
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A sample stream of dry gas is being withdrawn from a stack. The stack gases are at 200oC and 730 mm Hg. The stream flows through a heated filter, a set of cooled impingers, a small air pump, and then through u How meter, as shown in Figure 1.5« The rate of flow is determined to be 30.0 litors/miuute at 20 °C and 790 mm Hg. If 1.42 mg of solid particles are collected on the filler in 30 minutes, calculate the concentration of particles in the stack gas (in Pg/m3}.
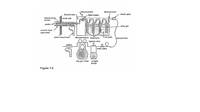
Transcribed Image Text:thermometer
thermometer
heated area
filter holder
check valve
temperature
sensor
stack wall
probe
silica gel
reverse-type
pitat tube
pitot manometer
thermometess inpingers
Lice bath
vacuum line
taypass vatve
Grit:ce
majn valve
dry gas meter airtight
pump
Figure 1.5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- NEED IT UNTIL 5:15PM Estimate the convective heat-transfer coefficient for natural convection from a horizontalsteam pipe. The outside surface temperature of the insulated pipe is 80°C. Thesurrounding air temperature is 25°C. The outside diameter of the insulated pipe is 10 cm. please help me if my answer is wrong.arrow_forwardIn a counter-current absorption tower, a process gas containing 0.04 (mole fraction) ammonia is scrubbed with pure water. The exit gas contains 0.002 (mole fraction) ammonia.The diameter of the tower is 1m, and the packing has a large area per volume of 200 m2m–3. The overall mass transfer coefficient based on the liquid side driving force, KL, is 1.5×10−5ms–1. The total gas and liquid concentrations are 0.6kmolm–3and 20 kmolm–3respectively and the gas flowrateis 0.03kmols–1. The actual liquid to gas ratio is 1.5 times that of the minimum liquid to gas ratio. The equilibrium for ammonia between the air and water is given by y* = 1.04x. Draw a rough sketch of the operating and equilibrium lines and label the slopes. How many transfer units are needed? What is the height of the tower?arrow_forward28.21 A 1 x 10-2 m spherical pellet is sprayed with a very thin coat of paint. The paint contains a volatile solvent. To dry the pellet, a 300 K and 1.013 × 105 Pa air stream flows around it with a bulk velocity of 1 m/s. The estimated loading of the solvent in the wet paint is 0.12 g solvent/cm³. Physical properties are vapor pressure of the solvent = 1.27 x 104 Pa mass diffusivity of solvent in air = 9.62 x 10-6 m²/s kinematic viscosity of air density of air = 1.569 x 10-5 m²/s = 1.177 kg/m³ thermal conductivity of air thermal diffusivity of air heat capacity of air = 2.624 x 10-2 J/m.s. K = 2.216 x 10-5 m²/s = 1.006 J/g. K = 78 g/g mole molecular weight of the solvent Use the McAdam's¹¹ equation Nu = 0.37(Redp) 0.6 (Pr) 1/3, where Redp dp vx V to evaluate (a) the heat-transfer coefficient, h; (b) the mass-transfer coefficient, ke; (c) the molar flux of the solvent into the air stream.arrow_forward
- In a counter-current absorption tower, a process gas containing 0.04 (mole fraction) ammonia is scrubbed with pure water. The exit gas contains 0.002 (mole fraction) ammonia.The diameter of the tower is 1m, and the packing has a large area per volume of 200 m2m–3. The overall mass transfer coefficient based on the liquid side driving force, KL, is 1.5×10−5ms–1. The total gas and liquid concentrations are 0.6kmolm–3and 20 kmolm–3respectively and the gas flowrateis 0.03kmols–1. The actual liquid to gas ratio is 1.5 times that of the minimum liquid to gas ratio. The equilibrium for ammonia between the air and water is given by y* = 1.04x. What is the mol fraction of ammonia in the liquid?arrow_forward8 i. Estimate the dimensions of a drying chamber for a spray dryer that has an output of 1000 kg/h of a heat-sensitive biological material at 60oC containing 5% moisture and having a mean particle size of 100 micrometers. The feed contains 40% solids by weight in an aqueous solution at 4oC. The inlet air has a humidity of 0.01 kg/kg dry air and is at 150oC, while the outlet air is at 80oC.arrow_forwardForced air at T = 25°C and V = 10 m/s is used to cool electronic elements on a circuit board. One such ele- ment is a chip, 4 mm X 4 mm, located 120 mm from the leading edge of the board. Experiments have revealed that flow over the board is disturbed by the elements and that convection heat transfer is correlated by an expression of the form Nu,= 0.04 Re0.85 P.1/3 V. T uz bog fr dW ninin tol 1 = 4 mm Chip Board 0:00 Wira L= 120 mm Estimate the surface temperature of the chip if it is dis- sipating 30 mW.arrow_forward
- P3arrow_forwardThe results of air temperature measurement obtained a dry bulb temperature of 37 ° C and a wet bulb temperature of 27.5 ° C. Using a psychrometric chart, determine the properties of the air as follows:a. RH:%b. Water content: kg water / kg airc. Specific volume: m3 / kgd. Enthalpy: kJ / kge. Condensation temperature: ° CIf the air is within 162 m3 space, determinef. Air weight (dry air and water vapor): kgg. the amount of water content in the space: kgarrow_forwardA continuous single-effect evaporator is to be fed with 5000 kg/hr of solution containing 1 wt% solute, the feed is at a temperature of 303 K. it is to be concentrated to a solution of 2 wt% solute. The evaporation is at atmospheric pressure (101.3 kPa) and the area of the evaporator is 69.7 m2 Saturated steam is supplied at 143.3 kPa for heating. It is assumed that the Cp of feed is the same with that of water which is 4.1 kj/kg-K. Assume no BPR. Calculate: overall heat transfer coefficientarrow_forward
- Q2\ A- A triple effect backward feed evaporator are used to concentrate NaOH solution of 10. percent and 1.25 Kg/s of feed which is initially at 297 K, using steam at 393 K and a vacuum such that the boiling point in the last effect is 325 K. If the total water vaporized from the three effects was only one kilogram per second, what are the steam consumption, the heat transfer areas, and the concentration for each effect. Assume the heat capacity of liquid 4.187 KJ/ Kg.K and the overall heat transfer coefficients are 2.5, 2, and 1.6 KW/m². K. respectively. Cp= 4.81kg/kg.karrow_forwardIn a counter-current absorption tower, a process gas containing 0.04 (mole fraction) ammonia is scrubbed with pure water. The exit gas contains 0.002 (mole fraction) ammonia.The diameter of the tower is 1m, and the packing has a large area per volume of 200 m2m–3. The overall mass transfer coefficient based on the liquid side driving force, KL, is 1.5×10−5ms–1. The total gas and liquid concentrations are 0.6kmolm–3and 20 kmolm–3respectively and the gas flowrateis 0.03kmols–1. The actual liquid to gas ratio is 1.5 times that of the minimum liquid to gas ratio. The equilibrium for ammonia between the air and water is given by y* = 1.04x. If the operator increases the gas flow by 20% while keeping the liquid flow and the entering gas and liquid compositions constant,what are the new mole fractions of ammonia in the exit gas and the exit liquid? Assume that the overall mass transfer coefficient does not change with the gas flow.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The