
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
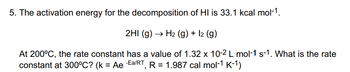
Transcribed Image Text:5. The activation energy for the decomposition of HI is 33.1 kcal mol-1.
2HI (g) → H₂ (g) + 12 (g)
At 200°C, the rate constant has a value of 1.32 x 10-2 L mol-1 s-1. What is the rate
constant at 300°C? (k = Ae Ea/RT, R = 1.987 cal mol-1 K-1)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please explainarrow_forward1 of 25 At a given temperature, the elementary reaction A B, in the forward direction, is first order in A with a rate constant of 0.0490 s-. The reverse reaction is first order in B and the rate constant is 0.0960 s-, What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction A B at this temperature? K = What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction B A at this temperature? K = %3D | privacy policy | contact us help terms of use about us careers prime W SapiA IIarrow_forwardAt a given temperature, the elementary reaction A = B, in the forward direction, is first order in A with a rate constant of 0.0230 s-1. The reverse reaction is first order in B and the rate constant is 0.0590 s-1. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction A =B at this temperature? K = What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction B =A at this temperature? K =arrow_forward
- At a given temperature, the elementary reaction A↽−−⇀B, in the forward direction, is first order in A with a rate constant of 0.0270 s−1. The reverse reaction is first order in B and the rate constant is 0.0540 s−1. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction A↽−−⇀B at this temperature? K = ? What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction B↽−−⇀A at this temperature? K = ?arrow_forwardThe rate constant of a certain reaction is known to obey the Arrhenius equation, and to have an activation energy E=22.0 kJ/mol. If the rate constant of this reaction is 1.1 x 108 M¹s¹ at 309.0 °C, what will the rate constant be at 277.0 °C? Round your answer to 2 significant digits. k = M¹ s ? dlarrow_forwardAt a given temperature, the elementary reaction A = B, in the forward direction, is first order in A with a rate constant of 0.0470 s-1. The reverse reaction is first order in B and the rate constant is 0.0610 s-1. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction A = B at this temperature? K = What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction B = A at this temperature? K =arrow_forward
- When the same reaction NO2(g) + CO(g) -----> NO(g) + CO2(g) was run at 550 K, the rate constant k2 = 3.80 M-1s-1 . Use the k value above of question #3 and this k2 to calculate the Ea for this reaction. k value from question #3: 1.90 M-1s-1 temperature from question #3: 540 Karrow_forwardThe reaction C,H3 (g) → 2C,H,(g) 4. has an activation energy of 262 kJ/mol. At 600.0 K, the rate constant, k, is 6.1 × 10-8 s-'. What is the value of the rate constant at 830.0 K? k = * TOOLS x10arrow_forwardGiven that the reaction 2 H2(g) + O2(g)-> 2 H₂O(g) is exothermic, which of the following is true of the reaction 2 H₂O(g) 2 H2(g) + O2(g)? Its activation energy is lower than that of 2 H2(g) + O2(g) -> 2 H₂O(g) Its activation energy is the same as that of 2 H2(g) + O2(g) -> 2 H₂O(g). Its activation energy is higher than that of 2 H2(g) + O2(g) ->2 H₂O(g)- O There is no relationship between its activation energy and that of 2 H2(g) + O2(g)-> 2 H₂O(g).arrow_forward
- For a certain reaction, the activation energy is found to be (1.77x10^1) kJ/mol. If the rate constant is (3.6x10^-5) at (3.78x10^2) K, what is the rate constant at (6.290x10^2) K? R = 8.314 J/Kmol; T(K) = T(°C) + 273 Report your answer in the same units as k1, with 2 sig figs.arrow_forwardCalculate the activation energy, in kJ/mol, for the reaction below A + 2 B ------> C + 2D Temp (°C) k (1/M·s) 5 5.12x103 40 6.0x105arrow_forwardConsider the following elementary reaction: NO(g) +Br,(g) → NOB1,(g) Suppose we let k, stand for the rate constant of this reaction, and k_, stand for the rate constant of the reverse reaction. -1 Write an expression that gives the equilibrium concentration of NO in terms of k,, k_, and the equilibrium concentrations of Br, and NOBr,. -1 [NO] = 0arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY