
Concept explainers
Activity-based costing in an insurance company
Umbrella Insurance Company carries three major lines of insurance: auto, workers' compensation, and homeowners. The company has prepared the following report for 20Y2:
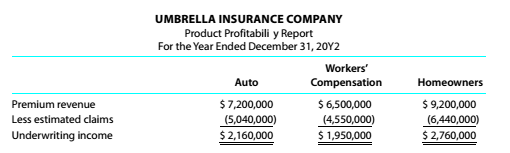
Management is concerned that the administrative expenses may make some of the insurance lines unprofitable. However, the administrative expenses have not been allocated to the insurance lines. The controller has suggested that the administrative expenses could be assigned to the insurance lines using activity-based costing. The administrative expenses are comprised of five activities. The activities and their rates are as follows:

Activity-base usage data for each line of insurance were retrieved from the corporate records and are shown below.
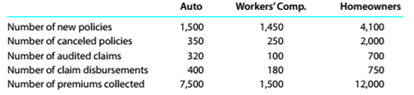
a.Complete the product profitability report through the administrative activities.
b.Determine the underwriting income as a percent of premium revenue.
C.Determine the Operating income as a percent of premium revenue, rounded to one decimal place.
d.Interpret the report.
(a)
Concept Introduction:
Activity based costing is one of the costing method that identify the important activities in the organisation and accordingly identify their cost drivers. Then cost is allocated on the basis of activities used by each product.
Through administrative activities complete the product profitability report.
Answer to Problem 10.25E
The product profitability report through the administrative activities is given in table below.
Explanation of Solution
The product profitability report through the administrative activities is below:
| Particulars | Auto (in $) | Worker compensation (in $) | Homeowner (in $) |
| New policy processing per new policy | | | |
| Cancellation processing per cancellation | | | |
| Claim audit per claim audit | 13y13 | Y13y3 | |
| Claim disbursement per claim disbursement | | | |
| Premium collection processing per premium | | | |
| Total administrative cost | | | |
Preparation of Income statement is as follows:
| Particulars | Auto (in $) | Worker compensation (in $) | Homeowner (in $) |
| Underwriting income before administrative expenses | | | |
| Less: Administrative expenses | | | |
| Underwriting net Income | | | |
(b)
Concept Introduction:
Activity based costing is one of the costing method that identify the important activities in the organisation and accordingly identify their cost drivers. Then cost is allocated on the basis of activities used by each product.
To compute:
The underwriting income as a percent of premium revenue.
Answer to Problem 10.25E
The underwriting income as a percent of premium revenue is
Explanation of Solution
Calcultion of underwriting income as a percent of premium revenue are as follows:
Underwriting income as a percent of premium revenue is:
So, the answer is
(c)
Concept Introduction:
Activity based costing is one of the costing method that identify the important activities in the organisation and accordingly identify their cost drivers. Then cost is allocated on the basis of activities used by each product.
The operating income as a percent of premium revenue.
Answer to Problem 10.25E
Operating income as a percent of premium revenue is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of operating income as a percent of premium revenue is as follows:
Operating income as a percent of premium revenue
So, the answer is
(d)
Concept Introduction:
Activity based costing is one of the costing method that identify the important activities in the organisation and accordingly identify their cost drivers. Then cost is allocated on the basis of activities used by each product.
The interpretation of report.
Answer to Problem 10.25E
The premium revenue's significant part is used in the administrative expenses.
Explanation of Solution
Underwriting income as a percent of premium revenue after reducing administrative expenses is
So, this clearly shows that important part of premium revenue is used in administrative expenses, which helps company in profitability.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
- Hi expert please help me this question general accountingarrow_forwardBix Corp. has a contribution margin ratio of 50%. This month, sales revenue was $250,000, and profit was $60,000. If sales revenue increases by $30,000, by how much will profit increase? A) $12,000 B) $5,500 C) $7,500 D) $15,000arrow_forwardMajestic Collectibles can produce keepsakes that will be sold for $75 each. Non-depreciation fixed costs are $1,200 per year, and variable costs are $55 per unit. What is the degree of operating leverage of Majestic Collectibles when sales are $8,250?arrow_forward
- Want to this question answer general Accountingarrow_forwardTanishk Manufacturing has gross sales of $45,000 for the year. Its cost for the goods sold is $28,000. Returns and allowances amounted to $3,500. It purchased equipment normally selling for $12,000 at a 25% discount. Based on these facts, what is its total gross income for the year? tutor please provide answerarrow_forwardMajestic Collectibles can produce keepsakes that will be sold for $75 each. Non-depreciation fixed costs are $1,200 per year, and variable costs are $55 per unit. What is the degree of operating leverage of Majestic Collectibles when sales are $8,250? Accurate answerarrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning





