
SWFT Comprehensive Volume 2019
42nd Edition
ISBN: 9780357233306
Author: Maloney
Publisher: Cengage
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
a. Compute XYZ's taxable income.
b. Compute XYZ's income tax liability.

Transcribed Image Text:XYZ owns 30% of the outstanding Hobble Corporation (HC) stock. Hobble Corporation reported $1,000,000 of Income for
the year. XYZ accounted for its Investment in HC under the equity method, and it recorded its pro rata share of HC's
earnings for the year. HC also distributed a $200,000 dividend to XYZ. For tax purposes, XYZ reports the actual dividend
received as Income, not the pro rata share of HC's earnings.
2of the $20,800 Interest Income, $5,200 was from a City of Seattle bond, $7,200 was from a Tacoma City bond, $6,200
was from a fully taxable corporate bond, and the remaining $2,200 was from a money market account.
This gain is from equipment that XYZ purchased in February and sold in December (I.e., it does not qualify as §1231 gain).
*This includes total officer compensation of $2,500,000 (no one officer received more than $1,000,000 compensation).
5This amount is the portion of Incentive stock option compensation that was expensed during the year (recipients are
officers).
6XYZ actually wrote off $27,500 of its accounts receivable as uncollectible.
Tax depreciation was $1,925,000.
In the current year, XYZ did not make any actual payments on warranties It provided to customers.
9XYZ made $500,000 of cash contributions to charities during the year
10 On July 1 of this year, XYZ acquired the assets of another business. In the process, it acquired $303,000 of goodwill. At
the end of the year, XYZ wrote off $30,500 of the goodwill as impaired.
11XYZ expensed all of its organizational expenditures for book purposes. XYZ expensed the maximum amount of
organizational expenditures allowed for tax purposes.
12 The other expenses do not contain any items with book-tax differences.
13 This is an estimated tax provision (federal tax expense) for the year. Assume that XYZ is not subject to state Income
taxes.
Estimated tax Information:
XYZ made four equal estimated tax payments totaling $360,000 ($90,000 per quarter). For purposes of estimated tax
liabilities, assume XYZ was in existence in 2023 and that in 2023 it reported a tax liability of $500,000. During 2024, XYZ
determined its taxable income at the end of each of the first three quarters as follows:
Quarter-end
First
Second
Cumulative taxable
income (loss)
$ 405,000
$ 1,105,000
Third
$ 1,425,000
Finally, assume that XYZ is not a large corporation for purposes of estimated tax calculations.
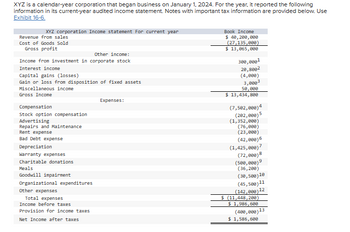
Transcribed Image Text:XYZ is a calendar-year corporation that began business on January 1, 2024. For the year, it reported the following
information in its current-year audited income statement. Notes with important tax information are provided below. Use
Exhibit 16-6.
XYZ corporation Income statement For current year
Revenue from sales
Book Income
Cost of Goods Sold
Gross profit
Other income:
Income from investment in corporate stock
Interest income
Capital gains (losses)
Gain or loss from disposition of fixed assets
Miscellaneous income
Gross Income
Compensation
Stock option compensation
Advertising
Repairs and Maintenance
Rent expense
Bad Debt expense
Depreciation
Warranty expenses
Charitable donations
Meals
Goodwill impairment
Organizational expenditures
Other expenses
Total expenses
Income before taxes
Provision for income taxes
Net Income after taxes
Expenses:
$ 40,200,000
(27,135,000)
$ 13,065,000
300,0001
20,8002
(4,000)
3,0003
50,000
$ 13,434,800
(7,502,000)4
(202,000)5
(1,352,000)
(76,000)
(23,000)
(42,000)6
(1,425,000)7
(72,000)8
(500,000)9
(36,200)
(30,500)10
(45,500)11
(142,000)
$ (11,448,200)
$ 1,986,600
12
(400,000) 13
$ 1,586,600
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Assume that a corporation has $100,000 of taxable income from operations plus $5,000 of interest income and $10,000 of dividend income. What is the company’s federal tax liability?arrow_forwardCalculate taxable income?arrow_forwardFielding Sporting Goods Corporation (FSGC) is a calendar-year corporation. What is the Book to Tax Reconciliation's Adjustments, and Taxable Income? 1) FSGC owns 40 percent of the outstanding Magnolia Corp. (MC) stock. Magnolia Corp. reported $1,000,000 of income for the year. FSGC accounted for its investment in MC under the equity method and it recorded its pro rata share of MC's earnings for the year. MC also distributed a $150,000 dividend to FSGC. Description Вook Income Adjustments Adjustments (Debit) (Credit) Тахable Income Income From Investment in 400,000 Corporate Stock Dividends Received Deductionarrow_forward
- Before the provision for Federal income tax, Karas Corporation had book income of $400,000 for the current year. The book income included $100,000 of dividends received from a 15% owned domestic corporation. What was Karas Corporation's taxable income for the current year?arrow_forwardWestern Corporation, a calendar year, accrual basis corporation, reported $500,000 of net income after tax on its financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP. The corporation’s books and records reveal the following information: Western’s book income included $15,000 of dividends, received from a domestic corporation in which Western owns less than 1 percent of the outstanding stock. Western’s depreciation expense per books was $55,000, and its MACRS depreciation was $70,000. Western earned $5,000 of interest from municipal bonds and $6,000 of interest from corporate bonds. Western’s capital losses exceeded its capital gains by $2,000. Western’s federal income tax expense per books was $103,000. Compute Western’s federal taxable income and regular tax liability. My Solutions: federal taxable income = $585,500, regular tax liability = $122,955 (This is a past homework problem that I got wrong. Could you please explain how to do this, I do not understand what I did…arrow_forwardWestern Corporation, a calendar year, accrual basis corporation, reported $500,000 of net income after tax on its financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP. The corporation’s books and records reveal the following information: Western’s book income included $15,000 of dividends, received from a domestic corporation in which Western owns less than 1 percent of the outstanding stock. Western’s depreciation expense per books was $55,000, and its MACRS depreciation was $70,000. Western earned $5,000 of interest from municipal bonds and $6,000 of interest from corporate bonds. Western’s capital losses exceeded its capital gains by $2,000. Western’s federal income tax expense per books was $103,000. Required: Compute Western’s federal taxable income and regular tax liability. Prepare a Schedule M-1, page 6, Form 1120, reconciling Western’s book and taxable income.arrow_forward
- sanarrow_forwardLuong Corporation, a calendar year, accrual basis corporation, reported $1.65 million of net income after tax on its financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP. The corporation's books and records reveal the following information: • Luong's federal income tax expense per books was $213,000. • Luong's book income included $23,000 of dividends received from a domestic corporation in which Luong owns a 25 percent stock interest, and $10,500 of dividends from a domestic corporation in which Luong owns a 5 percent stock interest. • Luong recognized $23,000 of capital losses this year and no capital gains. • Luong recorded $14,600 of book expense for meals not provided by a restaurant and $16,500 of book expense for entertainment costs. • Luong's depreciation expense for book purposes totaled $413,000. MACRS depreciation was $475,000. Required: a. Compute Luong's federal taxable income and regular tax liability. b. Prepare a Schedule M-1, page 6, Form 1120, reconciling Luong's…arrow_forwardLuong Corporation, a calendar year, accrual basis corporation, reported $1.15 million of net income after tax on its financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP. The corporation's books and records reveal the following information: • Luong's federal income tax expense per books was $203,000. • Luong's book income included $13,000 of dividends received from a domestic corporation in which Luong owns a 25 percent stock interest, and $5,500 of dividends from a domestic corporation in which Luong owns a 5 percent stock interest. Luong recognized $13,000 of capital losses this year and no capital gains. • Luong recorded $9,600 of book expense for meals not provided by a restaurant and $11,500 of book expense for entertainment costs. • Luong's depreciation expense for book purposes totaled $403,000. MACRS depreciation was $475,000. Required: a. Compute Luong's federal taxable income and regular tax liability. b. Prepare a Schedule M-1, page 6, Form 1120, reconciling Luong's book…arrow_forward
- During its first year of operation, K Corporation had a gross profit from operations of $180,000 anddeductions of $250,000 before considering its dividend income or dividends-received deduction. K receiveddividends of $50,000 from a taxable domestic corporation in which K owned 4.5 percent of the stock.Assuming its ownership of the dividend-paying corporation’s stock is not debt financed, what is KCorporation’s net operating loss for the year?arrow_forwarduong Corporation, a calendar year, accrual basis corporation, reported $1 million of net income after tax on its financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP. The corporation’s books and records reveal the following information: Luong’s federal income tax expense per books was $200,000. Luong’s book income included $10,000 of dividends received from a domestic corporation in which Luong owns a 25 percent stock interest, and $4,000 of dividends from a domestic corporation in which Luong owns a 5 percent stock interest. Luong recognized $10,000 of capital losses this year and no capital gains. Luong recorded $8,000 of book expense for meals not provided by a restaurant and $10,000 of book expense for entertainment costs. Luong's depreciation expense for book purposes totaled $400,000. MACRS depreciation was $475,000. Required: Compute Luong's federal taxable income and regular tax liability.arrow_forwardIn the current year, X Corp has the following items of income for tax purposes: gross profits from sales of goods of $500,000 and $100,000 dividends from a corporation in which X Corp owns 30% of the stock. It has $200,000 of operating expenses and a $60,000 capital loss and no capital gain. It has no NOL or capital loss carryovers. What is X Corp's taxable income in the current year? 400,000arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning






Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395083
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:Cengage Learning