
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
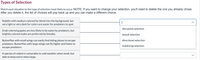
Transcribed Image Text:**Types of Selection**
Match each situation to the type of selection most likely to occur.
**NOTE:** If you want to change your selection, you'll need to delete the one you already chose. After you delete it, the list of choices will pop back up and you can make a different choice.
1. **Situation:** Rabbits with medium colored fur blend into the background, but very light or very dark fur colors are easier for predators to spot.
2. **Situation:** Drab colored guppies are less likely to be eaten by predators, but brightly colored males are preferred by females.
3. **Situation:** Butterflies with small wings can easily find hiding places to escape predators. Butterflies with large wings can fly higher and faster to escape predators.
4. **Situation:** A species of rodent is vulnerable to cold weather when small, but able to keep warm when large.
**Selection Types:**
- Disruptive selection
- Sexual selection
- Directional selection
- Stabilizing selection
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Kindly compute the the inbreeding coefficient (F) of the inbreds and the average inbreeding coefficient of the whole herd.arrow_forwardWhich of the following scenarios is an example of directional selection? A population of Sharks is evolving towards the average body size; small sharks fall prey to killer whales, large sharks can't get enough food A population of daisies is evolving away from pink individuals and towards white and red individuals. Pink flowers blend in whereas white or red can more easily be spotted by bees A population of snakes is evolving to become browner since lighter colored snakes are more easily spotted by predatorsarrow_forwardIn a Gecko population a group of Geckos skin color is controlled by one gene with two alleles "R"which codes for red and is dominant to "r" which codes for yellow and is recessive. If 100 Geckos are on the island and you gene test them to know their alleles you'll observe that 30 are homozygous red, 60 are heterozygous red, and 20 are homozygous recessive. Determine the Chi-square. assuming the original parents (Rr xRr).* Hint: determine the expected first before plugging into the equation awesome as this one? REGISTER NOW 13 5 11 4 Darrow_forward
- In a population of plants, individuals with medium-sized leaves have the highest survival and reproductive success because they can efficiently capture sunlight without losing too much water. Which type of selection is occurring in this scenario? Stabilizing selection Disruptive selection Frequency-dependent selection Directional selectionarrow_forwardGive an example of how variety in a population can lead to resilience when environments change. (Please make it short)arrow_forwardA wild population of pea plants has two alleles for flower colour in its gene pool. A dominant allele (P) specifies purple flowers; a recessive allele (p) specifies white flowers. If the frequency of allele P is 0.75, what is the expected frequency of parrow_forward
- Which form of conditioning is used most for behavior modification? Why does this form work better? Why would Classical Conditioning help someone in their daily life functioning? Which form of conditioning would you most likely see in a classroom setting? Create your own examples of each form of conditioning. Be sure to include the following information in your answer. In addressing classical conditioning: Identify UCS, UCR, NS, CS, and CR. Discuss any stimulus generalization that you observed. Discuss any extinction and spontaneous that occurred. In addressing operant conditioning: Identify negative and positive reinforcements and punishments. Label the schedule of reinforcement or punishment.arrow_forwardIn a population that had mice ranging in color from very light to very dark, which type of selection would result in a population of mostly dark mice? Group of answer choices Directional selection Disruptive selection Stabilizing selectionarrow_forwardIn a population of frogs, individuals with green coloration are camouflaged on leaves and are less likely to be eaten by predators. However, as the number of green frogs increases, predators learn to search for them more effectively, making it advantageous to be a less common color. What type of selection is occurring in this scenario? Disruptive selection 8888 Positive frequency-dependent selection Stabilizing selection Negative frequency-dependent selection Directional selectionarrow_forward
- Two males are fighting for territory that will increase the probability of mating success. Which term best describes this activity? O Intrasexual selection Intersexual selection Artificial selection O Mutationarrow_forwardSelection at one locus acts to locally maximize mean population fitness if: The population size is constant Selection is frequency independent The population is increasing in size Selection is frequency dependent The marginal fitness values are equalarrow_forwardA species of fox has a mean number of 3 Kits, while more or less kits is selected against. This is an example of diversifying selection." true or falsearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education