
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305251052
Author: Michael Cummings
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 4QP
Questions 4 through 6 refer to the following hypothetical pathway in which substance A is converted to substance C by enzymes 1 and 2. Substance B is the intermediate produced in this pathway:
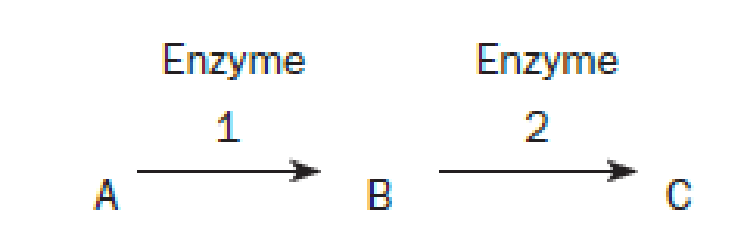
a. If an individual is homozygous for a null mutation in the gene that codes for enzyme 1, what will the result be?
b. If an individual is homozygous for a null mutation in enzyme 2, what will the result be?
c. What if an individual is heterozygous for a dominant mutation in which enzyme 1 is overactive?
d. What if an individual is heterozygous for a mutation that abolishes the activity of enzyme 2 (a null mutation)?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Find out about the organisations and the movements aimed at the
conservation of our natural resources. Eg Chipko movement and Greenpeace.
Make a project report on such an organisation.
What are biofertilizers and mention the significance
PCBs and River Otters: Otters in Washington State’s Green-Duwamish River have high levels of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in their livers. PCBs can bind to the estrogen receptors in animals and disrupt the endocrine system of these otters. The PCBs seem to increase the estrogen to androgen ratio, skewing the ratio toward too much estrogen.
How would increased estrogen affect the river otter population?
Based on your reading of the materials in this unit, what factors can affect fertility in humans?
Explain how each of the factors affecting human fertility that you described can disrupt the human endocrine system to affect reproduction.
Chapter 10 Solutions
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 1GRCh. 10.4 - Prob. 2GRCh. 10.7 - Prob. 1EGCh. 10.7 - Prob. 2EGCh. 10 - A couple was referred for genetic counseling...Ch. 10 - A couple was referred for genetic counseling...Ch. 10 - A couple was referred for genetic counseling...Ch. 10 - Many individuals with metabolic diseases are...Ch. 10 - Prob. 2QPCh. 10 - Enzymes have all the following characteristics...
Ch. 10 - Questions 4 through 6 refer to the following...Ch. 10 - Questions 4 through 6 refer to the following...Ch. 10 - Prob. 6QPCh. 10 - Prob. 7QPCh. 10 - Prob. 8QPCh. 10 - a. Compounds A, B, C, and D are known to be...Ch. 10 - b. Compounds A, B, C, and D are known to be...Ch. 10 - a. If an individual who is homozygous for the...Ch. 10 - Prob. 12QPCh. 10 - Suppose that in the formation of phenylalanine...Ch. 10 - If phenylalanine was not an essential amino acid,...Ch. 10 - Phenylketonuria and alkaptonuria are both...Ch. 10 - The normal enzyme required for converting sugars...Ch. 10 - Knowing that individuals who are homozygous for...Ch. 10 - Prob. 18QPCh. 10 - A person was found to have very low levels of...Ch. 10 - If an extra nucleotide is inserted in the first...Ch. 10 - Transcriptional regulators are proteins that bind...Ch. 10 - Prob. 22QPCh. 10 - Prob. 23QP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Other than oil and alcohol, are there other liquids you could compare to water (that are liquid at room temperature)? How is water unique compared to these other liquids? What follow-up experiment would you like to do, and how would you relate it to your life?arrow_forwardSelection of Traits What adaptations do scavengers have for locating and feeding on prey? What adaptations do predators have for capturing and consuming prey?arrow_forwardCompetition Between Species What natural processes limit populations from growing too large? What are some resources organisms can compete over in their natural habitat?arrow_forward
- Species Interactions Explain how predators, prey and scavengers interact. Explain whether predators and scavengers are necessary or beneficial for an ecosystem.arrow_forwardmagine that you are conducting research on fruit type and seed dispersal. You submitted a paper to a peer-reviewed journal that addresses the factors that impact fruit type and seed dispersal mechanisms in plants of Central America. The editor of the journal communicates that your paper may be published if you make ‘minor revisions’ to the document. Describe two characteristics that you would expect in seeds that are dispersed by the wind. Contrast this with what you would expect for seeds that are gathered, buried or eaten by animals, and explain why they are different. (Editor’s note: Providing this information in your discussion will help readers to consider the significance of the research).arrow_forwardWhat is the difference between Uniporters, Symporters and Antiporters? Which of these are examples of active transport?arrow_forward
- What are Amyloid Fibrils? What biological functions are these known to perform?arrow_forwardHow do histamine and prostaglandins help in the mobilization of leukocytes to an injury site? What are chemotactic factors? How do they affect inflammation process?arrow_forwardCompare and contrast neutrophils and macrophages. Describe two ways they are different and two ways they are similar.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning


Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Mitochondrial mutations; Author: Useful Genetics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GvgXe-3RJeU;License: CC-BY