
Concept explainers
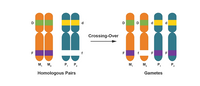
The image shows a pair of homologous chromosomes from a single parent before gamete production. M1 and M2 are maternal chromosomes, while P1 and P2 are paternal chromosomes. Two traits are shown: D represents seed color (D – green, d – yellow), while F represents flower color (F – purple, f – white). These two traits follow the patterns of basic
During crossing-over between the M2 F allele and the P1 f allele, a mutation occurred and the portion of P1 did not reattach to the chromosome.
Which of the following explains what would happen to the proportion of white flowers in a population resulting from this mutation?
A - There would be an increase in the proportion of white flowers because the f allele is distributed to more gametes.
B - There would be a decrease in the proportion of white flowers because the f allele is not distributed to as many gametes.
C - There would be an increase in the proportion of white flowers because the f allele would not be masked by the dominant trait.
D - There would be a decrease in the proportion of white flowers because the resulting gametes would be heterozygous for purple flowers.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- The diagrams represent two human somatic cells, one from a female and one from a male, and the letters in the cells represent alleles for two different traits. Male Female B = Brown hair (dominant) b = Blond hair (recessive) E = Brown eyes (dominant) e = Blue eyes (recessive) According to Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment, what are the allele combinations expected in each of the sperm cells and what combinations are expected in each of the eggs produced by these cells during meiosis? One sperm fertilized one egg, and the resulting child has blond hair and brown eyes. How is this possible given the parents' genotypes?arrow_forwardIn Drosophila, two genes w and s are X-linked and are 25 map units apart. A heterozygous female fly with a genotype w* s*/ws (w* and s* are wild-type alleles) is crossed to a male wild-type fly. What percent of progeny will have only the wild- type alleles of the w and s genes? O 50% 75% O 12.5% 37.5% 25%arrow_forwardIn the tomato, yellow flowers (Y) is dominant to white flowers (y). A true-breeding yellow flowered strain is crossed with a true-breeding white flowered strain.A. If the F1 generation is self crossed, what will be the genotypes and phenotypes of the progeny and in what portions are they expected? B. If an F1 plant were crossed with a plant from true-breeding white flowered strain, what will be the genotypes and phenotypes of the progeny and in what portions are they expected?arrow_forward
- In tomatoes, regular leaves (L) are multilobed and serrated and potato leaves (l) are broad, smooth, and single (Image 1). Red fruit (F) is dominant to yellow fruit (f). A cross is carried out between two pure lines of tomato plants, one having regular leaves and red fruit and the other having potato leaves and yellow fruit. The F1 generation all have regular leaves and red fruit. The F1individuals are then crossed with one another. Complete a Punnett square to determine the expected F2 progeny on the basis of Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment, which states that the alleles for one gene segregate independently of the alleles for other genes during gamete formation. Record the phenotypes and the phenotype ratio of the F2 generation in lowest terms.arrow_forwardMiniature wings in Drosophila result from an X-linked allele (w) that is recessive to the allele for long wings (+). In a cross of a long winged male with a long winged female, the following offspring were obtained: 100 long winged males, 106 miniature winged males, and 480 long winged females. Given this result, the female must be a carrier of the miniature wing allele. True Falsearrow_forwardThe eye ring color in wood ducks is under the control of a single, sex linked gene. The dominant allele (R) produces a white eye ring and the recessive allele (r) produces a green eye ring. Provide the results to the following crosses (note birds have ZZ:ZW sex determination). a) Provide the phenotypes and phenotypic ratios of a cross between a female with a white eye ring and a male with a green eye ring. b) Determine the phenotypes and phenotypic ratios for a cross involving an F1 female and an F1 male from the above cross.arrow_forward
- In one of his experiments, Mendel crossed homozygous yellow plants with homozygous green plants. The resulting F1 generation was allowed to self-fertilize. The F2 generation produced 930 yellow seeds and 305 green seeds. What are the genotypes of this F2 generation? O YY : yy O Yy : yy O Yy: yy O YY: Yy : yyarrow_forwardThese circles represent cells. The first cell is going through meiosis, and the 2 meiotic divisions are shown. Draw 4 chromosomes in the first cell. Two of these will be longer, and are homologs to each other; and two will be shorter and these will also be homologous to each other. Each pair of chromosomes will have exchanged parts due to “crossing over.” (Show crossover by shading or coloring, starting in the very first circle.) Follow the chromosomes through the 2 divisions.arrow_forwardIn Drosophila, a gene controls body color producing either normal body color or the mutant form black body color (bl. A second gene controls wings. The flies either have normal wings or are wingless (wn). A cross is made between a homozygous wild type fly and fly with black body and wingless. A test cross was then performed. The following progeny was observed: Phenotype # Observed Wild Type 405 Normal, wingless 85 Black, normal 100 Black, wingless 410 A. List the genotypes of the original parents. B. List the genotypes of the testcross. C. Are these two genes linked? How do you know? Edit Format Table 12pt v Paragraph v BIUAarrow_forward
- SET 2: In corn, the following allelic pairs have been identified in chromosome 3: +/b plant color booster vs. non-booster +/lg with ligule vs. without ligule +/v green plant vs. virescent A test cross between triple recessive plants and plants heterozygous for the three pairs gave the following progeny: + v lg 305 b + lg b v lg + + lg b v + 148 58 + + + 62 + y + 152 b + + 275 Total 1000 Calculate the parental and recombinant frequencies, the map distances between genes, and the coefficient of coincidence. Illustrate the gene map or sequence.arrow_forwardTwo fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) were crossed. The cross was between a homozygous red-eyed, wingless female and a white-eyed male heterozygous for wings. Recall that red eyes (R) is dominant over white eyes (r) and is inherited on the X chromosome (sex-linked) and as such, eye colour alleles should be written as superscript. In addition, the autosomal trait wings (W) is dominant over wingless (w). 1. List the female genotype 2. List the male genotype 3. Construct a Punnett Square for this dihybrid cross on a piece of paper, to determine what the offspring of such a cross would be with respect to sex, eye colour & wings. 4. Using the information from your Punnett Square answer the following: a. What genotypes did you get (list all genotype combinations; if you have more than one of the same kind, you do NOT have to re-list it.) b. What are the phenotypic ratios of the offspring with respect to sex, eye colour and wings?arrow_forwardO All three genes are linked, but need to do more crosses and data to determine the gene order. All three genes are linked with the flower color gene (F) in the middle. All three genes are linked with the seed weight gene (S) in the middle. All three genes are linked with the leaf size gene (L) in the middle.arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





