
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
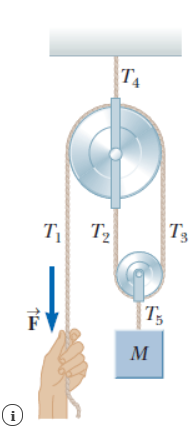
Consider the pulley system depicted in the figure. The block is prevented from moving by the applied force F.
Assume the pulleys are massless and frictionless.
An illustration shows a rectangular block of mass M suspended from a horizontal surface by a complex pulley system comprised of one large pulley, one small pulley, two short ropes, and one long rope.
- The pulleys are drawn such that the small pulley is some vertical distance below the large pulley and their axles are perpendicular to the page. The left side of the small pulley aligns vertically with the center of the large pulley.
- One of the short ropes suspends the block of mass M from the bottom of the small pulley's harness and has tension T5.
- The remaining short rope and the long rope are, respectively, anchored to the top and bottom of the large pulley's harness. This short rope has tension T4 and suspends the large pulley from the horizontal surface.
- The long rope extends from the large pulley and cradles the small pulley below, first passing along its left edge with tension T2 and then along its right edge with tension T3. The segment of tension T3 continues upward and passes over the large pulley from its right edge. The remaining segment of the long rope has tension T1 along the large pulley's left edge and is pulled with a downward force vector F.
(a) Determine the tension in each section of rope. (Use the following as necessary: M and g.)
T1=
T2=
T3=
T4=
T5=
(b) Find the magnitude of F. (Use the following as necessary: M and g.)
F =
(c) What If? What should the magnitude of the force F be if the mass M is to have an upward acceleration of magnitude a? (Use the following as necessary: M, g, and a.)
Transcribed Image Text:T4
T2
T3
T3
(i
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A object of mass 3.00 kg is subject to a force Fx that varies with position as in the figure below. A coordinate plane has a horizontal axis labeled x (m) and a vertical axis labeled Fx (N). There are three line segments. The first segment runs from the origin to (6,2). The second segment runs from (6,2) to (11,2). The third segment runs from (11,2) to (17,0). (a) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 0 to x = 6.00 m. J(b) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 6.00 m to x = 11.0 m. J(c) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 11.0 m to x = 17.0 m. J(d) If the object has a speed of 0.450 m/s at x = 0, find its speed at x = 6.00 m and its speed at x = 17.0 m. speed at x = 6.00 m m/s speed at x = 17.0 m m/sarrow_forwardA man pushing a crate of mass m = 92.0 kg at a speed of v = 0.870 m/s encounters a rough horizontal surface of length = 0.65 m as in the figure below. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and rough surface is 0.350 and he exerts a constant horizontal force of 279 N on the crate. (a) Find the magnitude and direction of the net force on the crate while it is on the rough surface. magnitude N direction ---Select--- (b) Find the net work done on the crate while it is on the rough surface. (c) Find the speed of the crate when it reaches the end of the rough surface. m/sarrow_forwardAs shown in the figure below, a box of mass m = 30.0 kg is sliding along a horizontal frictionless surface at a speed v₁ = 4.55 m/s when it encounters a ramp inclined at an angle of 0 = 28.0⁰. frictionless surface The coefficient of kinetic friction between the ramp and the box is μ = 0.0704 and the box slides a distance d up the ramp before coming momentarily to rest. (a) Determine the distance (in m) the box slides up the ramp before coming momentarily to rest. Ο OW₁ = -APE Wg OW, m (b) Determine which of the following statements is most correct about the box traveling up the ramp and coming momentarily to rest. OW.. = AKE Net = W Net ΔΕ = W cons + W noncons ΔΕ = ΔΚΕ + ΔΡΕ Ο O all of these rough surface TTO nonconsarrow_forward
- A student is skateboarding down a ramp that is 6.02 m long and inclined at 22.3° with respect to the horizontal. The initial speed of the skateboarder at the top of the ramp is 4.98 m/s. Neglect friction and find the speed at the bottom of the ramp.arrow_forwardThe figure shows a block of mass m resting on a 20o slope. The block has coefficients of friction us=0.64 and uk=0.54 with the surface of the slope. It is connected using a very light string over an ideal pulley to a hanging block of mass 2.0 kg. The string above the slope pulls parallel to the surface. What is the minimum mass m so the system will remain at rest when it is released from rest?arrow_forwardA man pushing a crate of mass m = 92.0 kg at a speed of v = 0.880 m/s encounters a rough horizontal surface of length ℓ = 0.65 m as in the figure below. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and rough surface is 0.354 and he exerts a constant horizontal force of 297 N on the crate. (a) Find the magnitude and direction of the net force on the crate while it is on the rough surface. magnitude N direction (b) Find the net work done on the crate while it is on the rough surface. J(c) Find the speed of the crate when it reaches the end of the rough surface. m/sarrow_forward
- reeee Two blocks and a spring are set up as shown in the picture. The spring is initially unstretched and uncompressed. The system is released from rest. The pulleys are massless. Static friction is not enough to hold it. The coefficient of kinetic friction is = 0.200 for both surfaces. [Use m₁ = 20.0kg, m₂ = 30.0kg, k=80.0, 0 = 30.0°] m a. What is the maximum stretch of the spring? b. How fast are the masses moving after the spring is stretched 0.250m. m, m₂arrow_forwardIn the very Dutch sport of Fierljeppen, athletes run up to a long pole and then use it to vault across a canal as shown in (Figure 1). At the very top of his arc, a 70 kg vaulter is moving at 2.9 m/s and is 5.5 m from the bottom end of the pole. What is the magnitude of the vertical force that the pole exerts on the vaulter? Express your answer with the appropriate units.arrow_forwardA man pushing a crate of mass m = 92.0 kg at a speed of v = 0.875 m/s encounters a rough horizontal surface of length ℓ = 0.65 m as in the figure below. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and rough surface is 0.354 and he exerts a constant horizontal force of 292 N on the crate. A man pushes a crate labeled m, which moves with a velocity vector v to the right, on a horizontal surface. The horizontal surface is textured from the right edge of the crate to a horizontal distance ℓ from the right edge of the crate. (a) Find the magnitude and direction of the net force on the crate while it is on the rough surface. magnitude N direction (b) Find the net work done on the crate while it is on the rough surface. J(c) Find the speed of the crate when it reaches the end of the rough surface. m/sarrow_forward
- an object with mass m shown in the figure is attached to a spring with a spring constant k in a horizontal arrangement without friction, and the object is compressed as much as d. After the system is released, the object can rise to the height of h in the friction inclined plane. find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the oblique order and the body?arrow_forwardAn online video daredevil is filming a scene where he swings across a river on a vine. The safety crew must use a vine with enough strength so that it doesn't break while swinging. The daredevil's mass is 82.0 kg, the vine is 11.0 m long, and the speed of the daredevil at the bottom of the swing has been determined to be 7.60 m/s. What is the minimum tension force (in N) the vine must be able to support without breaking?arrow_forwardCaroline takes her baby sister Hannah to the neighborhood park and places her in the seatof the children’s swing. Caroline pulls the L = 1.8 m long chain back to make an angle θ = 26◦ withrespect to the vertical and lets 14 kg Hannah (swing mass included) go. (a) Determine Hannah’s speed at the lowest point in the trajectory. (b) What is the tension in the swing chain at this low point? Assume the chain itself has negligible mass.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON