
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
A student is holding a mounted bicycle wheel that is rotating in the direction shown by the curved arrow. If she rotates the bicycle wheel 180° by switching the positions of her left and right hand, which direction will the angular momentum vector point ?
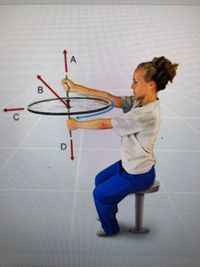
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts a young person sitting on a stool and holding a spinning wheel mounted on a vertical axis. The wheel is positioned horizontally, and several vectors are drawn around it to illustrate different forces and motions:
1. **Vector A** - This arrow points upward and represents the angular momentum of the spinning wheel. It indicates the direction of the axis of rotation.
2. **Vector B** - This arrow points diagonally across the plane of the wheel and may represent a force applied by the person’s hand.
3. **Vector C** - This arrow is horizontal, pointing to the left, and may represent another force or motion affecting the wheel, possibly the torque.
4. **Vector D** - This arrow points downward and could represent gravitational force acting on the system.
The person appears to be holding the spinning wheel with both hands, suggesting they are demonstrating principles of angular momentum and torque. The setup is likely used to explain concepts in physics such as rotational motion, gyroscopic effects, and conservation of angular momentum.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two children (m = 34.0 kg each) stand opposite each other on the edge of a merry-go-round. The merry-go-round, which has a mass of 1.60 × 10² kg and a radius of 1.4 m, is spinning at a constant rate of 0.32 rev/s. Treat the two children and the merry-go-round as a system. (a) Calculate the angular momentum of the system, treating each child as a particle. (Give the magnitude.) 583.1 kg. m²/s (b) Calculate the total kinetic energy of the system. 586 J (c) Both children walk half the distance toward the center of the merry-go-round. Calculate the final angular speed of the system. 2.61 X Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. rad/sarrow_forwardA student sits on a pivoted stool holding a pair of weights. The stool is free to rotate about vertical axes with negligible friction. The student is set in rotation with arms outstretched, holding a 5-kg mass in each hand. He is rotating about a vertical axis with an angular velocity of one revolution per second, arms outstretched. If he pulls the weights inward, what will the final angular velocity (in rev/s) be if his moment of inertia remains approximately constant at 5 kg×m2, and the distance of the masses from the axis changes from 1 m to 0.1 m?arrow_forward(c) Is mechanical energy of the bullet-door system constant in this collision? Answer without doing a calculation. O Yes O Noarrow_forward
- A projectile of mass .050 kg moves to the right with a speed of 4.0 m/s. The projectile strikes and sticks to the end of a rod of mass 0.8 kg, at length 1.2 m from the rod's centre. The rod may rotate freely around a stationary axle pinned through the rod's centre of mass. Find the magnitude of the angular velocity, ω, of the system right after the collision. Select one: a. 0.00 rad/s b. 0.27 rad/s c. 0.53 rad/s d. None of the other answers are correct e. 1.05 rad/sarrow_forwardIn the image below pivot is placed at the center of mass of the stick (mass = 0.097 kg). If the block (0.022 kg) is placed at 0.766 m it will rotate the block-stick system around the pivot. Calculate the following. (Istick = 1/12 ML^2)arrow_forwardA sphere of mass 1.0 kg and radius 0.21 m is suspended on the rod of length 0.49 m and mass 0.43 kg as it is shown in the figure. System can rotate around uppermost point. A bullet of mass 0.02 kg strikes the sphere as it shown in the figure (aiming directly to the center of the sphere) and embeds. Find minimum velocity of bullet which allows this system to just clear the top. The answer is 300.719752599215. Please show all steps on how to get to that answer.arrow_forward
- A projectile of mass .050 kg moves to the right with a speed of 4.0 m/s. The projectile strikes and sticks to the end of a rod of mass 0.8 kg, at length 1.2 m from the rod's centre. The rod may rotate freely around a stationary axle pinned through the rod's centre of mass. Find the magnitude of the angular velocity, ω, of the system right after the collision.arrow_forwardA bicycle is traveling north at 6.84 m/s. The mass of the wheel, 2.6 kg, is uniformly distributed along the rim(I=mr2), which has a radius of 17.89 cm. What are the magnitude(in kg m2/s) and direction of the angular momentum of the wheel about its axle?arrow_forwardA clown sits on a unicycle and rides it BACKWARDS (moving in the opposite direction he is facing). The wheel spins around its fixed rotation axis in normal fashion. In which direction does the angular momentum vector of the unicycle wheel point? Group of answer choices a) To his/her right b) To his/her left c) foward (the direction he is facing) d) backward (the direction of motion) e) In the upward direction (toward the sky)arrow_forward
- In Figure 2, two skaters, each of mass 52 kg, approach each other along parallel paths separated by 2.6 m. They have opposite velocities of 1.5 m/s each. One skater carries one end of a long pole of negligible mass, and the other skater grabs the other end as she passes. The skaters then rotate around the center of the pole. Assume that the friction between skates and ice is negligible and the skaters can be treated as mass points. Calculate (a) the angular speed of the skaters (b) the kinetic energy of the two-skater system Next, the skaters pull along the pole until they separated by 1.0 m. Calculate (c) the new angular speed of the skaters (d) the new kinetic energy of the two-skater system 1.5 m/s 2.6 m 1.5 m/s Figure 2arrow_forwardA bird flies overhead from where you stand at an altitude of 310.0ĵ m and at a velocity horizontal to the ground of 14.0î m/s. The bird has a mass of 1.8 kg. The radius vector to the bird makes an angle ? with respect to the ground. The radius vector to the bird lies in the xy-plane. What is the bird's angular momentum (in kg · m2/s) about the point where you are standing? (Express your answer in vector form.)arrow_forwardConsider the figure above consisting of three particles of mass m attached to a massless rod. Given an axis of rotation through point P, the rod rotates as shown in the figure. If the rod is released from rest in the horizontal position at t = 0. What is the angular acceleration of the system (rod and three particles) immediately after being released? Let d = 2.50 m.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON