
International Financial Management
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780357130698
Author: Madura
Publisher: Cengage
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
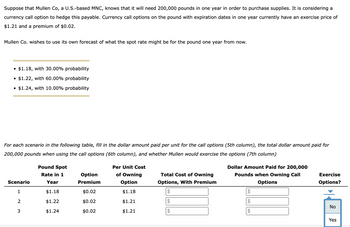
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that Mullen Co, a U.S.-based MNC, knows that it will need 200,000 pounds in one year in order to purchase supplies. It is considering a
currency call option to hedge this payable. Currency call options on the pound with expiration dates in one year currently have an exercise price of
$1.21 and a premium of $0.02.
Mullen Co. wishes to use its own forecast of what the spot rate might be for the pound one year from now.
• $1.18, with 30.00% probability
•
• $1.22, with 60.00% probability
•
$1.24, with 10.00% probability
For each scenario in the following table, fill in the dollar amount paid per unit for the call options (5th column), the total dollar amount paid for
200,000 pounds when using the call options (6th column), and whether Mullen would exercise the options (7th column)
Pound Spot
Rate in 1
Scenario
Year
Option
Premium
Per Unit Cost
of Owning
Option
Total Cost of Owning
Options, With Premium
Dollar Amount Paid for 200,000
Pounds when Owning Call
Options
Exercise
Options?
1
$1.18
$0.02
$1.18
$
$
2
$1.22
$0.02
$1.21
$
No
3
$1.24
$0.02
$1.21
$
$
Yes
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Suppose that Mullen Co, a U.S.-based MNC, knows that it will need 200,000 pounds in one year in order to purchase supplies. It is considering a currency call option to hedge this payable. Currency call options on the pound with expiration dates in one year currently have an exercise price of $1.21 and a premium of $0.02. On the following graph, use the blue points (circle symbols) to plot the contingency graph for hedging this payable with a call option. Plot the points from left to right in the order you would like them to appear. Line segments will connect automatically. Plot the 3 blue points for the following pound spot rates: $1.18, $1.21, $1.27. Note: The vertical axis measures dollar cash outflows from the hedge, which includes the price paid for pounds and any option premium. Dollar Cash Outflows from Hedge (Dollars per Pound) 1.27 1.26 1.25 1.24 1.23 1.22 1.21 1.20 1.19 1.18 1.17 1.16 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 1.22 1.23 1.24 1.25 1.26 Pound Spot Rate in One Year (Dollars per Pound)…arrow_forwardSuppose that Goodwin Co., a U.S. based MNC, knows that it will receive 200,000 pounds in one year. It is considering a currency put option to hedge this receivable. Currency put options on the pound with expiration dates in one year currently have an exercise price of $1.18 and a premium of $0.03. On the following graph, use the blue points (circle symbols) to plot the contingency graph for hedging this receivable with a put option. Plot the points from left to right in the order you would like them to appear. Line segments will connect automatically. Plot the 3 blue points for the following pound spot rates: $1.15, $1.18, $1.22. Note: The vertical axis measures dollar cash inflows from the hedge, which includes the price received for pounds and any option premium. Dollar Cash Received from Hedge (Dollars per Pound) 1.19 1.18 1.17 1.16 1.15 1.14 1.13 1.12 1.11 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 Pound Spot Rate in One Year (Dollars per Pound) Contingency Graph ?arrow_forwardKansas Corp., an American company, has a payment of €5.3 million due to Tuscany Corp. one year from today. At the prevailing spot rate of 0.90 €/$, this would cost Kansas $5,888,889, but Kansas faces the risk that the €/$ rate will fall in the coming year, so that it will end up paying a higher amount in dollar terms. To hedge this risk, Kansas has two possible strategies. Strategy 1 is to buy €5.3 million forward today at a one-year forward rate of 0.89 €/$. Strategy 2 is to pay a premium of $103,000 for a one-year call option on €5.3 million at an exchange rate of 0.88 €/$. a. Suppose that in one year the spot exchange rate is 0.85 €/$. What would be Kansas's net dollar cost for the payable under each strategy? (Round your answer to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Strategy 1 Strategy 2 Net Dollar Cost b. Suppose that in one year the spot exchange rate is 0.95 €/$. What would be Kansas's net dollar cost for the payable under each strategy? (Round your answer to the nearest whole…arrow_forward
- Kansas Corporation, an American company, has a payment of €5.9 million due to Tuscany Corporation one year from today. At the prevailing spot rate of 0.90 €/$, this would cost Kansas $ 6,555,556, but Kansas faces the risk that the €/S rate will fall in the coming year, so that it will end up paying a higher amount in dollar terms. To hedge this risk, Kansas has two possible strategies. Strategy 1 is to buy €5.9 million forward today at a one-year forward rate of 0.89 €/$. Strategy 2 is to pay a premium of $109,000 for a one-year call option on €5.9 million at an exchange rate of 0.88 €/$. Suppose that in one year the spot exchange rate is 0.85 €/$. What would be Kansas's net dollar cost for the payable under each strategy? Note: Round your answer to the nearest whole dollar amount. Suppose that in one year the spot exchange rate is 0.95 €/$. What would be Kansas's net dollar cost for the payable under each strategy? Note: Round your answer to the nearest whole dollar amount.arrow_forwardpls fill out the tablearrow_forwardA UK oil trader, Teresa, is considering purchasing oil on the spot market for speculative purposes. The current spot price is $18 a barrel. However, she expects the price to decline to $16 a barrel in one month's time. If she bought on the spot market today, she would hold the oil for one month at a cost of £0.002 a barrel for the month, after which she could sell the oil on the spot market. The current US dollar exchange rate is $1.50/£. If she expects the exchange rate to be $1.30/£1 in one month's time, what is her expected gain/loss on the oil deal? A. £0.306 gain per barrel B. £0.027 gain per barrel C. £1.540 loss per barrel D. £6.202 loss per barrelarrow_forward
- A Japanese exporter has a €1,000,000 receivable due in one year. To hedge the position, you will buy put options on euro True or False?arrow_forwardMalibu, Inc., is a U.S. company that imports British goods. It plans to use call options to hedge payables of 100,000 pounds in 90 days. Three call options are available that have an expiration date 90 days from now. Fill in the number of dollars needed to pay for the payables (including the option premium paid) for each option available under each possible scenario. Spot Rate of Pound Exercise Price Exercise Price Exercise Price 90 Days = $1.71; = $1.76; = $1.80; Scenario from Now Premium = $.04 Premium = $.06 Premium = $.03 1 $1.65 2 1.74 3…arrow_forwardThere is a project in DreamLand that an American-based company would like to invest in. The project would require DDD735,000 as initial investment. It is also estimated to generate cash inflows equal to DDD351,000 a year for the next 4 years. After that, the project will be worthless. The current spot exchange rate equals DDD1 = $3.4567. The risk-free rate in DreamLand is 3%, and it is 5% in the U.S.A. The applicable rate of return for projects inarrow_forward
- This question will compare two different arbitrage situations. Recall that arbitrage should equalize rates of return. We want to explore what this implies about equalizing prices. In the first situation, two assets, A and B, will each make a single guaranteed payment of $100 in 1 year. But asset A has a current price of $80 while asset B has a current price of $90.a. Which asset has the higher expected rate of return at current prices? Given their rates of return, which asset should investors be buying and which asset should they be selling?b. Assume that arbitrage continues until A and B have the same expected rate of return. When arbitrage ceases, will A and B have the same price?Next, consider another pair of assets, C and D. Asset C will make a single payment of $150 in one year while D will make a single payment of $200 in one year. Assume that the current price of C is $120 and that the current price of D is $180.c. Which asset has the higher expected rate of return at current…arrow_forwardPlease show and also explanation for the incorrect optionsarrow_forwardSuppose the spot and six-month forward rates on the Norwegian krone are NKr 9.14 and NKr 9.27, respectively. The annual risk-free rate in the United States is 3.8 percent, and the annual risk-free rate in Norway is 5.7 percent. What must the six-month forward rate be to prevent arbitrage? Note: Do not include the Norwegian krone sign (NKr). Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. Forward rate NKrarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
