
The enzyme pyruvate carboxylase is discovered in a bacterium that was thought not to contain it; in this case study, you’ll see how researchers study and characterize the enzyme, and, ultimately, show how it fits into a
Following purification of the PYC enzyme by avidin-Sepharose affinity chromatography, the investigators carried out several experiments to characterize the enzyme.
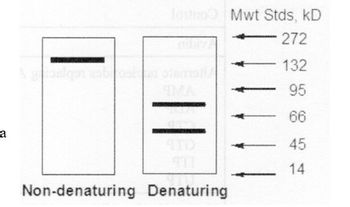
First, they ran samples of the enzyme on denaturing and non-denaturing gels; the results are shown in the figure to the right. In addition, they ran the protein through a calibrated gel filtration column, the results of which indicated that the PYC enzyme had a molecular weight of 540 kiloDaltons. In the figure, the rightmost column are where molecular weight standards of various sizes would occur if they’d been on the gels.
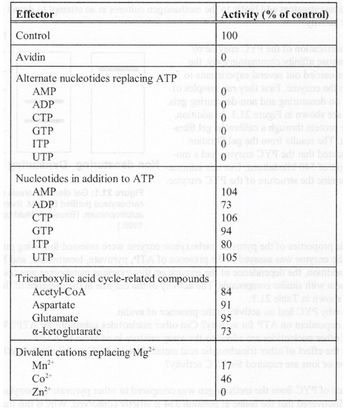
The catalytic properties of the PYC enzyme were assessed following purification. The activity of the enzyme was assayed in the presence of ATP, pyruvate, bicarbonate and Mg2+ ions (these latter ions were the control substance). In addition, the dependence of the enzyme on these various metabolites was tested by replacing them with similar compounds. The activity of the enzyme in the presence of these various molecules is shown in the table.
Part A} The amino acid sequence of PYC from the methanogen was compared to other pyruvate carboxylase enzymes, and it was discovered that the lysine at position 534 is strictly conserved. Why is this the case? Would this happen if the amino acid residue were not lysine?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

- A solution of [U 14C] glucose-1-phosphate (specific activity = 16,000 cpm/mmole) was incubated with glycogen and glycogen phosphorylase, an enzyme which adds glucose units on to glycogen. Radioactivity was incorporated into the glycogen primer at a rate = 2550 cpm/min. The rate of the enzymatic reaction in units of mmole glucose incorporated per minute is: (a) 0.016 mmol/min (b) 0.57 mmol/min (c) 0.16 mmol/min (d) 5.7 mmol/minarrow_forwardThe initial velocities of two different enzyme-catalyzed reactions were measured over a series of substrate concentrations. The following results were obtained: Enyme A: KM = 1.5 mM, Vmax = 10 μM s-1 Enyme B: KM = 5.0 mM, Vmax = 85 µM s-1 (a) Which enzyme binds to its substrate more tightly (assume k.1 >> k₂ in the Michaelis-Menten model)? (b) Calculate the initial velocities of each reaction when the substrate concentration is 2.5 mM. (c) Calculate the Kcat of each enzyme if the total enzyme concentration is 100 nM. (d) Which enzyme is the more efficient catalyst? Explain your answer. The enzyme carbonic anhydrase is strongly inhibited by the drug acetazolamide. A plot of the initial reaction velocity (as a percentage of Vmax) in the absence and presence of the inhibitor is shown below. What type of inhibition is taking place? Explain your reasoning. V (% of Vmax) 100 50 0.2 0.4 No inhibitor Acetazolamide [S] (MM) 0.6 0.8 1arrow_forwardThe enzyme aspartate transcarbamoylase catalyzes an early step in pyrimidine biosynthesis. The two states of the multi-subunit enzyme are shown below. Note that the binding of the regulatory molecule CTP (cytosine triphosphate) causes the enzyme complex to be inactive. Is this situation an example of positive or negative regulation? Explain why the use of CTP as the regulatory molecule is logical givén the overall function of this particular enzyme. INACTIVE ENZYME: T STATE catalytic subunits regulatory subunits OFF 6 CTP ON ACTIVE ENZYME: R STATEarrow_forward
- Match the following catalytic strategies with their example. Place a Letter on the picture. There are only two examples given. CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH он он OH OH + H20 OH OH OH но H. но но OH OH OH OH OH OH A. Oxidoreducatase B. Transferase C. Hydrolase D. Lyase NH3 E. Isomerase F. Ligase R-CH-COO "ooc-CH2-CH2-C-COO Amino acid a-Ketoglutaratearrow_forwardYou have discovered an organism incapable of performing the full gluconeogenic pathway. Further analysis tells you these is no issue with glycolysis in this organism, no glucose ever leaves the cell once it enters, and the cell contains unusually large concentrations of the molecules shown below. Which gluconeogenic enzyme is missing/non-functional in this organism? Defend your answer in as much detail as possible and make sure you identify the two compounds accumulating in your answer.arrow_forwardif there are twelve different intermediate products produced in the stage of a metabolic within a cell, we can expect that therearrow_forward
- Enolase has a glutamic acid residue in its active site. Describe the experiment that was done that provided evidence for the proposed function of the glutamic acid residue in catalysis by enolase.arrow_forwardIn bacteria, isocitrate dehydrogenase is regulated by phosphorylation of a specific Ser residue in the enzyme active site. X-ray structures of the phosphorylated and the nonphosphorylated enzyme show no significant conformational differences. How does phosphorylation regulate isocitrate dehydrogenase activity? O The phosphoryl group sterically hinders the substrate. O The phosphorylation bears a negative charge, which repels the substrate. O The phosphoryl group attracts positively charged Ca2* cations, which block the active site on the enzyme. None of the above.arrow_forwardExplain this to me, I’m confusedarrow_forward
- The glucose oxidase used in this experiment has a concentration of 27 U/mg. Calculate the mass (in g) of solid glucose oxidase required to react with all the glucose in 4.00 µL of10.0- mM glucose sample assuming the reaction proceeds for 30 minutes.arrow_forwardPlease atleast answer this question ?arrow_forwardThe lipase substrate emulsion contains 0.500 mg of olive oil per 3 mL Also, the molar mass of the olive oil is 885 g/mol. If all of the olive oil in a 3 mL reaction is "digested" by pancreatic lipase in a reaction, how many molecules of olive oil have been degraded?arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





