
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781133104261
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 74P
A stepladder of negligible weight is constructed as shown in Figure P10.73, with AC = BC = ℓ. A painter of mass m stands on the ladder a distance d from the bottom. Assuming the floor is frictionless, find (a) the tension in the horizontal bar DE connecting the two halves of the ladder, (b) the normal forces at A and B, and (c) the components of the reaction force at the single hinge C that the left half of the ladder exerts on the right half. Suggestion: Treat the ladder as a single object, but also treat each half of the ladder separately.
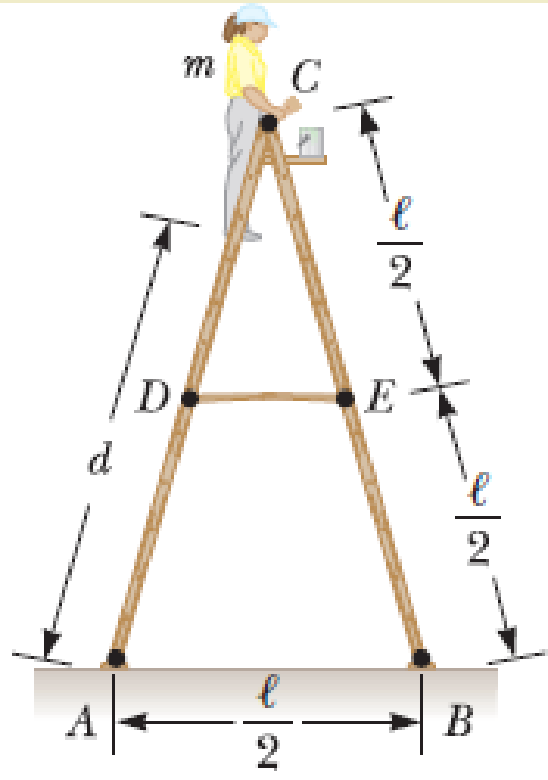
Figure P10.73 Problems 73 and 74.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Your answer is partially correct.
The system in the figure is in equilibrium. A concrete block of mass 333 kg hangs from the end of the uniform strut of mass 62.2 kg. For
angles o = 31.9° and e = 60.8°, find (a) the tension Tin the cable and the (b) horizontal and (c) vertical components of the force on the
strut from the hinge.
Strut
-Hinge
(a) Number
i
3061
Units
N
(b) Number
3058
Units
N
(c) Number
5776
Units
N
The system in the figure is in equilibrium. A concrete block of mass 327 kg hangs from the end of the uniform strut of mass 30.6 kg. For
angles = 31.8° and 0 = 48.3°, find (a) the tension T in the cable and the (b) horizontal and (c) vertical components of the force on the
strut from the hinge.
(a) Number 7857.127
(b) Number i 6663.22
(c) Number i 7668.123
Units
N
Units
Strut
z
0
Hinge
Units N
N
It's exciting watching the construction and renovation happening in Uptown
Columbus! On one construction site, you notice that a uniform beam of length 13.6
m and mass 47.9 kg is attached to a wall by a cable. The angle between the cable
and the beam is 59.5°. The beam is free to pivot about the point where it attaches to
the wall. What is the tension in the cable, if the beam is not moving?
Your Answer:
Answer
Chapter 10 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Ch. 10.1 - A rigid object is rotating in a counterclockwise...Ch. 10.2 - Consider again the pairs of angular positions for...Ch. 10.3 - Ethan and Joseph are riding on a merry-go-round....Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 10.4QQCh. 10.5 - (i) If you are trying to loosen a stubborn screw...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.6QQCh. 10.9 - A solid sphere and a hollow sphere have the same...Ch. 10.10 - A competitive diver leaves the diving board and...Ch. 10.12 - Two items A and B are placed at the top of an...Ch. 10 - A cyclist rides a bicycle with a wheel radius of...
Ch. 10 - Prob. 2OQCh. 10 - Prob. 3OQCh. 10 - Prob. 4OQCh. 10 - Assume a single 300-N force is exerted on a...Ch. 10 - Consider an object on a rotating disk a distance r...Ch. 10 - Answer yes or no to the following questions. (a)...Ch. 10 - Figure OQ10.8 shows a system of four particles...Ch. 10 - As shown in Figure OQ10.9, a cord is wrapped onto...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10OQCh. 10 - Prob. 11OQCh. 10 - A constant net torque is exerted on an object....Ch. 10 - Let us name three perpendicular directions as...Ch. 10 - A rod 7.0 m long is pivoted at a point 2.0 m from...Ch. 10 - Prob. 15OQCh. 10 - A 20.0-kg horizontal plank 4.00 m long rests on...Ch. 10 - (a) What is the angular speed of the second hand...Ch. 10 - Prob. 2CQCh. 10 - Prob. 3CQCh. 10 - Which of the entries in Table 10.2 applies to...Ch. 10 - Prob. 5CQCh. 10 - Prob. 6CQCh. 10 - Prob. 7CQCh. 10 - Prob. 8CQCh. 10 - Three objects of uniform densitya solid sphere, a...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10CQCh. 10 - If the torque acting on a particle about an axis...Ch. 10 - Prob. 12CQCh. 10 - Stars originate as large bodies of slowly rotating...Ch. 10 - Prob. 14CQCh. 10 - Prob. 15CQCh. 10 - Prob. 16CQCh. 10 - Prob. 17CQCh. 10 - During a certain time interval, the angular...Ch. 10 - A bar on a hinge starts from rest and rotates with...Ch. 10 - Prob. 3PCh. 10 - Prob. 4PCh. 10 - The tub of a washer goes into its spin cycle,...Ch. 10 - Why is the following situation impossible?...Ch. 10 - An electric motor rotating a workshop grinding...Ch. 10 - Prob. 8PCh. 10 - Prob. 9PCh. 10 - A wheel 2.00 m in diameter lies in a vertical...Ch. 10 - A disk 8.00 cm in radius rotates at a constant...Ch. 10 - Make an order-of-magnitude estimate of the number...Ch. 10 - A car traveling on a flat (unbanked), circular...Ch. 10 - Prob. 14PCh. 10 - A digital audio compact disc carries data, each...Ch. 10 - Figure P10.16 shows the drive train of a bicycle...Ch. 10 - Big Ben, the Parliament tower clock in London, has...Ch. 10 - Rigid rods of negligible mass lying along the y...Ch. 10 - A war-wolf, or trebuchet, is a device used during...Ch. 10 - Prob. 20PCh. 10 - Review. Consider the system shown in Figure P10.21...Ch. 10 - The fishing pole in Figure P10.22 makes an angle...Ch. 10 - Find the net torque on the wheel in Figure P10.23...Ch. 10 - Prob. 24PCh. 10 - Prob. 25PCh. 10 - Prob. 26PCh. 10 - A force of F=(2.00i+3.00j) N is applied to an...Ch. 10 - A uniform beam resting on two pivots has a length...Ch. 10 - Prob. 29PCh. 10 - Prob. 30PCh. 10 - Figure P10.31 shows a claw hammer being used to...Ch. 10 - Prob. 32PCh. 10 - A 15.0-m uniform ladder weighing 500 N rests...Ch. 10 - A uniform ladder of length L and mass m1 rests...Ch. 10 - BIO The arm in Figure P10.35 weighs 41.5 N. The...Ch. 10 - A crane of mass m1 = 3 000 kg supports a load of...Ch. 10 - An electric motor turns a flywheel through a drive...Ch. 10 - Prob. 38PCh. 10 - Prob. 39PCh. 10 - In Figure P10.40, the hanging object has a mass of...Ch. 10 - A potters wheela thick stone disk of radius 0.500...Ch. 10 - A model airplane with mass 0.750 kg is tethered to...Ch. 10 - Consider two objects with m1 m2 connected by a...Ch. 10 - Review. An object with a mass of m = 5.10 kg is...Ch. 10 - A playground merry-go-round of radius R = 2.00 m...Ch. 10 - The position vector of a particle of mass 2.00 kg...Ch. 10 - Prob. 48PCh. 10 - Big Ben (Fig. P10.17), the Parliament tower clock...Ch. 10 - A disk with moment of inertia I1 rotates about a...Ch. 10 - Prob. 51PCh. 10 - A space station is constructed in the shape of a...Ch. 10 - Prob. 53PCh. 10 - Why is the following situation impossible? A space...Ch. 10 - The puck in Figure 10.25 has a mass of 0.120 kg....Ch. 10 - A student sits on a freely rotating stool holding...Ch. 10 - Prob. 57PCh. 10 - Prob. 58PCh. 10 - A cylinder of mass 10.0 kg rolls without slipping...Ch. 10 - A uniform solid disk and a uniform hoop are placed...Ch. 10 - A metal can containing