
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
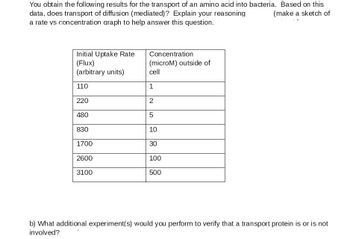
Transcribed Image Text:### Analysis of Amino Acid Transport into Bacteria
#### Data Interpretation
For the transport of an amino acid into bacteria, the following results were obtained:
| Initial Uptake Rate (Flux) (arbitrary units) | Concentration (microM) outside of cell |
|----------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------|
| 110 | 1 |
| 220 | 2 |
| 480 | 5 |
| 830 | 10 |
| 1700 | 30 |
| 2600 | 100 |
| 3100 | 500 |
#### Question a: Diffusion vs Mediated Transport
**Does the transport occur through simple diffusion or a mediated process? Explain your reasoning.**
To address this question, you can analyze the relationship between the initial uptake rate and the external concentration of the amino acid. Typically, for simple diffusion, the uptake rate increases linearly with an increase in concentration. However, for mediated transport, such as facilitated diffusion or active transport, the uptake rate often shows a hyperbolic relationship, where the rate increases rapidly at low concentrations and then plateaus as the carrier proteins become saturated.
**Graphical Representation:** Make a sketch of a rate vs concentration graph to help answer this question.
- Plot the data with the y-axis representing the Initial Uptake Rate (Flux) and the x-axis representing the Concentration (microM) outside of the cell.
- The shape of the curve will help determine if the transport is likely mediated:
- A linear curve suggests simple diffusion.
- A hyperbolic curve suggests mediated transport.
#### Question b: Additional Experiments
**What additional experiment(s) would you perform to verify that a transport protein is or is not involved?**
1. **Inhibition Studies:**
- Use specific inhibitors known to block transporter proteins and assess whether the uptake rate decreases.
2. **Saturation Kinetics:**
- Perform uptake experiments at increasing concentrations beyond 500 microM to see if saturation occurs, characteristic of transporter involvement.
3. **Temperature Dependence:**
- Measure the uptake rate at different temperatures. Mediated transport processes are more sensitive to temperature changes than simple diffusion.
4. **Transporter Mutants:**
- Use bacterial strains genetically modified to lack the suspected transporter protein to determine if the uptake rate is affected.
5. **Competition Experiments:**
- Introduce similar
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The dialysis bag membrane in the figure is permeable to water and to the simple sugars only. The final solute concentration will: • Stay same without change • Reach equilibrium on both sides. • Sucrose concentration will be higher inside the bag. "Environment" 0.01 M sucrose 0.01 M glucose "Cell" • Glucose concentration will be higher inside the bag. 0.03 M sucrose 0.02 M glucose 0,01 M fructose • Fructose concentration will be higher inside the bag.arrow_forwardYou have genetically modified a cell to have a thicker membrane than normal (25nm). To keepyour cells alive, you need to understand how diffusion of nutrients works. What is the flux ofglucose through the cell membrane given that: -The concentration of glucose in the media is 10mM -The concentration of glucose inside the cell is 2mM -The diffusivity of glucose is 6x10-10m2/sarrow_forwardWhat are three types of energy that can power an active transport pump? Provide an example of each type (eg Na/K pump)arrow_forward
- uring dialysis, a semi-permeable membrane with a molecular weight cutoff of 10,000 is used. Select the true statements from the list below (more than one answer could apply) Group of answer choices A monoclonal antibody with a 150 kDa MW is retained and does not diffuse across the membrane A small enzyme with 20 kDa MW diffuses readily across the membrane Buffer salts with molecular weights ranging between 100 and 500 Da diffuse across the membrane until equilibrium (equal concentration) is reached on both sides of the membrane None of the above statements are correct Please answer asaparrow_forwardList two differences you would expect to see in the composition of lipids in the E. coli membrane when the cells are incubated at 25 °C compared to incubation at 37 °C.arrow_forwardThe studies of Palade and colleagues used pulse chase labeling with radioactively labeled amino acids and auto radiography to visualize the location of newly synthesized proteins in pancreatic acinar cells. These early experiments provided invaluable information on protein synthesis and intercompartmental transport. New methods have replaced these early approaches, but two basic requirements are still necessary for any assay to study this type of protein transport. What are they, and how do recent experimental approaches meet these criteria?arrow_forward
- The classic demonstration that cell plasma membranes are composed ofbilayers depends on the following kinds of data:• The membrane lipids from 4.74 x 109erythrocytes will form a monolayer of area 0.89 m2when spread on a water surface.• The surface of one erythrocyte is approximately 100 μm2in area. Show that these data can be accounted for only if the erythrocyte membrane is a bilayer.arrow_forwardDescribes a process that can be optimized with the incorporation of a membrane bioreactorarrow_forwardOne question with 4 partsarrow_forward
- A cell with a K+1 concentration of 0.3 eq/L is placed into a solution with a K+1 concentration of 0.2 eq/L. It is assumed that the K+1 can pass through the cell membrane (the K+1 transport protein is open). Answer the following true or false questions. 1. K+1 will diffuse through the membrane down its concentration gradient due to Kinetic Theory 2. Movement of a solute through the membrane is called dialysis 3. K+1 will move out of the cellarrow_forwardVarious chemical methods can be used to permeabilize or lyse cells including the use of enzymes. List three important factors to consider when developing a lysis method using enzymes. Estimate the osmotic pressure drop across the membrane of an animal cell in a 0.10 M NaCl solution, assuming that the internal total solute concentration is 0.36 osM and temperature is 30.0°C. Do you think that this pressure drop would lyse cells? Why or why not?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON