
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
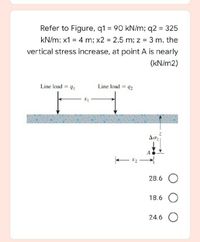
Transcribed Image Text:Refer to Figure, q1 = 90 kN/m; q2 = 325
%3D
%3D
kN/m; x1 = 4 m; x2 2.5 m; z = 3 m. the
vertical stress increase, at point A is nearly
(KN/m2)
Line load = 91
Line load = 42
Ao
28.6 O
18.6 O
24.6 O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the shear stress at points A, B, C andD for the following section. Also determine the maximum shear stress, then plot the shear stress distribution. Given: V = 10 kN.arrow_forwardGiven: 1. Structural Component: Beam 300 mm x 400 mm Column 400 mm x 400 mm Slab thickness 110 mm 2. Dead Load: Super Imposed dead load = 4.5 KPa (including slab weight) CHB = 3.11 KPa 3. Seismic Parameter: Soil Profile - Sb Closest distance to the source - 10 km Ductility Coefficient R = 8.0 Seismic Zone Z=0.40 Ct = 0.0731 A. Compute the DESIGN BASE SHEAR (V = Cv*I*W /R*T). B. Compute the Minimum DESIGN BASE SHEAR (V =0.11Ca*I*W).arrow_forward100 kN point load and 40 kN/m line load are applied on the ground surface as shown. Compute the variation of the vertical stress increment at the depth z = 5 m directly underneath line AB. Plot the results from Points A to B. 100 kN point load 40 kN/m line load - 5 m 10 m 5 m (Plane view)arrow_forward
- The velocity gradient is 1000 m/s. The viscosity u= is 1.2*10^-4* N-s/(m^2). The shear stress is (a) 0.12 N/m² (b) 12N/ (m^2) (c) 1.2x 107 N/m² (d) 12 * 10^-5 * N/(m^2)arrow_forwardPlease solve thisarrow_forward19).png + Add to t 12. What is the vertical effective stress at point, X in the soil profile given below? V 12 ft Water, Yw = 62.4 10 ft Loose sand, Ysar 115 pcf Dense sand, Ysa 130 pcf A. 1,878 psf B. 3,750 psf C. 4,499 psf D. None of the above. Q J 20 ft X C Ⓒ A Ca 6 7 Edit & Create v ENG INarrow_forward
- 4. Estimate the profile of vertical effective stresses for Zw= 100m and for Zw=3000m. Compare results. Z = 2 m A 16 Water surface Zw Soil surface Ysat = 17 K (108.3 pcf)arrow_forwardH.Q 5 Figure below shows an embankment load on a silty clay soil layer. Determine the stress increase at points A, B, and C that are located at a depth of 5 m below the ground surface. + 6 m I Center line IV:2H IV:2H 10m y=17 kN/marrow_forwardQ2: For the soil element shown in the figure. Draw Mohr circle, locate OP (origin point), then find the stresses inclined at: 1- 75° from the horizontal plane. 2- With the horizontal plane.arrow_forward
- Subject: Soil Mechanicsarrow_forwardIn a direct shear test on sand (C = 0), area of circular box was 50 cm², normal load was 750 kN and failure load was 460 kN, ☀ will be : (a) 31.5⁰ (c) 35⁰ (b) 29.3⁰ (d) 28.5⁰arrow_forwardA strip load of q = 100 kN/m2 is applied over a width, B = 10 m. Determine the increase in vertical stress at point A located z = 5 m below the surface. Given: x = 5 m. Please have the answer in four (4) decimal places. = load per unit area Figure 3.15arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning