
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
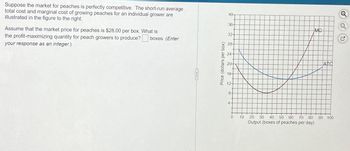
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose the market for peaches is perfectly competitive. The short-run average
total cost and marginal cost of growing peaches for an individual grower are
illustrated in the figure to the right.
Assume that the market price for peaches is $28.00 per box. What is
the profit-maximizing quantity for peach growers to produce? boxes. (Enter
your response as an integer.)
Price (dollars per box)
40-
36-
32-
28-
24-
20-
16-
12-
8-
4-
0
10
20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Output (boxes of peaches per day)
MC
ATC
90 100
oo
Q
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose that the market for polos is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. (? 50 45 40 35 30 ATC 25 20 15 AVC 10 MC 2 4 10 12 14 16 18 QUANTITY (Thousands of polos) PRICE (Dollars per polo) 20arrow_forwardSuppose the market price of sugar is 22 cents per pound. If a sugar farmer produces 100,000 pounds, the marginal cost of sugar is 30 cents per pound. Is the farmer maximizing profit? If not, should the farmer produce more or less sugar?arrow_forwardSuppose a firm engaged in the illegal copying of DVD’s has a daily short run total cost function given by: STC = (q^2)+25 If pirated DVD’s sell for $20, how many will the firm copy each day? What will its profits be? What is the firm’s short run producer surplus at P=20? Develop a general expression for this firm’s producer surplus as a function of the price of pirated DVD’s.arrow_forward
- The following table gives information about a firm’s short-run cost function in a perfectly competitive industry – candy manufacturing. a) What quantity will the firm supply when price of candy is $2? When price is $5? When price is $8? b) Consider the case where price = $2. Suppose that you have been renting capital (a candy-making machine) for a long time under a long-run capital rental agreement, but now the rental contract is about to expire. Should you renew your capital rental contract or not? Explain why or why not. How would your answer change if price is $5? How would your answer change if price is $8? Quantity Total Cost Average Variable Cost Average Total Cost Marginal Cost 0 10 1 15 5 15 5 2 17 3.5 8.5 2 3 18 2.66667 6 1 4 20 2.5 5 2 5 25 3 5 5 6 33 3.83333 5.5 8arrow_forward1. A company has the following average income (demand) curve: P=100-0.01Q. Where Q is weekly production and P is price, measured in cents per unit. The company's cost function is given by CT = 50Q + 30,000. Suppose the firm maximizes its profits.a) What is the level of production, the price and the total profit per week?b) The government decides to impose a tax of 10 cents per unit on this product. What would the level of output, price, and profit be as a result of this? CT(Total cost)arrow_forwardProblem 2.5 The cost function for Acme Laundry is TC(q) = 10 + 10q + q^2 so its marginalprod cost function is MC(q) = 10 + 2q where q is tons of laundry cleaned. Derive the firm's average cost and average variable cost curves. What q should the firm choose so as to maximize its profit if the market price is p? How much does it produce if the competitive market price is p = 50?arrow_forward
- The following relations describe monthly demand and supply for a wheat Qp = 32 – P Qs = P- 16 where P is the price (in cents) per pound and Q is the quantity (in millions) of pounds. What is the equilibrium price and output level? (a) Suppose that wheat industry is a perfectly competitive industry consisting of a large number of identical firms. For a typical firm, the cost function is TC = 100 + 1000q². (b) Identify the marginal revenue of a typical firm in the industry. (c) (d) Find the profit maximizing level of output produced by a firm. If all firms are profit maximizing, then how many firms can operate in this industry?arrow_forwardSuppose you are the manager of a watchmaking firm operating in a competitive market. Your cost of production is given by C= 300 + 29°, where q is the level of output and C is total cost. (The marginal cost of production, MC(q), is 4q; the fixed cost, FC, is $300). If the price of a watch is $80, how many watches should you produce to maximize profits? You should produce watches. (Enter your response as an integer.) What will the profit level be? Profit will be $ (Enter your response rounded to two decimal places.) At what minimum price will the firm produce a positive output? In the short run, the firm will produce if price is greater than $ per watch. (Enter your response as an integer.)arrow_forwardThe cost function for Acme Laundry is C(q) = 50 + 30q +q?, where q is tons of laundry cleaned. What q should the firm choose so as to maximize its profit if the market price is p? The output level at which the firm's profit is maximized as a function of p is q =|- (Properly format your expression using the tools in the palette. Hover over tools to see keyboard shortcuts. E.g., a fraction can be created with the / character.) If p= 60, then Acme Laundry should produce| units. (Enter your response as a whole number.)arrow_forward
- Question a) The average cost function of a competitive firm is AC= 5/Q+5+9*Q. The optimal quantity is: 10. How much is the profit? b) The average cost function of a competitive firm is AC= 3/Q +8 +9*Q The optimal quantity is: 3 How much is the profit? c) The marginal utility of x is 100-5x, and that of y is 200- 6y. The price of x is 1, the price of y is 2, the income of the consumer is 100. How many of y is there in the optimal basket?arrow_forwardSuppose that the market for dress shirts is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. 50 18, 42 45 40 35 30 ATC 25 20 15 AVC 10 MC 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 QUANTITY (Thousands of shirts) For each price in the following table, calculate the firm's optimal quantity of units to produce, and determine the profit or loss if it produces at that quantity, using the data from the graph to identify its total variable cost. Assume that if the firm is indifferent between producing and shutting down, it will produce. (Hint: You can select the purple points [diamond symbols] on the graph to see precise information on average variable cost.) Price Quantity Total Revenue Fixed Cost Variable Cost Profit (Dollars per shirt) (Shirts) (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) 12.50 7,500 135,000 27.50 135,000 45.00 135,000 If the firm shuts down, it must incur its fixed costs (FC) in the short run. In this case, the firm's fixed cost is…arrow_forwardThe table below shows the weekly marginal cost (MC) and average total cost (ATC) for Buddies, a purely competitive firm that produces novelty ear buds. Assume the market for novelty ear buds is a competitive market and that the price of ear buds is $6.00 per pair. Buddies Production Costs Quantity MC ATC of Ear Buds ($) ($) 20 1.00 25 2.00 1.20 30 2.46 1.41 35 3.51 1.71 40 4.11 2.01 45 5.43 2.39 50 5.99 2.75 55 8.47 3.27 Instructions: In part a, enter your answer as the closest given whole number. In parts b-d, round your answers to two decimal places. a. If Buddies wants to maximize profits, how many pairs of ear buds should it produce each week? pairs b. At the profit-maximizing quantity, what is the total cost of producing ear buds? 2$ c. If the market price for ear buds is $6 per pair, and Buddies produces the profit-maximizing quantity of ear buds, what will Buddies profit or loss be per week? 2$arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education