
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
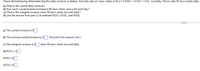
Transcribed Image Text:Pierce Manufacturing determines that the daily revenue, in dollars, from the sale of x lawn chairs is R(x) = 0.006x³ +0.02x² +0.6x. Currently, Pierce sells 90 lawn chairs daily.
a) What is the current daily revenue?
b) How much would revenue increase if 95 lawn chairs were sold each day?
c) What is the marginal revenue when 90 lawn chairs are sold daily?
d) Use the answer from part (c) to estimate R(91), R(92), and R(93).
(…)
a) The current revenue is $
b) The revenue would increase by $. (Round to the nearest cent.)
c) The marginal revenue is $when 90 lawn chairs are sold daily.
d) R(91) ≈ $
R(92) $
R(93) $
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose a firm engaged in the illegal copying of DVD’s has a daily short run total cost function given by: STC = (q^2)+25 If pirated DVD’s sell for $20, how many will the firm copy each day? What will its profits be? What is the firm’s short run producer surplus at P=20? Develop a general expression for this firm’s producer surplus as a function of the price of pirated DVD’s.arrow_forwardSuppose the Sunglasses Hut Company has a profit function given by P(q) - 0.01q² + 5q - 40, = where q is the number of thousands of pairs of sunglasses sold and produced, and P(q) is the total profit, in thousands of dollars, from selling and producing a pairs of sunglasses. A) Find a simplified expression for the marginal profit function. (Be sure to use the proper variable in your answer.) Answer: MP(q) = B) How many pairs of sunglasses (in thousands) should be sold to maximize profits? (If necessary, round your answer to three decimal places.) Answer: thousand pairs of sunglasses need to be sold. C) What are the actual maximum profits (in thousands) that can be expected? (If necessary, round your answer to three decimal places.) Answer: thousand dollars of maximum profits can be expected.arrow_forwardRoad Runner Co is a Pakistani manufacturer making Bicycles. It exports to two markets,Bangladesh and Sri Lanka. Demand for Bicycles in thesetwo markets is given by the following Functions: Bangladesh Q1 = 12 – P1 Sri Lanka Q2 = 8 – P2 Where Q1 and Q2 are respective quantities sold (in thousands) andP1 and P2 are the respective prices (in Pak. Rupees per unit) in the two markets. Total cost function is C = 5 + 2 (Q1+ Q2) (i) Company is effectively able to price discriminate in the two markets. What will be the total profits? (ii) Suppose the company does not engage in price discrimination. By charging the same price in the two markets what are the profit maximizing levels of price, output, and the total profits? (iii) Analyze, with graphs, the two alternative pricing strategies available to the company.arrow_forward
- Please help with h.arrow_forward7. Assume that the marginal cost curve is given by mc(q) = 100 + 2q. (a) If the price is $160, what is the optimal production for the firm? What if the price is $120? (ignore the shut-down decision for this part) (b) Assuming that the market is cleared at $160 (no shortage/surplus). If the market demand is equal to 10,000 units of the product. How many firms are currently operating (n) in the market? (Hint: if the market clears qª = n x q°) (c) If the total cost curve is TC 256 + 100g + q², what's the average total cost curve? %3| what's the break-even price? (d) If the demand curve is given by qd = 8, 452 – p, what's the long-run equilibrium price, the equilibrium quantity and the long-run total number of firms (n) in the industry?arrow_forwardLet's say jacky has a demand function for a product made in Ney york city given that the function D(q)=-1.15q+270, where q is the number of items in demand and D(q) is the price per item, in dollars, that can be charged when q units are sold. Say that the fixed costs of production for the item is $5,000 and variable costs are $10 per item produced. If 100 items are produced and sold, what are the finds :arrow_forward
- Pierce Manufacturing determines that the daily revenue, in dollars, from the sale of x lawn chairs is R(x)=0.005x³ +0.02x² +0.5x Currently, Pierce sells 90 lawn chairs daily a) What is the current daily revenue? b) How much would revenue increase if 95 lawn chairs were sold each day? c) What is the marginal revenue when 90 lawn chairs are sold daily? d) Use the answer from part (c) to estimate R(91), R(92), and R(93) a) The current revenue is $ b) The revenue would increase by $ (Round to the nearest cent.) c) The marginal revenue is $ when 90 lawn chairs are sold daily. d) R(91) $ R(92) $ R(93) $arrow_forwardQ3arrow_forwardSuppose that for a company manufacturing calculators, the cost, revenue, and profit equations are given by x² C = 70,000 + 30x, R=200x - A) Costs are increasing at the rate of $ (Simplify your answer.) where the production output in 1 week is x calculators. If production is increasing at a rate of 600 calculators per week when production output is 5,000 calculators. Find the rate of increase (decrease) in cost, revenue, and profit. B) Revenue is decreasing at the rate of $ (Simplify your answer.) C) Profits are (Simplify your answer.) 20 at the rate of $ P=R-C per week at this production level. per week at this production level. per week at this production level.arrow_forward
- On the graph input tool, change the number found in the Quantity Demanded field to determine the prices that correspond to the production of 0, 6, 12, 15, 18, 24, and 30 units of output. Calculate the total revenue for each of these production levels. Then, on the following graph, use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot the results. Calculate the total revenue if the firm produces 6 versus 5 units. Then, calculate the marginal revenue of the sixth unit produced. The marginal revenue of the sixth unit produced is________. Calculate the total revenue if the firm produces 12 versus 11 units. Then, calculate the marginal revenue of the 12th unit produced. The marginal revenue of the 12th unit produced is_________.arrow_forwardis profit maximisation seen as local minimum or maximum? Is part (b) the correct way of doing first derivative? There is image of the questions, another image of the answers of part (a) and (b).arrow_forwardPlease select all that are true regarding Minimum Efficient Scale (MES): if the quantity demanded is equal to Qmes, then the lowest cost solution is for one firm to supply the market MES is the quantity produced where average costs for a firm are at a minimum Long run average costs include fixed cost steps as quantities (scale) increase Quantities (x-axis) less than MES exhibit decreasing returns to scale due to diminishing marginal returns Short run average cost curves are for a given level of fixed cost, individually MES is the quantity demanded where total costs for a firm are at a minimum Quantities (x-axis) greater than MES exhibit decreasing returns to scale due to diminishing marginal returns Average costs do not include fixed cost since they don't changearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education