.148QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.149QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.150QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.151QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.152QPCh. 11 - How much heat must be added to 28.0 g of solid...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.154QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.155QPCh. 11 - Prob. 11.156QPCh. 11 - Nanotechnology, or technology utilizing 1100 nm...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Explain the phase diagram of CaO-MgO.arrow_forwardWould you expect the boiling points to increase or decrease in the following series? Explain. (a) Kr, Ar, Ne (b) Cl2, Br2, I2arrow_forwardConsider the melting points of the substances below (see figures for two compounds). Explain the trend in melting point using your knowledge of intermolecular forces. (In the structures below, carbon is black, hydrogen is white, and oxygen is red.) Substance Melting Point (°C) Molar Mass (g/mol) Cl2 −102 71 Ethyl formate (CH3CH2OCHO) −80 74 Propionic acid (CH3CH2COOH) −20 74 Br2 −7.2 160arrow_forward
- A (made-up) metal has a face-centered cubic crystal structure. Its density is 20.5 g/cm 3. Its molar mass is 189 g/mol. What is the radius of an atom of the metal? O 9.39 x 10 7 cm 1.39 x 10 8 cm 8.02 x 10 7 cm 2.60 x 10 -9 cm 1.84 cm x 108 2.69 x 10 8 cm 2.49 x 10 9 cm 1.51 x 10 8 cm O O Oarrow_forwardWhich of the following substances will have the highest melting point in hf, pcl3, f2arrow_forwardA (made-up) metal has a face-centered cubic crystal structure. Its density is 20.5 g/cm 3. Its molar mass is 189 g/mol. What is the radius of an atom of the metal? 9.39 x 10 -7 cm O 1.39 x 10 -8 cm O 8.02 x 10 - cm O 2.60 x 1o 9 cm -8 O 1.84 cmx 10 O 2.69 x 10-8 cm O 2.49 x 1o-9 cm O 1.51x 10 -8 cm Nextarrow_forward
- Aspirin has a higher molar mass compared to salicylic acid, however aspirin melts at a lower temperature than salicylic acid. Provide a brief explanation for this observation. Table 1 Compound: Formula: Salicylic Acid C;H6O3 Aspirin C9H3O4 Molar Mass: 138.12 Melting point: Ka 158-160°C 1.08 x 10³ 180.15 140-142°C 2.72 x 10$ pKa Solubility (g/100ML) 2.99 4.57 0.18 0.25arrow_forward1) Palladium (electron configuration is [Kr]4d¹) crystallizes in a face-centered cubic unit cell. its density is 12.0 g/cm³. (NA = 6.02 x 10²³) (a) What is the total mass of palladium atoms contained within one unit cell? (b) Calculate the atomic radius (r) of Pd.arrow_forwardplease solveee 1. Tantalum is rare, hard, blue-gray, lustrous transition metal that is highly corrosion-resistant. It has a density of 16.4 kg/L and a molecular weight of 180.948 g/mol. What is the (A) atomic radius in cm, (B) volume in cm^3 of Ta if it adopts the body centered cubic unit structure and (C) volume of unit cellarrow_forward
- How many of the following forms a molecular solid? Ag • CO2 • RbI • Al203 • H20 Gold С10Н22 I2 3 5 4arrow_forwardWhat are the various phases of SiO2?arrow_forwardMethane clathrate also called methane hydrate is a form of ice in which methane gas has been trapped inside the crystal structure. Methane hydrate has the formula CH4·5¾ H2O or 4CH4·23H2O. Large quantities of methane hydrate have been discovered in ocean sediments around the world. Mining these deposits to obtain methane (i.e. natural gas) has been discussed for years. Determine the percent water in methane hydrate. How many moles of methane could be recovered from 1.00 ton (2000 lbs) of methane hydrate? [1 kg = 2.2 lbs]arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Viscosity, Cohesive and Adhesive Forces, Surface Tension, and Capillary Action; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P_jQ1B9UwpU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY