
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
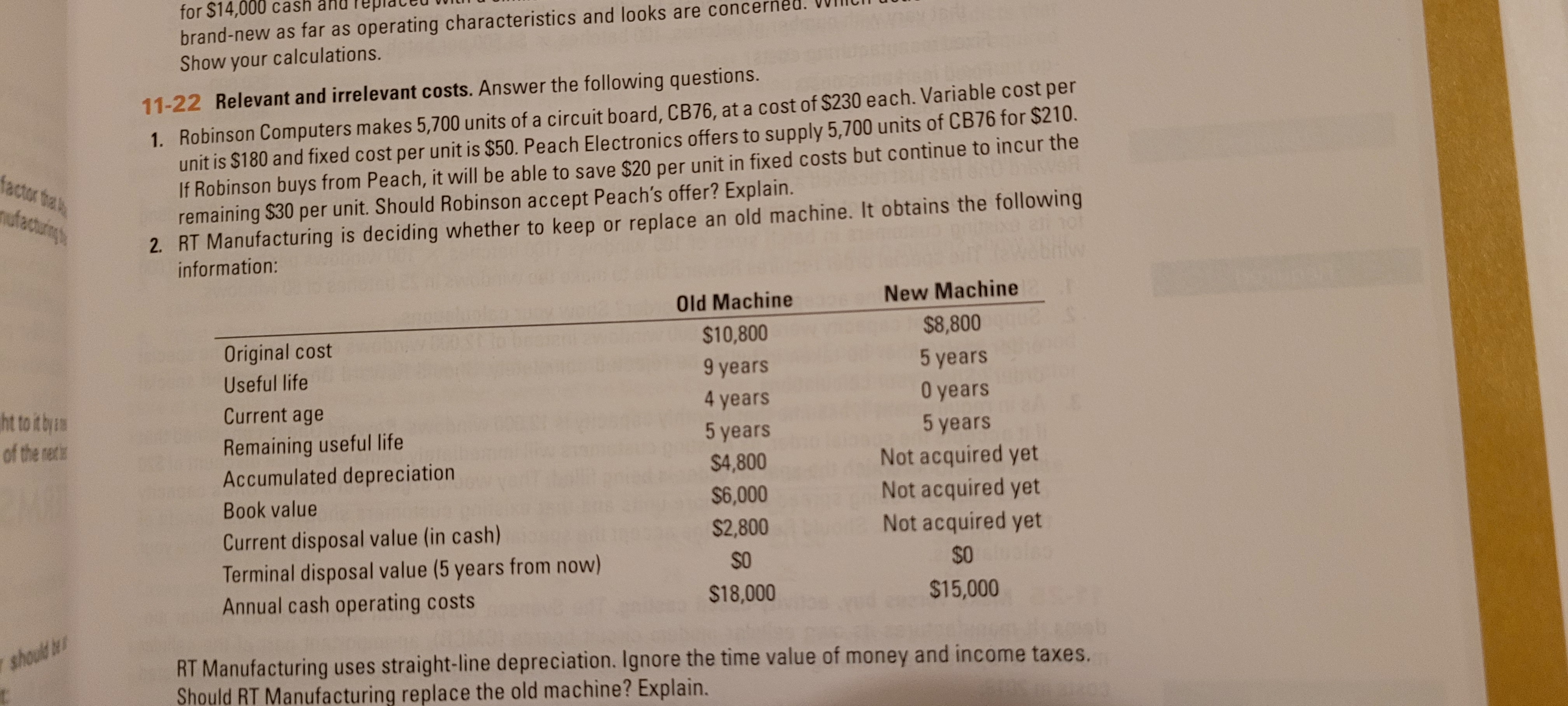
Transcribed Image Text:Robinson Computers makes 5,700 units of a circuit board, CB76,
unit is $180 and fixed cost per unit is $50. Peach Electronics offers to supply 5,700 units of CB76 for $210.
If Robinson buys from Peach, it will be able to save $20 per unit in fixed costs but continue to incur the
remaining $30 per unit. Should Robinson accept Peach's offer? Explain.
RT Manufacturing is deciding whether to keep or replace an old machine. It obtains the following
information:
Old Machine
New Machine
$10,800
$8,800
Original cost
Useful life
9 years
5 years
Current age
4 years
O years
5 years
5 years
Remaining useful life
Accumulated depreciation
Not acquired yet
Not acquired yet
Not acquired yet
Oales
$4,800
Book value
$6,000
$2,800
Current disposal value (in cash)
Terminal disposal value (5 years from now)
SO
$0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Tupper Inc. and Victory Inc. are two small clothing companies that are considering leasing a dyeing machine together. The companies estimated that in order to meet production, Tupper needs the machine for 950 hours and Victory needs it for 700 hours. If each company rents the machine on its own, the fee will be $85 per hour of usage. If they rent the machine together, the fee will decrease to $80 per hour of usage. Read the requirements. Requirement 1. Calculate Tupper's and Victory's respective share of fees under the stand-alone cost-allocation method. (Do not round intermediary calculations. Only round the amount you input in the cell to the nearest dollar.) Stand-alone Tupper Victoryarrow_forwardSki Boards, Inc., wants to enter the market quickly with a new finish on its ski boards. It has three choices: (a) refurbish the old equipment at a cost of $250, (b) make major modifications at the cost of $1,000, or (c) purchase new equipment at a net cost of $1,750. If the firm chooses to refurbish the equipment, materials and labor will be $1.20 per board. If it chooses to make modifications, materials and labor will be $0.75 per board. If it buys new equipment, variable costs are estimated to be $0.40 per board. a) On the graph to the right, use the line drawing tool to draw the total cost curve for each option. Label the curves TC2, TC b, and TCC, respectively. Note: Carefully follow the instructions above and only draw the required objects. Dollars 8,000- 7,500- 7,000- 6,500- 6,000- 5,500- 5,000- 4,500- 4,000 3,500 3,000- 2,500- 2,000- 1,500- 1,000- 500- 0- 0 1,000 2,000 3,000 4,000 5,000 Boards ☑arrow_forwardDiamond Boot Factory normally sells its specialty boots for $23 a pair. An offer to buy 105 boots for $16 per pair was made by an organization hosting a national event in Norfolk. The variable cost per boot is $8, and special stitching will add another $3 per pair to the cost. Determine the differential income or loss per pair of boots from selling to the organization.$ Should Diamond Boot Factory accept or reject the special offer?arrow_forward
- Leo Consulting enters into a contract with Highgate University to restructure Highgate's processes for purchasing goods from suppliers. The contract states that Leo will earn a fixed fee of $80,000 and earn an additional $16,000 if Highgate achieves $160,000 of cost savings. Leo estimates a 50% chance that Highgate will achieve $160,000 of cost savings. Assuming that Leo determines the transaction price as the expected value of expected consideration, what transaction price will Leo estimate for this contract? Transaction price for the contractarrow_forward"That old equipment for producing oil drums is worn out,” said Jillian Rafuse, president of Hondrich Company. "We need to make a decision quickly." The company is trying to decide whether it should rent new equipment and continue to make its oil drums internally or whether it should discontinue production and purchase them from an outside supplier. The alternatives follow: Alternative 1: Rent new equipment for producing the oil drums for $100,000 per year. Alternative 2: Purchase oil drums from an outside supplier for $17.40 each. Hondrich Company's costs per unit of producing the oil drums internally (with the old equipment) are given below. These costs are based on a current activity level of 40,000 units per year: Direct materials Direct labour Variable overhead Fixed overhead ($1.25 supervision, $1.80 depreciation, and $4.00 general company overhead) Total cost per unit $ 6.00 8.00 3.20 7.05 $24.25 The new equipment would be more efficient and, according to the manufacturer, would…arrow_forwardMighty Safe Fire Alarm is currently buying 61,000 motherboards from MotherBoard, Inc. at a price of $63 per board. Mighty Safe is considering making its own motherboards. The costs to make the motherboards are as follows: direct materials, $34 per unit; direct labor, $11 per unit; and variable factory overhead, $14 per unit. Fixed costs for the plant would increase by $80,000. Which option should be selected and why? a.make, $244,000 increase in profits b.buy, $164,090 more in profits c.buy, $80,000 more in profits d.make, $164,090 increase in profitsarrow_forward
- Markland Manufacturing manufactures desk lamps intends to increase capacity by obtaining new equipment. Two vendors have presented proposals. The purchase cost for proposal A is $30,000, and for proposal B, $80,000. Each proposal will produce lamps of the same quality. Proposal A is expected to produce lamps at $15.00/lamp, while proposal B is significantly more efficient and will produce them at $10.00/lamp. The revenue generated by the sale of each lamp is $20.00/unit. A. What is the point of indifference?B. The manufacturer expects to sell 12,000 lamps and has informed the vendors that it has chosen proposal B. The vendor of proposal A has offered to re-negotiate the purchase price of its proposal in order to win the contract. What purchase price will cause the manufacturerto reconsider its decision?arrow_forwardA distributor of fasteners is opening a new plant and considering whether to use a mechanized process or a manual process to package the product. The manual process will have a fixed cost of $36,234 and a variable cost of $2.14 per bag. The mechanized process would have a fixed cost of $84,420 and a variable cost of $1.85 per bag. The company expects to sell each bag of fasteners for $2.75. a) What is the break-even point for the manual process (in units)? b) What is the break-even point for the mechanized process (in units)? c) A point of indifference for two processes is quantity at which each process generates the same amount of profit (review video). What is the point of indifference for the two processes? (Hint: 1) Use equations to set profit of manual process equal to mechanized process and solve for quantity; 2) (Excel) If you have a break-even for each process - have only one cell that represents quantity that be used to calculates costs/revenues for each process and use Goal…arrow_forwardNovak Inc. makes unfinished bookcases that it sells for $60. Production costs are $38 variable and $10 fixed. Because it has unused capacity, Novak is considering finishing the bookcases and selling them for $72. Variable finishing costs are expected to be $9 per unit with no increase in fixed costs. Prepare an analysis on a per-unit basis that shows whether Novak should sell unfinished or finished bookcases. (If an amount reduces the net income then enter with a negative sign preceding the number, e.g. -15,000 or parenthesis, e.g. (15,000).) Net Income Sell Process Further Increase (Decrease) $ $ $ Sales per unit Variable cost per unit Fixed cost per unit Total per unit cost $ Net income per unit The bookcases processed further. $ $arrow_forward
- Before Coronado could give Langston's Landscape Company an answer, the company received a special order from Benson Building & Supply for 13,500 fireplaces. Benson is willing to pay $67 per fireplace but it wants a special design imbedded into the fireplace that increases cost of goods sold by $55,350. The special design also requires the purchase of a part that costs $5,500 and will have no future use for Coronado Company. Benson Building & Supply will pick up the fireplaces so no shipping costs are involved. Due to capacity limitations, Coronado cannot accept both special orders. Which order should be accepted? Document your decision by preparing an incremental analysis for Benson's order. (Enter loss using either a negative sign preceding the number e.g. -2,945 or parentheses e.g. (2,945).) Reject order Revenues $ Costs Cost of Goods Sold Operating Expenses Unique part Net Income $ Coronado should accept the order from Accept order $ Net Income Increase (Decrease) $ $ $arrow_forwardProvide answerarrow_forwardRadar Company sells bikes for $490 each. The company currently sells 3.700 bikes per year and could make as many as 5,000 bikes per year. The bikes cost $275 each to make: $160 in variable costs per bike and $115 of fixed costs per bike. Radar received an offer from a potential customer who wants to buy 800 bikes for $440 each. Incremental fixed costs to make this order are $47,000. No other costs will change if this order is accepted. Compute Radar's additional income (ignore taxes) if it accepts this order. Contribution margin Incremental Amount per Unit Incremental Fixed Costs Incremental income (loss) from new business The company should Incremental Income from New Businessarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education