
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
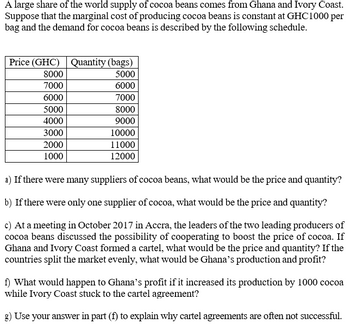
Transcribed Image Text:A large share of the world supply of cocoa beans comes from Ghana and Ivory Coast.
Suppose that the marginal cost of producing cocoa beans is constant at GHC1000 per
bag and the demand for cocoa beans is described by the following schedule.
Price (GHC) Quantity (bags)
5000
6000
7000
8000
9000
10000
11000
12000
8000
7000
6000
5000
4000
3000
2000
1000
a) If there were many suppliers of cocoa beans, what would be the price and quantity?
b) If there were only one supplier of cocoa, what would be the price and quantity?
c) At a meeting in October 2017 in Accra, the leaders of the two leading producers of
cocoa beans discussed the possibility of cooperating to boost the price of cocoa. If
Ghana and Ivory Coast formed a cartel, what would be the price and quantity? If the
countries split the market evenly, what would be Ghana's production and profit?
f) What would happen to Ghana's profit if it increased its production by 1000 cocoa
while Ivory Coast stuck to the cartel agreement?
g) Use your answer in part (f) to explain why cartel agreements are often not successful.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- omework 4 - Compatibility Mode O Seah Joseph References Mailings Review View Help Table Design Layout A A Aa A 三 T AaBbCcI AaBbCcI AaBbC AaB AaBbCcC A D- A 三三三三|三。 田 1 Normal 1 No Spac. Heading 1 Title Subtitle Paragraph Styles 3. The supply and demand schedules below describe the market for compact fluorescent lightbulbs (CFLS). Demand Same Supply Q now at higher price with tax (millions) 200 Price + Supply (millions) Price (millions) tax $2.00 400 200 $2.50 350 250 250 $3.00 300 300 300 $3.50 250 350 350 $4.00 200 400 400 $4.50 150 450 450 $5.00 100 500 500 a. Graph the supply and demand curves, drawing them to scale. i. What is the equilibrium price? ii. What is the equilibrium quantity? Focus hp ho fg 144arrow_forward(Figure: Avocado Market 2) You're an economist for the U.S. Department of Agriculture, analyzing how incorrect assessments of demand conditions lead avocado producers to overproduce avocados, as illustrated in the accompanying diagram. Price ($ per pound) Actual quantity Marginal cost 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 Marginal benefit 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Quantity of avocados (thousands of pounds) The deadweight loss from the excess of marginal cost over marginal benefit is: O $0. O $5,000. O $20,000. 0 $800,000.arrow_forwardOn the graph input tool, change the number found in the Quantity Demanded field to determine the prices that correspond to the production of 0, 6, 12, 15, 18, 24, and 30 units of output. Calculate the total revenue for each of these production levels. Then, on the following graph, use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot the results. Calculate the total revenue if the firm produces 6 versus 5 units. Then, calculate the marginal revenue of the sixth unit produced. The marginal revenue of the sixth unit produced is________. Calculate the total revenue if the firm produces 12 versus 11 units. Then, calculate the marginal revenue of the 12th unit produced. The marginal revenue of the 12th unit produced is_________.arrow_forward
- Only typed solutionarrow_forwardSOME S&D PROBLEMS 1. A. Find Pe and Qe Price per unit (dollar 8 8 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 200 400 600 Quantity B. What is the effect of a ceiling price of $40? 800 Do 1,000arrow_forwardThe market for lemonade is currently in equilibrium and the cost of lemons rises (an input How will this affect the lemonade market Price will rise and sales will increase Price will rise and sales will fall Price will fall and sales will rise Price will fall and sales will fallarrow_forward
- You are given this demand schedule for new boats. Which of the following demand curves accurately represents the demand schedule and has proper formatting? The demand schedule for new boats Price ($) Quantity Demanded $500 5500 $1000 5000 $1500 4500 $2000 3500 $2500 3000 $3000 2000 $3500 1000 $4000 150 O 3100 10 NEW 3000 1000 THE None of the demand curves accurately represent the data in the schedule 9000 1000 3000 2000 . 1000 New Boats 1000 4000 New Boats Demanded New Boats 200 6000 7000arrow_forwardFigure 12-6 Price (dollars per pound) Market 3 price 2 0 10 20 30 MC ATC D=MR 40 Quantity (thousands of pounds) Figure 12-6 shows the demand, marginal cost (MC) and average total cost (ATC) curves for Jason's House of Apples. Refer to Figure 12-6. Jason is currently producing 20 thousand pounds of apples. To maximize his profit Jason should keep production at 20 thousand pounds. O increase production to the output rate indicated by point e. increase production to the output rate indicated by point d. O decrease production to the output rate indicated by point a.arrow_forwardQuantity of Miami Dade Shades 1st pair 2nd pair 3rd pair 4th pair Marginal Cost (dollars) producer surplus will equal $105. there will be a surplus; as a result, the price will fall to $95. $60 95 140 185 Refer to Table 4-4. The table above lists the marginal cost of sunglasses by Miami Dade Shades, a firm that specializes in producing designer sunglasses. If the market price for a pair of Miami Dade Shades sunglasses is $130, A they will produce three pairs. B producer surplus from the first pair is $35.arrow_forward
- QUESTION 17 The table provided below represents the market demand for pens. There are no fixed costs associated with procurement of pens and the marginal cost of each pan is $2.50. 0 0 0 Calculate the total revenue for a price of $4.00 O a. $17.50 Ob $28.00 O $2.50 Od $10.00arrow_forwardPrice ($) 1000 500 300 0 300 500 Supply Demand What is the total cost of producing 300 iPads? 1000 Quantityarrow_forwardTable 17-2 The information in the table depicts the total demand for wireless Internet subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each wireless Internet operator pays a fixed cost of $100,000 (per year) to provide wireless Internet in the market area and that the marginal cost of providing the wireless Internet service to a household is zero. Quantity 0 2000 4000 6000 8,000 Price (per year) $180 $150 $120 $90 $60 10,000 $30 12,000 $0 Refer to Table 17-2. Assume that there are two profit-maximizing wireless Internet companies operating in this market. Further assume that they are not able to "collude" on price and quantity of wireless Internet subscriptions to sell. How many wireless Internet subscriptions will be collectively sold (by both firms) when this market reaches a Nash equilibrium? Oa. 2000 Ob.4000 OC. 6000 O d. 58000arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education