condensed mushroom soup has...Ch. 10 - A tennis ball is a hollow sphere with a thin wall....Ch. 10 - Prob. 63PCh. 10 - Review. A mixing beater consists of three thin...Ch. 10 - A long, uniform rod of length L and mass M is...Ch. 10 - The hour hand and the minute hand of Big Ben, the...Ch. 10 - Two astronauts (Fig. P10.67), each having a mass...Ch. 10 - Two astronauts (Fig. P10.67), each having a mass...Ch. 10 - Prob. 69PCh. 10 - Prob. 70PCh. 10 - The reel shown in Figure P10.71 has radius R and...Ch. 10 - Review. A block of mass m1 = 2.00 kg and a block...Ch. 10 - A stepladder of negligible weight is constructed...Ch. 10 - A stepladder of negligible weight is constructed...Ch. 10 - A wad of sticky clay with mass m and velocity vi...Ch. 10 - Prob. 76PCh. 10 - Prob. 77PCh. 10 - Review. A string is wound around a uniform disk of...Ch. 10 - Prob. 79PCh. 10 - Prob. 80PCh. 10 - A projectile of mass m moves to the right with a...Ch. 10 - Figure P10.82 shows a vertical force applied...Ch. 10 - A solid sphere of mass m and radius r rolls...Ch. 10 - Prob. 84PCh. 10 - BIO When a gymnast performing on the rings...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A stepladder of negligible weight is constructed as shown in Figure P12.40, with AC = BC = = 4.00 m. A painter of mass m = 70.0 kg stands on the ladder d = 3.00 m from the bottom. Assuming the floor is frictionless, find (a) the tension in the horizontal bar DE connecting the two halves of the ladder, (b) the normal forces at A and B, and (c) the components of the reaction force at the single hinge C that the left half of the ladder exerts on the right half. Suggestion: Treat the ladder as a single object, but also treat each half of the ladder separately. Figure P12.40 Problems 40 and 41.arrow_forwardA uniform beam resting on two pivots has a length L = 6.00 m and mass M = 90.0 kg. The pivot under the left end exerts a normal force n1 on the beam, and the second pivot located a distance = 4.00 m from the left end exerts a normal force n2. A woman of mass m = 55.0 kg steps onto the left end of the beam and begins walking to the right as in Figure P10.28. The goal is to find the womans position when the beam begins to tip. (a) What is the appropriate analysis model for the beam before it begins to tip? (b) Sketch a force diagram for the beam, labeling the gravitational and normal forces acting on the beam and placing the woman a distance x to the right of the first pivot, which is the origin. (c) Where is the woman when the normal force n1 is the greatest? (d) What is n1 when the beam is about to tip? (e) Use Equation 10.27 to find the value of n2 when the beam is about to tip. (f) Using the result of part (d) and Equation 10.28, with torques computed around the second pivot, find the womans position x when the beam is about to tip. (g) Check the answer to part (e) by computing torques around the first pivot point. Figure P10.28arrow_forwardA uniform beam of mass m is inclined at an angle θ to the horizontal. Its upper end (point P) produces a 90° bend in a very rough rope tied to a wall, and its lower end rests on a rough floor (as shown). Let μs represent the coefficient of static friction between beam and floor. Assume μs is less than the cotangent of θ. (a) Find an expression for the maximum mass M that can be suspended from the top before the beam slips. Determine (b) the magnitude of the reaction force at the floor and (c) the magnitude of the force exerted by the beam on the rope at P in terms of m, M, and μs.arrow_forward
- A horizontal L=1.0 m long mb=12 kg uniform bar is hinged on the left end and pulled at the right end by a cable. The cable makes 24° angle with horizontal. A 20 kg store sign is suspended below the bar at d=0.18 m from the right end. Find the magnitude of horizontal hinge force.arrow_forwardIn the figure, suppose the length L of the uniform bar is 3.5 m and its weight is 150 N. Also, let the block's weight W = 350 N and the angle @ = a maximum tension of 410 N. (a) What is the maximum possible distance x before the wire breaks? With the block placed at this maximum x, what are the (b) horizontal and (c) vertical components of the force on the bar from the hinge at A? 39°. The wire can withstand Com B. (a) Number Units (b) Number Units (c) Number Unitsarrow_forwardYour answer is partially correct. The system in the figure is in equilibrium. A concrete block of mass 261 kg hangs from the end of the uniform strut of mass 58.1 kg. For angles = 33.2° and 0= 46.7°, find (a) the tension Tin the cable and the (b) horizontal and (c) vertical components of the force on the strut from the hinge. Strut Hinge i 8609.9 Units N. (a) Number Units i 7456.4 (b) Number Units i 7432.13 (c) Number i eTextbook and Mediaarrow_forward
- The system in the figure is in equilibrium. A concrete block of mass 298 kg hangs from the end of the uniform strut of mass 61.4 kg. For angles o = 29.3° and e= 58.1°, find (a) the tension T in the cable and the (b) horizontal and (c) vertical components of the force on the strut from the hinge. em plem Strut blem oblem roblem Hinge Problem (a) Number Units Problem (b) Number Units (c) Number Units ults by Study Click if you would like to Show Work for this question: Open Show Work Question Attempts: 0 of 10 used SAVE FOR LATER SUBMIT ANSWER Agreement Privacy Policy I 9 2000-2020 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. AlI Rights Reserved. A Division of John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Version 4.24.20.1arrow_forwardYour answer is partially correct. The system in the figure is in equilibrium. A concrete block of mass 221 kg hangs from the end of the uniform strut of mass 45.1 kg. For angles = 39.4° and 0 = 55.7°, find (a) the tension T in the cable and the (b) horizontal and (c) vertical components of the force on the strut from the hinge. (a) Number i 98100 (b) Number i (c) Number i T Strut 0 -Hinge Units Units Units N <arrow_forwardIn the figure, a uniform beam with weight W and length is hinged at its lower end, and a horizontal force of magnitude F acts at its upper end. The beam is held vertical by a cable that makes angle with the ground and is attached to the beam at height h. NOTE: Give your answer in terms of the variables given. (a) What is the tension in the cable? T = Fl h cos(0) (b) What is the x-component of the force on the beam from the hinge? FF-Tcos(0) Fu L X (c) What is the y-component of the force on the beam from the hinge? Tsin(0) = h Xarrow_forward
- A uniform ladder of length ℓ rests against a smooth, vertical wall (as shown). The mass of the ladder is m, and the coefficient of static friction between the ladder and the ground is μs = 0.40. Find the minimum angle θmin at which the ladder does not slip.arrow_forwardA ladder of weight 600 N and length 10.0 m is placed against a smooth vertical wall. A person weighing 1000 N stands on the ladder 6.0 m from the bottom as measured along the ladder. At a height of 7.0 m the ladder is on the point of slipping. Find: (a) Calculate the force exerted by the wall. (b) Calculate the normal force exerted by the floor on the ladder. (c) The force of friction between the floor and ladder. (d) Calculate the coefficient of static friction if the ladder is on the point of slipping when the person is 8.0 m up the ladder.arrow_forwardA uniform L = 6.71 m long horizontal beam that weighs WB= 363N is attached to a wall by a pin connection that allows the beam to rotate. Its far end is supported by a cablewith tension Tthat makes an angle of 50.0° with the horizontal, and a person of weight WP= 427.5N is standing d = 2.38m from the pin. Find the magnitude of the force R exertedon the beam by the wall if the beam is in equilibrium. A)532N B)534N C)536N D)538Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Static Equilibrium: concept; Author: Jennifer Cash;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0BIgFKVnlBU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY