
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
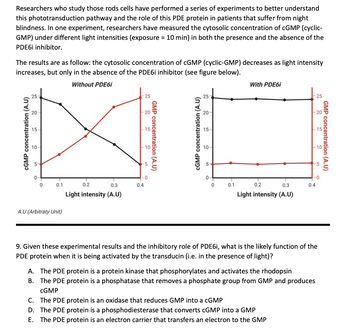
Transcribed Image Text:Researchers who study those rods cells have performed a series of experiments to better understand
this phototransduction pathway and the role of this PDE protein in patients that suffer from night
blindness. In one experiment, researchers have measured the cytosolic concentration of cGMP (cyclic-
GMP) under different light intensities (exposure = 10 min) in both the presence and the absence of the
PDE6i inhibitor.
The results are as follow: the cytosolic concentration of cGMP (cyclic-GMP) decreases as light intensity
increases, but only in the absence of the PDE6i inhibitor (see figure below).
Without PDE6i
cGMP concentration (A.U)
25
20
15-
10-
0
0
0.1
A.U (Arbitraty Unit)
0.2
0.3
Light intensity (A.U)
25
-20
-15
-10
-5
0.4
0
GMP concentration (A.U)
cGMP concentration (A.U)
25
20-
15-
10
0-
0
0.1
With PDE6i
0.2
0.3
Light intensity (A.U)
-20
C. The PDE protein is an oxidase that reduces GMP into a cGMP
D. The PDE protein is a phosphodiesterase that converts cGMP into a GMP
E. The PDE protein is an electron carrier that transfers an electron to the GMP
25
0.4
A. The PDE protein is a protein kinase that phosphorylates and activates the rhodopsin
B. The PDE protein is a phosphatase that removes a phosphate group from GMP and produces
CGMP
15
-0
5
9. Given these experimental results and the inhibitory role of PDE6i, what is the likely function of the
PDE protein when it is being activated by the transducin (i.e. in the presence of light)?
GMP concentration (A.U)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What effect does binding of the IRF protein to the IRE in the mRNA encoding ferritin have on the production of ferritin? Briefly explain why this effect is observed.arrow_forward3. a. Estimate the molecular weight of sphingosine kinase in kiloDaltons. b. Interpret the results of the experiment with the reducing agent. What does the result of Lane 2 and Lane 3 migrations tell you about the primary, secondary or tertiary structure of the sphingosine kinase?arrow_forwardTo further investigate the cellular response in photoreceptor cells, we will now look at the actual effect of cGMP within the phototransduction pathway. Again, we will compare what happens in the dark and in the presence of light to understand how an electric signal is generated in either condition. Comparing both conditions (in the dark or under the light), researchers have measured the molar concentration of cytosolic cGMP and recorded the membrane potential of rod cells by placing micro-electrodes on either side of their plasma membrane (see figure below). A negative membrane potential means that there are more negatively charged ions inside the cell compared to outside the cell, or equivalently, that there are less positively charged ions inside the cell compared to outside the cell. ● A positive membrane potential means that there are more negatively charged ions outside the cell compared to inside the cell, or equivalently, that there are less positively charged ions outside the…arrow_forward
- Consider the biochemical pathway shown here. Suppose that a strain of bacteria must synthesize compound 4 to survive and divide. Successful survival and division of bacteria is observed as growth of colonies on an agar plate. This strain of bacteria can grow colonies on minimal medium as long as it is supplemented with compound 1. You are in a lab that has isolated several mutants of this strain. You find that these mutants cannot grow on minimal medium supplemented with compound 1, though they can grow colonies if supplemented with compound 4. Considering what you know about the Beadle-Tatum experiments, which of the following statements would be one that should be true?arrow_forwardThe following kinetic data were collected for prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase, an enzyme involved in pain and inflammation. Using data in the first two columns, use a graphical analysis to determine the Vmax and the Km of the enzyme. Ibuprofen (Advil) is an inhibitor of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase. By inhibiting this enzyme, ibuprofen helps to reduce pain and fever. Using the data in the first and third columns, determine the type of inhibition that ibuprofen exerts on prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase. In the presence of the inhibitor, determine the Vmax and the Km of the enzyme. [S] mM Product formed Product formed (mmol/min) with 10 mg/mL ibuprofen mmol/min) 0.5 23.5 16.67 1.0 32.2 25.25 1.5 36.9 30.49 2.5 41.8 37.04 3.5 44.0 38.91arrow_forwardFor the following problem, indicate whether enzyme is repressed (-) or produced (+). Please show all possible outcomes.arrow_forward
- 16carrow_forwardInterleukin-6 is an important pro-inflammatory cytokine released in response to a variety of infections. Tocilizumab is a monoclonal antibody that blocks the action of IL-6. This drug cannot be given orally. Provide a biochemical explanation for this.arrow_forwardAmoeboid cells that migrate through our tissues, such as the class of white blood cells known as neutrophils, often do so in a directed manner, triggered, for instance, by chemical signals released by pathogens such as bacteria. Directed migration in response to a chemical stimulus is known as chemotaxis. Part of an efficient chemotactic response is the ability of cells to polarize. As is the case with our structurally-polar polymers like F-actin or microtubules, polarization here refers to an asymmetry in the cells, rather than an electrical charge. In this case, it involves one part of the cell becoming the “front” (or leading edge) and another the rear. In a well-polarized, migrating cell, it’s been observed that an active form of Rac (which, in turn, can activate ARP 2/3) is concentrated towards the front of the cell, whereas an active form of Rho (which, in turn, can activate formin, inhibit ADP, and activate myosin II) is found toward the rear of the cell. Based on your…arrow_forward
- The purified OXA-M290 enzyme can now be tested to determine which β-lactamase inhibitor is most effective. This inhibitor could be prescribed in combination with a β-lactam antibiotic to treat the infection caused by the E. coli KGH1 strain. Before testing inhibitors against OXA-M290, the kinetic activity of this enzyme must first be measured. The activity of OXA-M290 is measured using nitrocefin, a chromogenic β-lactam antibiotic. When nitrocefin is hydrolyzed by a β-lactamase, it changes from yellow to red in colour. The nitrocefin hydrolysis product has an extinction coefficient of 20,500 M-1 cm-1 at 486 nm. The hydrolysis of 60 μM nitrocefin by 1 nM OXA-M290 is monitored using a microplate reader. The absorbance of the wells in the plate is measured at 486 nm every 30 seconds. This experiment is carried out with three replicates, generating the following data: Time (min) Absorbance of Replicate 1 Absorbance of Replicate 2 Absorbance of Replicate 3 0.5 0.0984…arrow_forwardAssume that two pigments, red and bluc, mix to give the normal purple color of petunia petals. Separate biochemical pathways synthesize the two pigments, as shown in pathways I and Il in the accompanying diagram. "White" refers to compounds that are not pigments (total lack of pigment results in a white petal). Red pigment forms from a yellow intermediate that is normally at a concentration loo kow to color petals. Bluc mixed with yellow makes green. Assume that no mutations are lethal. Pathway I.. White Blue Pathway I White, Yellow Red Pathway II White, White, A third pathway, whose compoundk do not contribute pelal pigmentation, normally docs not allfect the bluc and red pathways. However, if one of its intermediates (white3) should build up in concentration, it can be converted into the ycllow intermediate of the red pathway. In the diagram, the letiers A through E represent enzymes. The enzymes' correspoonding genes, all of which are unlinked, may be symbolized by the same letters.…arrow_forwardThe enzymatic activity of PFK1 is generally measured by set- ting up a coupled enzyme assay system whereby aldolase, triose phos- phate isomerase, and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase are added to the assay mixture. For the latter enzyme, NADH is added and its change in concentration is readily monitored at 340 nm. Write the chain of reactions catalyzed by these enzymes using structural formulas, label substrates and products, and explain why the coupled en- zyme assay system leads to oxidation of NADH. While the chain of reac- tions is similar to those in glycolysis, there is a critical difference because of the dehydrogenase enzyme. Describe how this enzyme causes the chain of reactions to differ from those in glycolysis.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education