
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
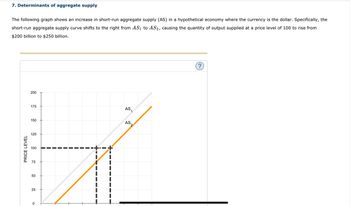
Transcribed Image Text:7. Determinants of aggregate supply
The following graph shows an increase in short-run aggregate supply (AS) in a hypothetical economy where the currency is the dollar. Specifically, the
short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right from AS₁ to AS2, causing the quantity of output supplied at a price level of 100 to rise from
$200 billion to $250 billion.
PRICE LEVEL
200
175
150
125
100
75
50
25
0
+
AS₁
AS
2
?

Transcribed Image Text:F
75
50
25
0
0
50
100
150 200 250 300
QUANTITY OF OUTPUT
Regulations on the firm
Human capital
Input prices
350
The following table lists several determinants of short-run aggregate supply.
400
Complete the table by selecting the changes in each scenario necessary to increase short-run aggregate supply.
Change Necessary to Increase AS
111
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. The theory of liquidity preference and the downward-slopingaggregate demand curve Suppose the money market for some hypothetical economy is given by the following graph, which plots the money demand and money supply curves. Assume the central bank in this economy (the Fed) fixes the quantity of money supplied. Suppose the price level increases from 90 to 105. Shift the appropriate curve on the graph to show the impact of an increase in the overall price level on the market for money. INTEREST RATE (Percent) 18 15 12 8 3 0 0 20 Money Supply Money Demand 40 60 80 MONEY (Billions of dollars) 100 120 Money Demand Money Supply Following the price level increase, the quantity of money demanded at the initial interest rate of 9% will be supplied by the Fed at this interest rate. As a result, individuals will attempt to bonds and other interest-bearing assets, and bond issuers will realize that they restored in the money market at an interest rate of % than the quantity of money their money…arrow_forwardThe following graph shows a hypothetical economy in long-run equilibrium at an expected price level of 120 and a natural output level of $300 billion. Suppose a stock market boom increases household wealth and causes consumers to spend more. Using the graph, shift the short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve or the aggregate demand (AD) curve to show the short-run impact of the stock market boom. PRICE LEVEL 3 AS 200 AD -α- 180 8 0 100 200 300 AD 400 500 600 OUTPUT (Billions of dollars) AS (?) In the short run, the increase in consumption spending associated with the stock market expansion causes the price level to level people expected and the quantity of output to the price the natural level of output. The stock market boom will cause the unemployment rate to ▼the natural rate of unemployment in the short run. Again, the following graph shows a hypothetical economy experiencing long-run equilibrium at the expected price level of 120 and natural output level of $300 billion, prior to the…arrow_forwardOne of the reasons given for the downward sloping aggregate demand curve is the foreign price effect. Clearly explain, step by step, how an increase in the price level will lead to a decrease in the aggregate demand, indicating a downward sloping aggregate demand curve.arrow_forward
- Following an increase in consumer confidence, the US economy is experiencing a significant increase in aggregate spending. Using a correctly labeled aggregate demand and aggregate supply diagram, show how the change in aggregate spending will affect each of the following in the short run -Output -The price levelarrow_forwardPrice Level a b c AS AD AD₁ Real GDP Refer to the figure above. If the aggregate supply curve shifted from ASo to AS₁, we could say that: aggregate supply has increased, and the equilibrium price level has risen to Og aggregate supply has decreased, equilibrium real output has increased, and the equilibrium price level has decreased aggregate supply has decreased, equilibrium real output has decreased, and the equilibrium price level has increased aggregate supply has increased, equilibrium real output has decreased, and the equilibrium price level has increased an increase in the amount of real output supplied has occurredarrow_forwardWhy the aggregate demand curve slopes downward The graph below shows the aggregate demand (AD) curve for a hypothetical economy. At point X, the quantity of output demanded is $300 billion, and the price level is 140. Moving down along the AD curve from point X to point Y, the quantity of output demanded rises to $500 billion, and the price level falls to 120. As the price level falls, the cost of borrowing money will (REMAIN THE SAME or RISE or FALL), causing the quantity of output demanded to (REMAIN THE SAME or RISE or FALL). This phenomenon is known as the (EXCHANGE RATE or INTEREST RATE or WEALTH) effect. Additionally, as the price level falls, the impact on the domestic interest rate will cause the real value of the dollar to (RISE or FALL) in foreign exchange markets. The number of domestic products purchased by foreigners (exports) will therefore (RISE or FALL or REMAIN THE SAME), and the number of foreign products purchased by domestic consumers and firms (imports)…arrow_forward
- The following graph represents the short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS) based on an expected price level of 120. The economy's full- employment output level is $9 trillion. Major unions across the country have recently negotiated three-year wage contracts with employers. The wage contracts are based on an expected price level of 120, but the actual price level turns out to be 160. Show the short-run effect of the unexpectedly high price level by dragging the curve or moving the point to the appropriate position. PRICE LEVEL (CPI) 240 200 160 40 0 0 3 SRAS[120] 6 9 12 REAL GDP (Trillions of dollars) 15 18 SRAS[120] 0 (?) Interpret the change you drew on the previous graph by filling in the blanks in the following paragraph:arrow_forwardBy using aggregate supply and demand curves to illustrate your points, discuss the impacts of the following events on the price level and on equilibrium GDP (Y) in the short run: a. A tax cut holding government purchases constant with the economy operating at near full capacity b. An increase in the money supply during a period of high unemployment and excess industrial capacity c. An increase in the price of oil caused by a war in the Middle East, assuming that the Central Bank attempts to keep interest rates constant by accommodating inflation d. An increase in taxes and a cut in government spending supported by a cooperative Fed acting to keep output from fallingarrow_forwardThe following graph shows the economy in long-run equilibrium at the expected price level of 120 and the natural level of output of $600 billion. Suppose a stock market boom increases household wealth and causes consumers to spend more. Shift the short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve or the aggregate demand (AD) curve to show the short-run impact of the stock market boom. 240 AS 200 AD 160 AS 120 80 AD 40 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 OUTPUT (Billions of dollars) In the short run, the increase in consumption spending associated with the stock market expansion causes the price level to the price level people expected and the quantity of output to the natural level of output. The stock market boom will cause the unemployment rate to the natural rate of unemployment in the short run. Again, the following graph shows the economy in long-run equilibrium at the expected price level of 120 and the natural level of output of $600 billion, before the increase in consumption spending associated with…arrow_forward
- Suppose that the full employment level of nominal GDP rises in one year from $16.8 to $18.0 trillion. The long-run equilibrium price level, however, remains unchanged at 120. By how much (in real dollars) has the long-run aggregate supply curve shifted to the right from one year to the next? $ trillion. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)arrow_forwardThe graphs illustrate an initial equilibrium for the economy. Suppose that the Federal Reserve raises interest rates. Use the graphs to show the new positions of aggregate demand (AD), short-run aggregate supply (SRAS), and long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) in both the short run and the long run, as well as the short-run and long-run equilibriums resulting from this change. Then, indicate what happens to the price level and GDP in the short run and in the long run. Aggregate price level Short-run graph GDP In the short run, the price level LRAS Real GDP SRAS Short-run equilibrium AD and Aggregate price level Long-run graph LRAS Real GDP In the long run, the price level GDP SRAS Long-run equilibrium AD andarrow_forwardDiscuss how the economy returns to equilibrium in response to changes in aggregate demand (AD) and aggregate supply (AS) in both the short run and long runarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education