
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
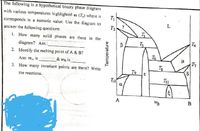
Transcribed Image Text:The following is a hypothetical binary phase diagram
with various temperatures highlighted as (T) where n
corresponds to a numeric value. Use the diagram to
L
T2
answer the following questions:
1. How many solid phases are there in the
T4
diagram? Ans.:_
2. Identify the melting point of A & B?
Ans: m, is
& mg is
T7
3. How many invariant points are there? Write
To
the reactions.
Tu
A
WB
Temperature
to
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Shown to the right is the solid-liquid phase behavior for mixtures of component A and component B at 1 atm. Use the phase diagram to answer the following questions. a) Specify the melting point of substance B at 1 atm b) What is the maximum composition (mole fraction) of component B that is possible for the mixture to exist in phase S2? At what temperature does this occur? c) 20mol of component A and 180mol of component B are mixed at 350°C and 1 atm. The mixture is cooled at constant pressure to 200°C. i) What phases are present at the final state? ii) What is the composition of each phase at the final state? iii) What is the number of moles of each phase at the final state?arrow_forwardUse the Cu-Ag Phase Diagram below to answer the following questions Composition (at% Ag) 20 40 60 80 100 2200 1200 A 2000 Liquidus 1000 Liquid 1800 Solidus C F a +L 1600 * 800 779 C (T) B+L E G 91.2 (Ceg 8.0 71.9 1400 (Cg). 1200 600 Solvus 1000 a +B 800 400 600 200 o 400 100 20 40 60 80 (Cu) Composition (wt% Ag) (Ag) Temperature ("C) Temperature ("F)arrow_forward100 atm 1 atm 0.118 atm 114 °C 184 °C 535 °C Temperature (not to scale) a.) Use the above generic phase diagram, clearly identify where you would find the following: Gas, Liquid, Solid, Triple Point, Draw arrows and label to indicate the six transitions (melting, freezing, sublimation, deposition, vaporization and condensation) b.) Based on the above phase diagram, what phase would you be in at a pressure of 50 atm and 300°C? c.) Based on the above phase diagram at what temperature in °C would vaporization occur under normal conditions? d.) If the pressure was 0.050 atm and 425°C, what phase would you be in? e.) If the pressure was 0.118 atm and temperature was 114°C, what phase(s) would you be in? f.) At approximately what temperature would the normal freezing point be in °C? g.) If the pressure was 0.105 atm and starting at a temperature of 32°C to 450°C what phase changes would occur (put in increasing temperature order). Pressure (not to scale)arrow_forward
- Answer part (iv) and (v)arrow_forwardhelp pls A two-phase phase diagram is shown. Answer the following questions t -1300 1500+ Temperature 1100 0 34 54! 166 482 80 Composition of Ni % 20 What is the composition (in % Cu) of the solid phase corresponding to the red dot in between the solidus and liquidus lines in the phase diagram? Just write the number. Do not write the % symbol. Question 17 2.33 100 An alloy is being made with 66% Ni and 34% Cu. When it is cooled from 1500°C to the temperature corresponding to the red dot in the phase diagram, how many kg of liquid is present in the mixture?arrow_forwardUse the first image to solve two part questionarrow_forward
- 4. For the A-B alloy the phase diagram below, use the lever rule to find the amount of liquid and solid states and their compositions at Temperature T. Let Cx = 25%B, C =40%B, Cy = 60 %B Complete solubility of two metals in liquid and solid states (Ni -Cu ,Sb - Bi) TA M EM T EMa T Cy A B Concentration of B in A www.substoch com Temperaturearrow_forwardXCu versus temperature, liquid-solid phase- equilibrium diagram of a system consisting of Ag and Cu is given. a) Identify each zone and point O b) Define the temperatures T1, T2 and T3 c) Find the degrees of freedom for the points R, T, U, V and Y (f).arrow_forwardTemperature (°C) 700 600 0 500 400 300 0 (AI) a 5 a+L 10 Composition (at% Cu) 10 20 a +0 L 30 Composition (wt% Cu) 20 0+ L 0 (CuAl₂) 40 30 50 1200 1000 800 600 Temperature (°F) a) For the alloy represented by the phase diagram above, what is the wt% content of eutectic if an alloy of 2.5 wt% Cu is cooled very slowly from the molten state to 300°C? b) What phases are present in 2.5 wt% Cu material if it is quenched from 550°C?arrow_forward
- 5. [Phase Diagram] (1) Here is Cu-Ag phase diagram and two cases (composition and temperature) are given below. At each case, (i) cite the phase(s) present(s), (ii) estimate the phase composition(s), (iii) weight fraction of the phase(s) and (iv) sketch its microstructure for the following alloy. () a. 71.9 wt% Ag-28.1 wt% Cu at just above 779 °C b. 71.9 wt% Ag-28.1 wt% Cu at just below 779 °℃ Temperature (°C) 1200 A 1000 800 600 400 0 200 0 α C (Cu) B 8.0 (Ca E) -Solidus Solvus 20 20 a + L Composition (at% Ag) -Liquidus 779°C (TE) 40 40 a + B Liquid 60 Composition (wt% Ag) 60 E 71.9 (CE) 80 80 B+L 91.2 (CBE) G 100 B H 2200 2000 1800 F 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 100 (Ag) Temperature (°F)arrow_forwardPlease answer within 2hr. I will give good ratings.arrow_forwardP-4 Please I need help with this question needed a very clear and step-by-step explanation and needed with clear handwriting please, will be really appreciated your help.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY