
Concept explainers
A special vehicle brake is clamped at O when the brake force P1 is applied (see figure). Force P1= 50 lb and lies in a plane that is parallel to the x-z plane and is applied at C normal to line BC. Force P2= 40 lb and is applied al B in the -y direction.
(a) Find reactions at support O.
(b) Find internal stress resultants N, V, T. and M at
the mid-point of segment OA.
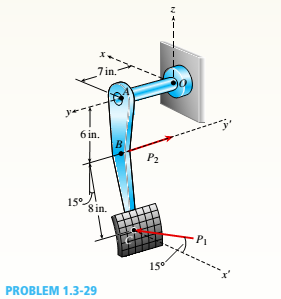
(a)
Reactions at support O.
Answer to Problem 1.3.29P
The correct answers are:
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
You have following figure with all relevant information:
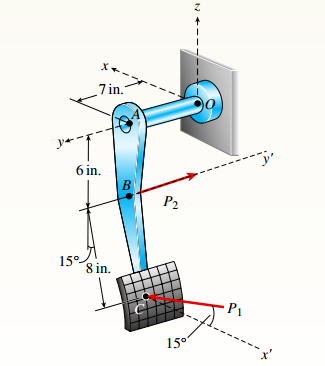
and
Draw free body diagram of joints and use equilibrium of forces to determine the unknown facts.
Calculation:
Draw free body diagram as shown in the following figure:
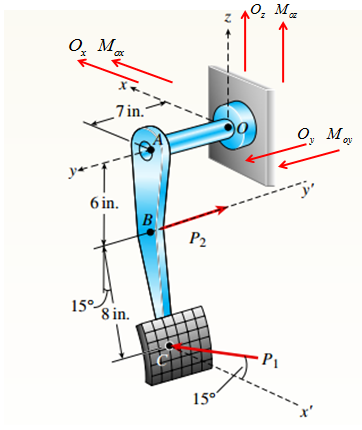
The forces and corresponding position vectors are:
| Force | Position vector |
Take equilibrium of forces vector from:
The vector equation yields three equations in components form as below:
Put
Now take equilibrium of moments about O in vector form as:
Put
Conclusion:
Therefore the forces are:
(b)
Internal stress resultants N,V,T, and M at the mid pint of segment OA.
Answer to Problem 1.3.29P
The correct answers are:
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
You have following figure with all relevant information,
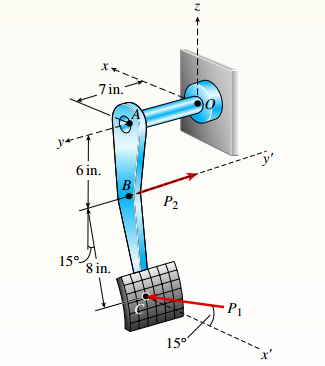
and
Draw free body diagram of joints and use equilibrium of forces to determine the unknowns.
Calculation:
Draw free body diagram as shown in the following figure,
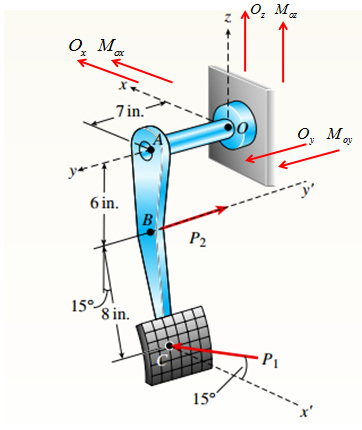
The forces and corresponding position vectors are:
| Force | Position vector |
Take equilibrium of forces vector form:
The vector equation yields three equations in components form as below:
Put
Now take equilibrium of moments about O in vector form as:
Put
Calculation of internal resultants:
Consider the following free body diagram,
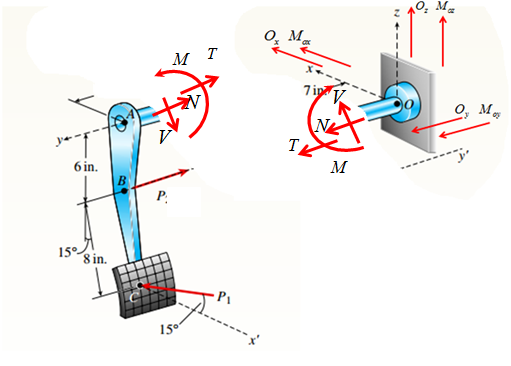
Analyze the right hand side of the free body diagram in the above figure.
Take equilibrium of torques in y-direction as,
Take equilibrium of forces in y-direction as,
Take equilibrium of forces in xz-plane as:
Calculate bending moment as:
Conclusion:
Therefore the internal stress resultants are:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
- The answer to the problem is 2.93 ft/s. Please show me how to get the final answerarrow_forwardExample(3): 0.15 kg/s steam at atmospheric pressure and superheated to 400 K is bled into an air stream at 320 K and 20 per cent relative humidity. What is the temperature, enthalpy, and relative humidity of the mixed stream if the air is flowing at 5 kg/ s? How much steam would be required to provide an exit temperature of 330 K and what would be the humidity of this mixture? 11:39 مarrow_forwardThe answer to the problem is 31.3rad/s. Please show me how to get the final answerarrow_forward
- A cylindrical tank of diameter D is currently filled with water to a height h, as shown in the figure to the right. Water enters the tank through the pipe at (1) with a cross-sectional area A₁ and a uniform velocity V₁. The height of water in the tank is increasing at a constant rate of 5 mm/s. Given the parameters below, find the volumetric flow rate in the pipe at (2), V2, in cm³/s, and classify it as an inflow or outflow. D = 20 cm h = 0.5 m A₁ = 1 cm² V₁ = 0.1 m/s h 1 V₁ D Pwater = 1,000 kg/m³ V2 2arrow_forwardThe answer to the problem is 2.33 rad/s. Please show me how to get the final answerarrow_forwardThe answer to the problem is 0.14 rad/s. Please show me how to get the final answerarrow_forward
- Marks) culate numerically the temperatures of the internal s shown in Fig. 3. The temperature of all boundaries is and the circle (arc) radius is 3m. The temperature PDE is: эт дх + ат 0. 3 = 2 ду Ay -3m Fig. (3)arrow_forwardThe answer to the problem is 58.7 ft/s^2. Please show me how to get the final answerarrow_forwardThe answer to the problem is 21.4 rad/s. Please show me how to get the final answerarrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
