
Use technology and a t-test to test the claim about the population
Claim: u > 78; a = 0.01 Sample statistics: × = 79.3, s = 3.6, n = 28
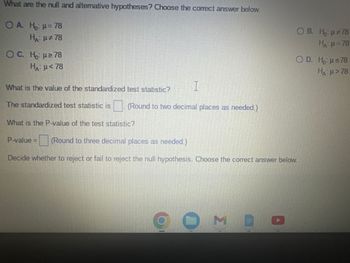
What are the null and alternative hypotheses? Choose the correct answer below.
O A. Ho: M = 78
H: 4*78
О c. Ha: u₴78
Hai n< 78
OB. H: 4478
H: M=78
O D. H: 4 s78
H: 4>78
What is the value of the standardized test statistic?
The standardized test statistic is__
. (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
What is the P-value of the test statistic?
P-value=__(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. Choose the correct answer below.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

- Use the random sample data to test the claim that the mean travel distance to work in California is less than 35 miles. Use 1% level of significance. Sample data: x¯=32.4 mis=8.3 min=35 Identify the tail of the test. Find the P-value Will the null hypothesis be rejected? Is the initial claim supported?arrow_forwardUse technology to help you test the claim about the population mean, µ, at the given level of significance, a, using the given sample statistics. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: u> 1260; a= 0.01; o = 203.23. Sample statistics: x= 1278.79, n = 300 Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. O A. Ho: H> 1260 O B. Ho: Hs 1278.79 HaiHS 1260 HaiH> 1278.79 O C. Ho: H2 1260 HaiH 1260 E. Ho: H> 1278.79 O F. Ho: H2 1278.79 HaiHS 1278.79 Ha:u< 1278.79arrow_forwardUse technology to help you test the claim about the population mean, µ, at the given level of significance, a, using the given sample statistics. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: µ> 1170; a = 0.07; o = 212.01. Sample statistics: x= 1185.03, n= 300 Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. Ο Α. Ho μ2 1185.03 Ο Β. Ho : με 1185.03 Ha: µ 1185.03 O C. H μ2 1170 O D. Ho: µ> 1170 Ha: H 1185.03 Ha: µ> 1170 Ha: us1185.03 Calculate the standardized test statistic. The standardized test statistic is (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value. P = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Determine the outcome and conclusion of the test. Ho. At the 7% significance level, there enough evidence to the claim.arrow_forward
- Listed in the accompanying table are heights (in.) of mothers and their first daughters. The data pairs are from a journal kept by Francis Galton. Use the listed paired sample data, and assume that the samples are simple random samples and that the differences have a distribution that is approximately normal. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that there is no difference in heights between mothers and their first daughters. ... Question content area top right Part 1 Mother 62.0 65.0 64.7 65.5 65.0 67.0 66.0 66.5 63.0 58.5 Daughter 68.0 69.0 66.5 63.0 68.0 62.0 66.5 66.7 63.5 66.5 Question content area bottom Part 1 In this example, μd is the mean value of the differences d for the population of all pairs of data, where each individual difference d is defined as the daughter's height minus the mother's height. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test? H0:…arrow_forwardSuppose that you want to perform a hypothesis test for a population mean. Assume that the population standard deviation is unknown and that the sample size is relatively small. In each part, the distribution shape of the variable under consideration is given. Decide whether you would use the t-test, the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, or neither. a. Triangular b. Symmetric bimodal c. Left skewedarrow_forwardA null hypothesis states that p=.7, the observed sample proportion is p=.653 with a sample size of n=90. Determine the z-score. -0.97 O 0.92 -1.48 O 1.35arrow_forward
- You want to compare differences in prior arrests across ethnicity in your study, you measured ethnicity as white =0 black =1 hispanic=2, and other =3. Prior arrests was recorded as the number of prior arrests. which test would you perform to see if arrests differ across diffrent ethnic categories? A. ANOVA B. T-testarrow_forwardUse the random sample data to test the claim that the mean travel distance to work in California is less than 35 miles. Use 1% level of significance. Sample data: x¯=32.4 mi s=8.3 mi n=35 Identify the tail of the test. Find the P-value Will the null hypothesis be rejected? Is the initial claim supported?arrow_forwardWhat does the t test for the difference between the means of 2 independent populations assume? A. The sample sizes are equal. B. The sample variances are equal. C. The populations are approximately normal. D. All of the abovearrow_forward
- Researchers studied the mean egg length (in millimeters) for a bird population. After taking a random sample of eggs, they obtained a 95% confidence interval of (45,60). What is the value of the margin of error? Choose the correct answer below. A. 15 mm B. 52.5 mm O c. 7.5 mm O D. 1.96arrow_forwardAccording to an expert for the automotive industry, 68% of Americans know how to drive a manual transmission vehicle. Suppose 220 Americans are sampled. (Give results accurate to at least 4 decimal places.) a. Of the 220 people sampled, 160 respond that they know how to drive a manual transmission vehicle. What is the sample statistic p? p = b. Under the assumption that the industry expert's claim that 68% of Americans know how to drive a manual transmission vehicle is valid, what is the probability that the survey in part (a) would result in a p that is at least as high as the one found? c. Under the assumption that the industry expert's claim that 68% of Americans know how to drive a manual transmission vehicle is valid, what is the probability that the survey in part (a) would result in a p that is between 66% and 71%?arrow_forwardA large sample size is needed to show significance in a test of two population standard deviation. O True O Falsearrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





