
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
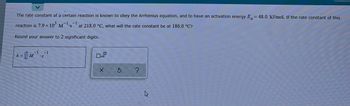
Transcribed Image Text:The rate constant of a certain reaction is known to obey the Arrhenius equation, and to have an activation energy E= 48.0 kJ/mol. If the rate constant of this
-1
reaction is 7.9 x 10³ M
at 218.0 °C, what will the rate constant be at 186.0 °C?
Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
-1
= M¹ S
X
Ś
k=
4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The rate constant of a certain reaction is known to obey the Arrhenius equation, and to have an activation energy E, = 8.0 kJ/mol. If the rate constant of this reaction is 1.1 x 10° M -1 -1 'S at 160.0 °C, what will the rate constant be at 108.0 °C? Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forwardThe rate constant k for a certain reaction is measured at two different temperatures: temperature k 314.0 °C 2.1 x 10¹1 384.0 °C 4.3 × 10¹1 Assuming the rate constant obeys the Arrhenius equation, calculate the activation energy E for this reaction. a Round your answer to 2 significant digits. kJ E = x10 a mol X Ś ?arrow_forwardThe rate constant of a certain reaction is known to obey the Arrhenius equation, and to have an activation energy E,=64.0 kJ/mol. If the rate constant of this -1 reaction is 0.0021 M - 1 S. at 40.0 °C, what will the rate constant be at -32.0 °C? Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 1 |M - 1 k = •S Ox10arrow_forward
- A certain catalyzed reaction is known to have an activation energy E= 11.0 kJ/mol. Furthermore, the rate of this reaction is measured at 296. K and found to be 1.1 × 10 M/s. Use this information to answer the questions in the table below. Suppose the concentrations of all reactants is kept the same, but the temperature is raised by 10% from 296. K to 326. K. How will the rate of the reaction change? Suppose the concentrations of all reactants is kept the same, but the catalyst is removed, which has the effect of raising the activation energy by 5%, from 11.0 kJ/mol to 11.6 kJ/mol. How will the rate of the reaction change? The rate will The rate will choose one choose one choose one stay the same rise about 5% rise more than 5% rise less than 5% fall about 5% fall more than 5% fall less than 5% Varrow_forwardThe rate constant k for a certain reaction is measured at two different temperatures: temperature k 248.0 °C 9.9 x 108 169.0 °C 9.8 x 107 Assuming the rate constant obeys the Arrhenius equation, calculate the activation energy E for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. kJ E = x10 mol X S ?arrow_forwardWhen a reaction is performed at a temperature of 314. K, the rate constant is 1.9 x 10-6 s-1. When performed at 457. K, the rate constant is 8.5 x 104s-1. Calculate the activation energy_(Ea) of this reaction, in units of kJ/mol.arrow_forward
- The rate constant of a certain reaction is known to obey the Arrhenius equation, and to have an activation energy E, = 9.0 kJ/mol. If the rate constant of this reaction is 1.1 x 10 M 's -1 at 226.0 °C, what will the rate constant be at 146.0 °C? 10° Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forwardSketch a potential energy diagram for the decomposition of nitrous oxide. N2O(g) →→ N2(g) + O(g) The activation energy for the forward reaction is 171 kJ; If the activation energy for the reverse reaction is 99 kJ, calculate the standard enthalpy change for this reaction. Transfer all the information into an energy diagram. label appropriatelyarrow_forwardWhat is the activation energy of a reaction if it has the following rate constants?arrow_forward
- When heated, cyclopropane is converted to propene. Rate constants for this reaction at 470. °C and 510. °C are k1 = 1.10 × 10-4 s-1 and k2 = 1.02 × 10-3 s-1, respectively. Determine the activation energy, Ea, from these data. Ea = kJ/molarrow_forwardThe rate constant k for a certain reaction is measured at two different temperatures: temperature 311.0 °C E = a 246.0 °C Assuming the rate constant obeys the Arrhenius equation, calculate the activation energy E for this reaction. a Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 0 kJ k 1.4 × 10¹⁰ 2.0 × 10⁹ mol x10 × Sarrow_forwardThe rate constant k for a certain reaction is measured at two different temperatures: temperature k 407.0 °C 4.8 x 10¹0 268.0 °C 2.3 × 10 ¹0 a Assuming the rate constant obeys the Arrhenius equation, calculate the activation energy E for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. kJ E = x10 a mol X 3 ?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY