
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
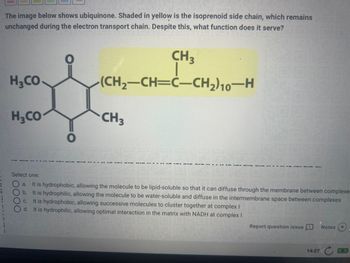
Transcribed Image Text:The image below shows ubiquinone. Shaded in yellow is the isoprenoid side chain, which remains
unchanged during the electron transport chain. Despite this, what function does it serve?
CH3
(CH₂-CH=C-CH₂) 10-H
H3CO
H3CO
I
DOO
CH3
--
Select one:
a. It is hydrophobic, allowing the molecule to be lipid-soluble so that it can diffuse through the membrane between complexe.
b. It is hydrophilic, allowing the molecule to be water-soluble and diffuse in the intermembrane space between complexes
C. It is hydrophobic, allowing successive molecules to cluster together at complex I
d. It is hydrophilic, allowing optimal interaction in the matrix with NADH at complex I
Report question issue Notes +
14:27 -
CO
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- You are studying a biochemical pathway that requires ATP as an energy source. To your dismay, the reactions soon stop, partly because the ATP is rapidly used up and partly because an excess of ADP builds up and inhibits the enzymes involved. You are about to give up when the following table from a biochemistry textbook catches your eye. A. ذن فه B. Substrates C. Creatine + ATP ATP + H₂O Pyrophosphate + H₂O Glucose-6-phosphate + H₂O Enzyme A Enzyme B Enzyme C Enzyme D Products Creatine-phosphate + ADP Which of the following reagents is/are most likely to revitalize your reaction? a vast excess of ATP glucose 6-phosphate and enzyme D creatine phosphate and enzyme A D. pyrophosphate ADP + Phosphate 2 Phosphate Glucose + Phosphate AG (kJ/mol) +3 -7.3 -7.0 -3.3arrow_forwardV-class proton pumps run backward relative to the F-class ATP synthase. Consider the cartoon, which shows the conformations of the beta-subunits and ATPIADP + Pj of the F-class synthase. Which of the following associations between the conformation of the beta subunit and ATP/ADP + P¡ is correct for V- Binding Change Mechanism loose binding ADP+P ATP ATP class pumps? C repeat ADP + P, ADP АТР tight binding АТР +P оpen АТР O The open conformation releases ATP. Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP + P¡ drives the change from tight to loose. O Binding of ADP + P¡ drives change from open to loose. Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP + Pj drives the change from open to loose.arrow_forwardExplain which of the following substances ATP, CoA-SH, FAD and NAD+ have the subunits in their structure? A.Have 2 two ribose subunits.arrow_forward
- 3) The overall reaction for photosynthesis is: 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + ATP C6H₁2O6+ 60₂ (or more accurately 2x C₂H603) a. On this diagram identify where each of these reactants and products are found. b. Why don't you see the water or oxygen in this diagram? C. We can find the electrons from the water on here, where are they? Figure 8.17-3 3 ADP My 32ATP W 3P Phase 3: Regeneration of RuBP RuBP Input 3 as 3 CO₂ Rubisco 5000℗ G3P 300dogoe P 6000℗ 3-Phosphoglycerate Calvin Cycle Phase 1: Carbon fixation 600 10000 G3P Output 6 P G3P 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate 6 ATP 6 ADP 6 P₁ 6 NADP+ Glucose and other organic compounds 6 NADPH Phase 2: Reductionarrow_forwardWhat would be the most direct result if NAG (N-acetylglucosamine acid) could not be synthesized? The outer membrane would have nothing to attach to The tetrapeptide chain beneath NAM could not be formed There would be no way to form a dimer with NAM (N-acetylmuramic acid) One of the domains of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) could not be madearrow_forwardGive detailed Solution with explanation needed of all options..don't give Handwritten answer..don't use Ai for answering this....give correct answerarrow_forward
- Loss of this enzyme would be lethal to the cell CH₂-CH-CH₂ OH OH Glycerol- phosphate Loss of this enzyme would severely reduce the exchange of lipids between the cytosol and lumen P CH₂-CH-CH₂ O O I =C C=O Loss of this enzyme would lead to membrane phospholipids with identical phosphate head groups Phosphatase Acyl transferase Loss of this enzyme would result in membranes deficient in phosphatidylcholine Choline head Cytosol group ER lumen Choline phosphotransferase Loss of these enzymes would prevent lipid transfer between the ER and mitochondria Flippase lipid exchange proteinsarrow_forwardSay cholesterol were synthesized using acetate labeled with C15 at Carbon 1. What percentage of the cholesterol carbons would be C15? 100% O 0% O 75% O 25% O 50%arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is true O Sphingomyelin posses phosphoryl serine in addition to two long hydrocarbon chains, one contributed by a fatty acid and the other by sphingosine OLipid compositions of membrane mono-layers are symmetrical O Unsaturated fatty acids have double bond(s) in the cis configuration In ABO blood typing, lack of glycosyltransferase and galactosyltransferase produces AB blood grouparrow_forward
- Amino acids are linked through peptide bonds to form proteins. This linkage of amino acids in the formation of proteins accomplished by [ Select ] reaction V [ Select ] Hydrolysis Fission Condensation Fusionarrow_forwardHO molecule E HO. (CH12 CH, OH NH, HO molecule F HO molecule D molecule C H,C-(CH),3 of H,C-(CH,) H,C-(CH molecule B H3C-(CHa)12 H,C-(CH) но molecule Aarrow_forwardCarbon dioxide is considered to be a "waste" product of cellular respiration. Yet, there are still electrons, in the bonds between the C and O atoms. Provide an explanation as to why the electrons in these covalent bonds of CO2 are not good for "harvesting" and putting into the ETC, unlike all the other bonds that were in the original glucose molecule.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON