
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
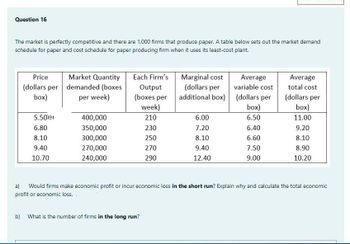
Transcribed Image Text:Question 16
The market is perfectly competitive and there are 1,000 firms that produce paper. A table below sets out the market demand
schedule for paper and cost schedule for paper producing firm when it uses its least-cost plant.
Price
(dollars per
box)
5.50lei
6.80
8.10
9.40
10.70
Market Quantity
demanded (boxes
per week)
400,000
350,000
300,000
270,000
240,000
Each Firm's
Output
(boxes per
week)
210
230
250
270
290
Marginal cost
(dollars per
additional box)
b) What is the number of firms in the long run?
6.00
7.20
8.10
9.40
12.40
Average
variable cost
(dollars per
box)
6.50
6.40
6.60
7.50
9.00
Average
total cost
(dollars per
box)
11.00
9.20
8.10
8.90
10.20
a) Would firms make economic profit or incur economic loss in the short run? Explain why and calculate the total economic
profit or economic loss.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Describe a firm’s shutdown decision.arrow_forwardMaria manages a bakery, that specializes in ciabatta bread, and has the following information on demand and costs: Ciabatta Bread Sold Per Hour (Q) Price (P) Total Cost (TC) 0 $6.00 $1.50 1 5.50 6.00 2 5.00 9.50 3 4.50 12.50 4 4.00 15.00 5 3.50 17.00 6 3.00 18.50 7 2.50 20.50 8 2.00 23.50 a. To maximize profits, Maria should sell nothing loaves of ciabatta bread per hour. (Enter your response as an integer.)arrow_forwardSuppose Poornima runs a small business that manufactures teddy bears. Assume that the market for teddy bears is a competitive market, and the market price is $25 per teddy bear. The following graph shows Poornima's total cost curve. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for teddy bears quantities zero through seven (inclusive) that Poornima produces. Calculate Poornima's marginal revenue and marginal cost for the first seven teddy bears she produces, and plot them on the following graph. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot marginal revenue and the orange points (square symbol) to plot marginal cost at each quantity. Poornima's profit is maximized when she produces teddy bears. When she does this, the marginal cost of the last teddy bear she produces is , which is than the price Poornima receives for each teddy bear she sells. The marginal cost of producing an additional teddy bear (that…arrow_forward
- Consider the perfectly competitive market for dress shirts. The following graph shows the marginal cost (MC), average total cost (ATC), and average variable cost (AVC) curves for a typical firm in the industry. 100 80 42.5, 60 ATC. 20 AVC 10 MO-O 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 50 QUANTITY (Thousands of shirts) For each price in the following table, use the graph to determine the number of shirts this firm would produce in order to maximize its profit. Assume that when the price is exactly equal to the average variable cost, the firm is indiſferent between producing zero shirts and the profit-maximizing quantity. Also, indicate whether the firm will produce, shut down, or be indifferent between the two in the short run. Lastly, determine whether it will make a profit, suffer a loss, or break even at each price. Price Quantity (Shirts) (Dollars per shirt) Produce or Shut Down? Profit or Loss? 10 20 32 40 50 60 On the following graph, use the orange points (square symbol) to plot points along the…arrow_forwardThe graph attached illustrates the Demand, Marginal Revenue, Marginal Costs, Average Total Costs and Average variable Cost curves for a firm in a perfectly competitive market. What is the breakeven price? Explain your answer. What is the shot down price? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardAmos McCoy is currently raising corn on his 100-acre farm and earning an accounting profit of $100 per acre. However, if he raised soybeans, he could earned an accounting profit of $200 per acre. Is he currently earning an economic profit?arrow_forward
- Suppose Hubert runs a small business that manufactures shirts. Assume that the market for shirts is a price-taker market, and the market price is $10 per shirt. The following graph shows Hubert's total cost curve. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue, and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for the first seven shirts that Hubert produces, including zero shirts. TOTAL COST AND REVENUE (Dollars) 125 100 75 50 25 -25 -50 0 0 1 2 ☐ ■ U 3 4 5 QUANTITY (Shirts) L 6 Total Cost 7 8 Total Revenue Profit ? Calculate Hubert's marginal revenue and marginal cost for the first seven shirts he produces, and plot them on the following graph. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot marginal revenue and the orange points (square symbol) to plot marginal cost.arrow_forwardThe figure below shows a perfectly competitive firm. Revenue and cost (dollars per unit) 25 20 15 10 5 0 10 MC ATC 40 20 30 50 Output (thousands of units per year) If the market price is $15, the firm is incurring an economic loss is making an economic profit is making zero economic profit will immediately shut down might shut down but more information is needed about the AVCarrow_forwardTulip growing is perfectly competitive and all growers have the same costs. The market price is $25 a bunch, and each grower maximizes profit by producing 2,000 bunches a week. The average total cost is $20 a bunch, and the average variable cost is $15 a bunch. The minimum average variable cost is $12 a bunch. Please draw graphs where necessary. What is the economic profit that each grower is making in the short run? What is the price at the grower’s shutdown point? What is each grower’s economic profit at the shutdown point?arrow_forward
- 1) The cost curves for a firm in a perfectly competitive industry are given below. Complete the table. If the firm operates in a perfectly competitive market, and the market price is $25 per unit, what Quantity should this firm produce at? TFC TC TVC AVC ATC MC TR S100 S100 1 S100 S130 2 S100 S150 S100 S160 S100 S172 5 S100 S185 6 S100 $210 S100 $240 S100 $280 S100 $330 10 S100 $390 Table 9.1arrow_forwardAnswer the question on the basis of the following demand and cost data for a specific firm. Demand Data Cost Data (1) Price (2) Price (3) Quantity Output Total Cost $11.00 $10.00 6 6 $61 9.99 8.86 7 7 62 9.00 8.00 8 8 64 8.00 7.00 9 9 67 7.10 6.10 10 10 72 6.00 5.00 11 11 79 5.15 4.15 12 12 86 Suppose that entry into the industry changes this firm's demand schedule from columns (1) and (3) to columns (2) and (3). Economic profit will: a.decline to about zero b.increase by $10. c. fall by $10 d. fall by $6arrow_forwardWhat is a “price taker” firm?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education