
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
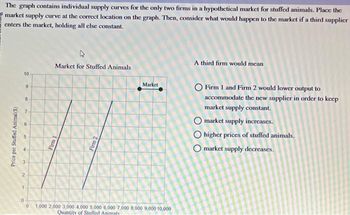
Transcribed Image Text:The graph contains individual supply curves for the only two firms in a hypothetical market for stuffed animals. Place the
market supply curve at the correct location on the graph. Then, consider what would happen to the market if a third supplier
enters the market, holding all else constant.
Price per Stuffed Animal (5)
10
9
8
A
6
0
5
m
0
Market for Stuffed Animals
Firm I
Firm 2
Market
1,000 2,000 3,000 4,000 5,000 6,000 7,000 8,000 9,000 10,000
Quantity of Stuffed Animals
A third firm would mean
O Firm 1 and Firm 2 would lower output to
accommodate the new supplier in order to keep
market supply constant.
O market supply increases.
O higher prices of stuffed animals.
O market supply decreases.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please explain correctly and clearly.arrow_forwardA hotel rents rooms to customers by the night. The hotel determines that if it sets the price of the room to be $160 per night, 145 rooms will be rented. In order to rent 195 rooms, it must lower the price to $110 per night. If the hotel sets the price to be $110 per night, what is the marginal revenue? The marginal revenue is $ per room. (Round answer to nearest dollar. If more than one answer, separate with a comma.)arrow_forwardThe following graph shows the daily market for small cardboard boxes in San Diego. PRICE (Dollars per small box 10 9 Demand 0 161 6 QUANTITY (Millions of small boxes) 2 Supply 19 10 Suppose that Talero is one of more than a hundred competitive firms in San Diego that produce such cardboard boxes. Based on the preceding graph showing the daily market demand and supply curves, the price Talero must take as given isarrow_forward
- 3.14 Each of the 10 firms in a competitive market has a cost function of C = 25+q². The market demand function is Q = 120-p. Determine the equilibrium price, quantity per firm, and market quantity. Marrow_forward3. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for frying pans is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 100 90 Profit or Loss 80 70 ATC 60 50 40 30 AVC 20 MC 10 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 QUANTITY (Thousands of pans per day) In the short run, at a market price of $50 per pan, this firm will choose to produce 37,500 pans per day. PRICE (Dollars perpan)arrow_forwardThe table below shows the weekly marginal cost (MC) and average total cost (ATC) for Buddies, a purely competitive firm that produces novelty ear buds. Assume the market for novelty ear buds is a competitive market and that the price of ear buds is $6.00 per pair. Buddies Production Costs Quantity MC ATC of Ear Buds ($) ($) 20 1.00 25 2.00 1.20 30 2.46 1.41 35 3.51 1.71 40 4.11 2.01 45 5.43 2.39 50 5.99 2.75 55 8.47 3.27 Instructions: In part a, enter your answer as the closest given whole number. In parts b-d, round your answers to two decimal places. a. If Buddies wants to maximize profits, how many pairs of ear buds should it produce each week? pairs b. At the profit-maximizing quantity, what is the total cost of producing ear buds? 2$ c. If the market price for ear buds is $6 per pair, and Buddies produces the profit-maximizing quantity of ear buds, what will Buddies profit or loss be per week? 2$arrow_forward
- The following graph illustrates the market for small moving trucks in Eugene, OR, during Oregon's fall move-in week. PRICE (Dollars per small truck) 100 Demand 90 Supply 80 70 28 80 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 8 9 10 QUANTITY (Hundreds of small trucks) Suppose that Zoomba is one of over a dozen competitive firms in the Eugene area that offers moving truck rentals. Based on the preceding graph showing the weekly market demand and supply curves, the price Zoomba must take as given is Fill in the price and the total, marginal, and average revenue Zoomba eams when it rents 0, 1, 2, or 3 trucks during move-in week. Quantity (Trucks) Price Total Revenue (Dollars per truck) (Dollars) 0 1 2 3 Marginal Revenue (Dollars) Average Revenue (Dollars per truck) 0 The demand curve faced by Zoomba is identical to which of its other curves? Check all that apply. Supply curve Average revenue curve Marginal cost curve Marginal revenue curvearrow_forward8. Refer to the information in the table below to answer the following questions: TVC €0 10 15 Quantity of fruit baskets 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 TFC €50 50 50 50 50 50 50 21 31 46 68 TC MC -- 10 5 6 10 15 22 a) The firm sells fruit baskets in a perfectly competitive market. Calculate the firm's total cost for each level of production and complete the table. b) Assume that the market price of a fruit basket is €15. To maximize profit, how many fruit baskets should the firm sell? c) At the profit-maximizing quantity, what is the profit?arrow_forward4 The Competitive Equilibrium Model—Deriving Supply] Negar owns a trendy and sustainable shoe factory. The total cost of producing a given number of pairs of shoes is displayed in the table below. Assume Negar can only produce the integer quantities of pairs of shoes specified in the table. Number of pairs Total Cost 0 400 10 410 20 430 30 460 40 500 50 580 60 680 70 800 b. Draw the supply curve for Negar’s shoe factory. c. Suppose the wholesale market for shoes that sell to retail stores is competitive, with a market price of $10 per pair (i.e., $100 per 10 pairs). If Negar’s goal is to maximize profits, how many pairs will she choose to sell? d. What are Negar’s profits when she sells the number of pairs from (c) at the market price of $10? e. Calculate Negar’s producer surplus given the price and quantity from part (c). How does this compare to the profit calculated in part (d)?arrow_forward
- 19 Market Representative Firm MC i of A $7 a MR = P АТС b $5 AVC $2 D1 18,000 70 100 115 Quantity (Q) Output (Q) The diagram above shows a Perfectly Competitive market on the left, and a representative firm supplying in that market on the right. If the entry of new firms into the market caused the equilibrium Price to decrease to $5, the representative firm would: Select one: а. earn a positive Economic Profit. b. earn a negative Economic Profit. c. shut down in the short-run. d. earn zero Economic Profit. Price $$$arrow_forwardHow low would the market price haveto fall before the firm decided to produce nothing?arrow_forwardHomework (Ch 06) Back to Assignment Attempts Do No Harm / 1 3. Effects of rent control Rent controls force landlords to price apartments below the equilibrium price level. An immediate effect is a shortage (excess demand) of apartments, because the quantity of apartments demanded is greater than the quantity supplied at the regulated price. When cities prevent landlords from charging market rents, which of the following are common long-run outcomes? Check all that apply. O Landlords earn lower profits from renting housing units, but the rent charged has no effect on either the quantity or quality of rental units. O The future supply of rental housing units increases. O Black markets develop. O The quality of rental housing units falls.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education