
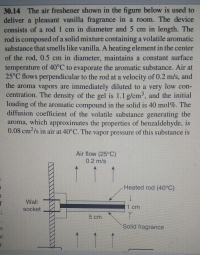
The air freshener shown in the figure below is used to deliver a pleasant vanilla fragrance in a room. The device consists of a rod 1cm in diameter and 5cm in length. The rod is composed of solid mixture containing a volatile aromatic substance that smells like vanilla. A heating element in the center of the rod, 0.5cm in diameter, maintains a constant surface temperature of 40°C to evaporate the aromatic substance. Air at 25°C flows perpendicular to the rod at a velocity of 0.2m/s, and the aroma vapors are immediately diluted to a very low concentration. The density of the gel is 1.1g/cm^3, and the initial loading of the aromatic compound in the solid is 40 mol%. The diffusion coefficient of the volatile substance generating the aroma, which approximates the properties of benzaldehyde, is 0.08cm^2/s in air at 40°C. The vapor pressure of this substance is 428Pa at 40°C

Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 9 images

- Analyze the following diagram. What is the heat rate to the left side of the heater? What is the heat rate to the right side of the heater? Tin = 16°C W h = 40- T = -20°C u = 188 m2K 60mm Air 60mm 10mm 6mm 10mm 14mm 6mm 2mm 2mm Blue: Epoxy Grey: Aluminum Green: Fiberglass Yellow: Silicone Orange: Heater Blanket, 2000w Note: Treat the outer left wall as flat plates in external convection. Note: Ignore the thickness of the heater blanket.arrow_forwardA 10 cm thick piece of beef steak will be frozen in the freezer room -40 ° C. This product has a moisture content of 73%, a density of 970 kg / m³, and a thermal conductivity (frozen) of 1.1 W / (m K). Estimate the freezing time. using the Plank equation. This product has an initial freezing temperature of -1.75 ° C, and the movement of air in the freezing room gives a convective heat transfer coefficient of 15 W / (m² K). t f = hourarrow_forwardEstimate the thermal conductivity of tomato juice at 35 ° C. (Water content = 87.0% wet basis). Thermal conductivity of material = AnswerW / m ° Carrow_forward
- Heat Conduction The wall (thickness L) of a furnace, with inside temperature 800° C, is comprised of brick material [thermal conductivity = 0.02 W m-¹ K-¹)]. Given that the wall thickness is 12 cm, the atmospheric temperature is 0° C, the density and heat capacity of the brick material are 1.9 gm cm-³ and 6.0 J kg ¹ K¹ respectively, estimate the temperature profile within the brick wall after 2 hours. Solve the partial differential equation ƏT = pc at Ə əx (NOT) k subject to the initial condition TX 2L and = T(x,0) = 800 sin and boundary conditions at the inner (x = L) and outer (x = 0) walls of T = 0 x = 0 = 0 ƏT at x = L əx Find the temperature profile at T = 7200 seconds at = 2 hours.arrow_forward(a) What is the heat loss per unit length of the pipe?(b) The pipe material is switched to PTFE (k = 0.38 W/(m⋅K)). To maintain the same heat loss as theprevious question, if all other parameters are to remain the same as before, what is the required thicknessof the pipe wall in centimeters?arrow_forwardInsulating material is used to reduce heat loss from the heating furnace walls to the room. The surface temperature of the insulating material is 100 ° C and the other surfaces 25 ° C. Allowable heat loss up to 160 W / m2 from the wall. If the thermal conductivity of the insulation material is 0.05 W / (m ° C), calculate the required thickness of insulation. insulation thickness = Answer cmarrow_forward
- When two objects at different temperatures are brought into contact with one another (such as a hot steel bar dropped into cold water), the cold object will O increase in temperature to the same temperature as the hot object before being placed in the water. O lose as much heat as the hot object loses the cold object will remain unchanged O gain as much heat as the hot object losesarrow_forwarda piece of beef steak 7 cm thick will be frozen in the freezer room -40 degrees Celsius This product has a moisture content of 73% density 970 kg / m³ and a thermal conductivity of 1.1 W / (m K) frozen using the plank equation. This product has an initial freezing temperature of -1.75 degrees Celsius and the movement of air in the raw chamber gives a convection heat transfer coefficient of 10 W / (m² K). tf =arrow_forwardA piece of beef steak 7 cm thick will be frozen in the freezer room -30 ° C. This product has a moisture content of 73%, a density of 970 kg / m³, and a thermal conductivity (frozen) of 1.1 W / (m K). Estimate the freezing time. using the Plank equation. This product has an initial freezing temperature of -1.75 ° C, and the movement of air in the freezing room gives a convective heat transfer coefficient of 15 W / (m² K). t f = ... hour.arrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





