
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
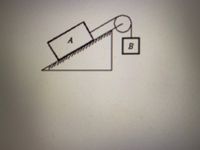
Block A, with a mass of 13 kg, sits on an incline of 0.34 radians above the horizontal.
An attached (massless) string passes through a massless, frictionless pulley at the top of the incline as shown:
The coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and the incline is given as 0.47.
When the system is released from rest, block B accelerates downward at 2.4 m/s2.
What is the mass of block B?
Express your answer in kg, to at least one digit after the decimal point.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A cart with mass 15.7 kg is intitally at rest. You get it moving by pushing on the cart at an angle of 0 = 37° as shown above. The magnitude of your force as a function of time is given by: Fyc(t) = Foe-bt, where b = 0.55 s-1 and Fo = 138.1 N. You can assume that the wheels roll perfectly on the ground. What is the speed of the cart when t = 3.3 s? Don't Know Where to Start? ... A Hint About N2L A Hint About the Proces ...... ........................ Vf = 10.25m/sarrow_forwardTwo blocks with masses Mj and M2 are connected by a massless string that passes over a massless pulley as shown. M has a mass of 2.25 kg and is on an incline of 0 41.5° with coefficient of kinetic friction u = 0.205. M2 has a mass of 5.25 kg and is on an incline of 02 = 34.5° with coefficient M2 of kinetic friction u, = 0.105. The two-block system is in M1 motion with the block of mass M2 sliding down the ramp. Find the magnitude az of the acceleration of M, down the incline. Figure is not to scale. a2 = m/s?arrow_forwardTwo blocks are connected by a massless rope over a massless, frictionless pulley, as shown in the figure. The mass of block 2 is m2 12.1 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction 0.200. The angle 0 of between block 2 and the incline is µk the incline is 33.5°. If block 2 is moving up the incline at 2 constant speed, what is the mass mj of block 1? 1 kg M¡ =arrow_forward
- You are using a modified block and tackle pulley system to lift a concrete block. You need to lift the concrete block (mass=200kg) a distance of 5 meters upward. The system is designed to reduce the force loaded by a factor of 4. How much rope must you pull down on the other side of the pulley to lift the block the proper distance?arrow_forwardA uniformly-dense equilateral triangle with weights hanging from each vertex is fixed at its center of mass as shown below: The triangle has a mass of 2kg and each side has a length of 0.50 meters, and it is held so that the vertex connected to F3 is at an angle of 40° from the horizontal. All weights hang vertically downwards, where F1=20 N, F2=15 N and F3=20 N. What is the magnitude of the angular acceleration when the triangle is released and allowed to rotate, in rad/s?? Justify your answer with your rationale and equations used. Itriangle = ML? L r = V3 Hint: Be careful with the angles you use for your calculation! Remember what the angles between vertexes of an equilateral triangle are.arrow_forwardYou and your family take a road trip on a long holiday weekend. In a certain section of the trip where the road is particularly uneven, the car goes over a bump that is curved downward with a radius of 16.0 m. See diagram below. The mass of the car and its passengers is 1200 kg. (a) When the car is at the highest point of the bump its speed is 7.05 m/s. Determine the magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the road on the car at this highest point. magnitude direction N |---Select-- v (b) If the speed at the highest point is above a certain maximum value the car will lose contact with the road. Calculate this maximum speed. m/sarrow_forward
- As shown in the figure below, a box of mass m = 58.0 kg (initially at rest) is pushed a distance d = 57.0 m across a rough warehouse floor by an applied force of FA = 248 N directed at an angle of 30.0° below the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the floor and the box is μk = 0.121. Determine the following. (For parts (a) through (f), give your answer to the nearest multiple of 10.) (a) Calculate the value of the normal force. FN = N (b) Calculate the magnitude friction force. Ff = N (c) Calculate work done by the force of gravity Wg = J (d) Calculate the work done by the normal force WN = J (e) Calculate the work done by the force of friction. Wf = J (f) Calculate the done by the applied force. WA = Jarrow_forwardThe figure shows a container of mass m₁ = 1.7 kg connected to a block of mass m₂ by a cord looped around a frictionless pulley. The cord and pulley have negligible mass. When the container is released from rest, it accelerates at 1.0 m/s² across the horizontal frictionless surface. What are (a) the tension in the cord and (b) mass m₂? (a) Number (b) Number i Units Units m₁ mq >arrow_forwardIn the figure, a 4.00 kg block is sent sliding up a plane inclined at 0 = 39.0° while a horizontal force of magnitude F = 45.0 N acts on it. The %3D coefficient of kinetic friction between block and plane is 0.30. What is the magnitude and direction (up or down the plane) of the block's acceleration?arrow_forward
- A uniformly-dense equilateral triangle with weights hanging from each vertex is fixed at its center of mass as shown below: The triangle has a mass of 2kg and each side has a length of 0.50 meters, and it is held so that the vertex connected to F3 is at an angle of 50° from the horizontal. All weights hang vertically downwards, where F1=10 N, F2=15 N and F3=20 N. What is the magnitude of the angular acceleration when the triangle is released and allowed to rotate, in rad/s?? Justify your answer with your rationale and equations used. Screopchotarrow_forwardTwo ideal pulleys (massless and frictionless) form a pulley system that can lift a weight by pulling on the end of a massless rope, as shown below. The upper pulley is attached to the ceiling at point A, and the lower pulley is connected to a box of mass M = 10.0kg. (a) What is the tension in the rope if the box is accelerating upwards with a = 2.00 m/s^2? (b) What is the tension force at point A at the ceiling?arrow_forwardThe figure shows a block of mass m resting on a 20o slope. The block has coefficients of friction us=0.64 and uk=0.54 with the surface of the slope. It is connected using a very light string over an ideal pulley to a hanging block of mass 2.0 kg. The string above the slope pulls parallel to the surface. What is the minimum mass m so the system will remain at rest when it is released from rest?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON