
Concept explainers
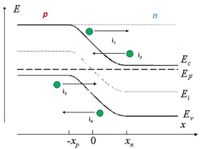
4 - The figure below shows a part of the energy band diagram of a p-n semiconductor junction. According to the situation shown in the figure, in the equilibrium condition, we can identify the currents as follows:
*image attached*
( ) i1:hole diffusion current, i2:electron drift current, i3:hole drift current and i4:electron diffusion current.
( ) i1:hole drift current, i2:electron diffusion current, i3:hole diffusion current and i4:electron drift current.
( ) i1:electron diffusion current, i2:electron diffusion current, i3:hole drift current and i4:hole drift current.
( ) i1:electron drift current, i2:electron diffusion current, i3:hole diffusion current and i4:hole drift current.
( ) i1:hole drift current, i2:electron drift current, i3:hole diffusion current and i4:electron diffusion current.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

- A p-type semiconductor joined to an n-type semiconductor ... Pick those that apply. Will not allow current to flow in either direction. Has electron current flowing from the n-type to the p-type material Makes a diode Allows positive current flow from the p-type to the n-type materialarrow_forwardHelli. I only need the last part. Plotting power vs voltage if used as a solar cell and give the definition of fill factor. Tnxarrow_forwardA. Why does the conductivity of a semiconductor and some insulators change with impurity content? Compare this with the behaviour of metallic conductors. B. Discuss the location of the Fermi levels of intrinsic and extrinsic (n-type and p-type) semiconductors in low temperature and high temperature ranges. C. Discuss why the structure of the p-n junction is so important to modern technologies that impact our daily life.arrow_forward
- When a p-and n-type semiconductor are joined at an interface their Fermi energies equilibriate. If we extend this thinking and apply it to an interface between a metal and (p-or n-type) semiconductor to make a metal-semiconductor heterojunction, what will the expected outcome be? Use diagrams and words to explain.arrow_forwardC and D pleasearrow_forwardConsider four of semiconductor samples: solid A is orange, solid B is black, solid C is white, and solid D is yellow. Given their colors, rank these semiconductors in order of increasing band gap. A. B < A < D < c B. B < D < A < C C. C < D < A < B D. C < A < D < Barrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





