
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
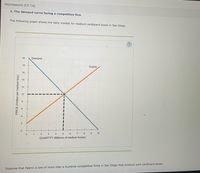
Transcribed Image Text:Homework (Ch 14)
2. The demand curve facing a competitive firm
The following graph shows the daily market for medium cardboard boxes in San Diego.
20
Demand
18
Supply
16
14
12
10
8.
1
2 3
4.
6.
7
8
10
QUANTITY (Millions of medium boxes)
Suppose that Falero is one of more than a hundred competitive firms in San Diego that produce such cardboard boxes.
PRICE (Dollars per medium box)
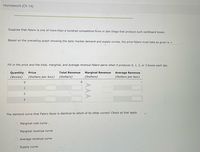
Transcribed Image Text:Homework (Ch 14)
Suppose that Falero is one of more than a hundred competitive firms in San Diego that produce such cardboard boxes.
Based on the preceding graph showing the daily market demand and supply curves, the price Falero must take as given is $
Fill in the price and the total, marginal, and average revenue Falero earns when it produces 0, 1, 2, or 3 boxes each day.
Quantity
Price
Total Revenue
Marginal Revenue
Average Revenue
(Вохes)
(Dollars per box)
Dollars)
(Dollars)
(Dollars per box)
1
2
3
The demand curve that Falero faces is identical to which of its other curves? Check all that apply.
O Marginal cost curve .
O Marginal revenue curve
O Average revenue curve
O Supply curve
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3. Profit maximization using total cost and total revenue curves Suppose Sam runs a small business that manufactures shirts. Assume that the market for shirts is a perfectly competitive market, and the market price is $20 per shirt. The following graph shows Sam's total cost curve. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for the first seven shirts that Sam produces, including zero shirts. TOTAL REVENUE, TOTAL COST, AND PROFIT (Dollars) 200 175 150 125 100 75 50 25 a -25 0 3 6 QUANTITY OF OUTPUT (Shirts) 2 4 5 Total Cost 7 8 O Total Revenue Profit (?)arrow_forward35 3. The components of marginal revenue Raphael's Fire Engines is the sole seller of fire engines in the fictional country of Pyrotania. Initially, Raphael produced five fire engines, but he has decided to increase production to six fire engines. The following graph shows the demand curve Raphael Faces. As you can see, to sell the additional engine, Raphael must lower his price from $160,000 to $120,000 per fire engine. Note that although Raphael gains revenue from the additional engine he sells, he also loses revenue from the initial five engines because he sells them all at the lower price. Use the purple rectangle (diamond symbols) to shade the area representing the revenue lost from the initial five engines by selling at $120,000 rather than $160,000. Then use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to shade the area representing the revenue gained from selling an additional engine at $120,000. 200 180 100 5 5 5 5 PRICE (Thousands of dollars par fra angina) 35 Domand Revenue Last 0…arrow_forwardCENGAGE MINDTAP Assignment 8 (Ch 14) 1 + 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 QUANTITY (Millions of small boxes) Suppose that Talero is one of more than a hundred competitive firms in Houston that produce such cardboard boxes. $5 Based on the preceding graph showing the daily market demand and supply curves, the price Talero must take as given is Fill in the price and the total, marginal, and average revenue Talero earns when it produces 0, 1, 2, or 3 boxes each day. Average Revenue (Dollars per box) Total Revenue Quantity (Вохes) Price Marginal Revenue (Dollars per box) (Dollars) (Dollars) 1 1 2 The demand curve that Talero faces is identical to which of its other curves? Check all that apply. Marginal revenue curve Marginal cost curve Supply curve AAAarrow_forward
- The following graph illustrates the market for small moving trucks in Bloomington, IN, during Indiana's fall move-in week. PRICE (Dollars per small truck) 100 90 80 70 80 50 40 30 20 10 0 Demand I 01 5,50 2 3 8 5 6 7 QUANTITY (Hundreds of small trucks) Supply 9 10 ? Suppose that SendIt is one of over a dozen competitive firms in the Bloomington area that offers moving truck rentals. Based on the preceding graph showing the weekly market demand and supply curves, the price SendIt must take as given is Sarrow_forward2. Calculating marginal revenue from a linear demand curve The blue curve on the following graph represents the demand curve facing a firm that can set its own prices. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. PRICE (Dollars per unit) 160 TOTAL REVENUE (Dol 140 120 2250 2000 1750 1500 1250 On the graph input tool, change the number found in the Quantity Demanded field to determine the prices that correspond to the production of 0, 10, 20, 25, 30, 40, and 50 units of output. Calculate the total revenue for each of these production levels. Then, on the following graph, use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot the results. 1000 750 500 250 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 QUANTITY (Units) 200 Demand 10 120 -40 15 30 35 QUANTITY (Number of units) 45 Graph Input Tool…arrow_forward2. Calculating marginal revenue from a linear demand curve The blue curve on the following graph represents the demand curve facing a firm that can set its own prices. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. Market for Goods Quantity Demanded (Units) Demand Price (Dollars per unit) On the graph input tool, change the number found in the Quantity Demanded field to determine the prices that correspond to the production of 0, 8, 16, 20, 24, 32, and 40 units of output. Calculate the total revenue for each of these production levels. Then, on the following graph, use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot the results. Calculate the total revenue if the firm produces 8 versus 7…arrow_forward
- 6. Deriving the short-run supply curve The following graph plots the marginal cost (MC) curve, average total cost (ATC) curve, and average variable cost (AVC) curve for a firm operating in the competitive market for sun lamps. 100 90 80 70 60 50 ATC 40 30 20 10 0 0 5 AVC MOD 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 QUANTITY (Thousands of lamps) For every price level given in the following table, use the graph to determine the profit-maximizing quantity of lamps for the firm. Further, select whether the firm will choose to produce, shut down, or be indifferent between the two in the short run. (Assume that when price exactly equals average variable cost, the firm is indifferent between producing zero lamps and the profit-maximizing quantity of lamps.) Lastly, determine whether the firm will earn a profit, incur a loss, or break even at each price. Price (Dollars per lamp) 10 20 32 40 50 60 Quantity (Lamps) Produce or Shut Down? Profit or Loss? On the following graph, use the orange points (square…arrow_forwardSuppose that the market for polos is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Esc 50 PRICE (Dollars per polo) 78°F Sunny 45 40 F1 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 + 0 + 2 F2 MC -0- + 4 ATC AVC 6 8 10 12 14 QUANTITY (Thousands of polos) F3 0+ F4 69 16 18 F5 20 a F6 i I F7 4- F8 Q+ H F9 F10 FO F11 F12 Fn Lock Insarrow_forward1) Briefly explain how the total revenue for a profit-seeking film is determined 2)Briefly explain what is meant by the term "fixed costs" and provide three examples of same. What determines a firm's level of fixed costs? 3)Contrast the rold of fixed costs and variable costs in economic decisions about future prodiction 4)Briefly compare and contrast the perceived demand curve for a monopolitically competitive firm and a perfectly competitive firm. 5)Briefly explain what quantity a profit maximizing monopolistic competitor will seek. Why not this type of competitive frim is productively efficient?arrow_forward
- Consider the competitive market for rhenium. Assume that no matter how many firms operate in the industry, every firm is identical and faces the same marginal cost (MC), average total cost (ATC), and average variable cost (AVC) curves plotted in the following graph. 0 90 80 70 60 V 50 40 ATC 30 20 AVC MC D COSTS (Dollars per pound) PRICE (Dollars per pound) 100 90 80 70 60 The following graph plots the market demand curve for rhenium. 50 40 30 Use the orange points (square symbol) to plot the initial short-run industry supply curve when there are 10 firms in the market. (Hint: You can disregard the portion of the supply curve that corresponds to prices where there is no output since this is the industry supply curve.) Next, use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the short-run industry supply curve when there are 20 firms. Finally, use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot the short-run industry supply curve when there are 30 firms. 20 100 10 10 0 0 0 5 0 15 20 30 35 40…arrow_forwardHand written solutions are strictly prohibitedarrow_forward3. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for frying pans is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 100 90 Profit or Loss 80 70 ATC 60 50 40 30 AVC 20 MC 10 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 QUANTITY (Thousands of pans per day) In the short run, at a market price of $50 per pan, this firm will choose to produce 37,500 pans per day. PRICE (Dollars perpan)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education