
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134753119
Author: Sheldon Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
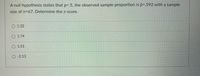
Transcribed Image Text:A null hypothesis states that p=.5, the observed sample proportion is p=.592 with a sample
size of n=67. Determine the z-score.
O 1.22
O 1.74
O 1.51
O -2.13
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, probability and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 9:56 AM Sat Dec 19 * 67% +: 0 3) For the sample below, find the range, quartiles, interquartile range, and 5-number summary. 27, 28, 30, 31, 31, 32, 34, 36, 39, 41, 44, 45 2 19 >arrow_forwardThe average American gets a haircut every 43 days. Is the average different for college students? The data below shows the results of a survey of 11 college students asking them how many days elapse between haircuts. Assume that the distribution of the population is normal. 32, 46, 49, 45, 50, 49, 43, 45, 38, 46, 42 What can be concluded at the the a =0.01 level of significance level of significance? a. For this study, we should use Select an answer b. The null and alternative hypotheses would be: Họ: ? Select an answer v H. Select an answer Y C. The test statistic ? (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) d. The p-value - (Please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) e. The p-value is 2 f. Based on this, we should Select an answer the null hypothesis, g. Thus, the final conclusion is that, The data suggest the populaton mean is significantly different from 43 ata = 0.01, so there is fficient evidence tr conrlide that -he nonulation.arrow_forward24arrow_forward
- Use technology to help you test the claim about the population mean, p, at the given level of significance, a, using the given sample statistics. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: u > 1280; a = 0.07; o = 196.31. Sample statistics: x= 1308.11, n= 200 H p> 1280 Ha: p 1308.11 O D. Ho: Hs 1308.11 Ha ps 1308.11 Ha: p> 1308.11 O E. H, p> 1280 O F. Ho: µ2 1280 Ha: u< 1280 Ha ps 1280 Calculate the standardized test statistic. The standardized test statistic is 2.03. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value. P 3D (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardUse the Standard Normal Table to determine the z-score that corresponds to the 33rd percentile A) -0.44 b.-0.33 C. 0.33 d.0.44 Draw a grapharrow_forwardK The population of ages at inauguration of all U.S. Presidents who had professions in the military is 62, 46, 68, 64, 57. Why does it not make sense to construct a histogram for this data set? Choose the correct answer below. O A. With a data set that is so small, the true nature of the distribution cannot be seen with a histogram. OB. There must be an even number of data values in the data set to create a histogram. OC. This data set would yield a histogram that is not bell-shaped. O D. Adequate class boundaries for a histogram cannot be found with this data set.arrow_forward
- Please give me the Right answer.arrow_forwardStatistics students believe that the mean soore on a first statistics test is 65. The instructor thinks that the mean score is higher. She samples 10 statistics students and obtains the scores: Grades 96 69 83.2 69 65 85.5 74.4 65 85.5 66.5 Test grades are believed to be normally distributed. Use a significance level of 5%. A. State the alternative hypothesis: H: Ομ 65 B. State the mean of the sample: (Round to two decimal places.) C. State the standard error of the sample means: (Round to four decimal places.) D. State the test statistic: t = (Round to four decimal places.) E. State the D-value; (Round to four decimal places.) F. Decision: O Do not reject the null hypothesis. O Reject the null hypothesis. Submit Questionarrow_forwardUse technology to help you test the claim about the population mean, , at the given level of significance, a, using the given sample statistics. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: u> 1240; a = 0.09; o = 208.13. Sample statistics: x= 1267.96, n= 300 O E. Ho: us 1267.96 O F. Ho µ> 1267.96 Ha p> 1267.96 Ha µs 1267.96 Calculate the standardized test statistic. The standardized test statistic is (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value. P = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Determine the outcome and conclusion of the test. V Ho. At the 9% significance level, there V enough evidence to the claim.arrow_forward
- State the hypotheses and identify the claim. Compute the test statistic Find the P-value. Make the decision. Write the conclusion. Assume all populations are normally distributed. Test all claims at 0.05 . Do male and female college students have the same distribution of living arrangements? Suppose that 250 randomly selected male college students and 300 randomly selected female college students were asked about their living arrangements. The results are in the table. Test the claim that male and female college students have the same distribution of living arrangement. Dormitory Apartment With Parents Other Males 72 84 49 45 Females 91 86 88 35arrow_forwardDetermine the Test statistic. Determine the P-Value. State the final conclusion that addresses the original claim.arrow_forwardThe number of students who belong to the dance company at each of several randomly selected small universities is shown below. Round sample statistics and final answers to at least one decimal place. 29, 29, 27, 26, 25, 22, 21, 47, 40, 35, 32, 30, 30, 26, 26. Estimate the true population mean size of a university dance company with 90% confidence. Assume the variable is normally distributed. ____< u < ____arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:PEARSON
