
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
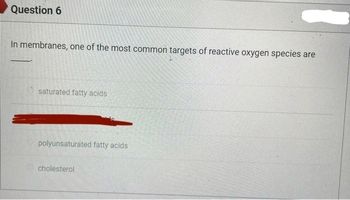
Transcribed Image Text:Question 6
In membranes, one of the most common targets of reactive oxygen species are
saturated fatty acids
polyunsaturated fatty acids
cholesterol
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Question 21 Two macromolecules, such as proteins, can adhere tightly and specifically to each other. How can weak intermolecular forces lead to such strong adherence? O the weak forces are readily converted to covalent bonds, thus leading to strong adherence between molecules O if the weak forces are correctly aligned they can become as strong as covalent bonds O adhesion is strong because the weak forces can be involved in condensation reactions O the weak forces can become very strong once non-polar groups are excluded from the inside of the molecules O adherence can be quite strong by having many weak forces involved in molecular adhesion • Previousarrow_forwardQuestion 12 Which of the following best explains the relatively more complex folded structure that an RNA molecule assumes? A B с D RNA molecules do not contain a pentose sugar in their backbone, which allows them to be more structurally flexible. RNA molecules contain the nitrogenous base uracil, which can pair with several other ni- trogenous bases in the RNA molecule. RNA molecules contain negatively charged phosphate groups in their backbone, which allows the molecule to bend into complex shapes. RNA molecules are made of only four types of nucleotides, which allows their nitroge- nous base to pair more readily.arrow_forwardQuestion 7 The malate transporter in the mitochondrial inner membrane is involved in two important biochemical processes: one catabolic, and one anabolic. What are they? Transport of NAD* from glycolysis from the cytosol to the matrix for oxidative phosphorylation, and the last step of glycolysis O A. The citric acid cycle, and the last step of glycolysis OB. The glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle system, and the first gluconeogenesis bypass Transport of FADH, from beta oxidation from the cytosol to the matrix for oxidative phosphorylation, and the first gluconeogenesis bypass OF Transport of NADH from glycolysis from the cytosol to the matrix for oxidative phosphorylation, and the first gluconeogenesis bypassarrow_forward
- Question 5 Which of the following subunits of ATP synthase is correctly described? a: site of ATP synthesis y: protons are transferred to this subunit, determines the number of protons transferred per ATP formed a: contains two half channels for transferring protons across the membranearrow_forwardQUESTION 5 Many bioactive compounds are derived from amino acids. This compound, illegal in most countries, is used as a hallucinogen used both for ritualistic purposes in some cultures and as a recreational drug. It is derived from an amino acid through removal of the backbone carboxylic acid group and dimethylation of the amino group. The amino acid from which it is derived must be: (Write out the entire name; Spelling matters, but case does not; Do not include L- or D- in the name; For acidic amino acids write the full name, e.g. "so-and-so acid") N ZIarrow_forwardQUESTION 20 Some of the stem cells in bone become osteoclasts during differentiation. Researchers have shown that chemical signals called cytokines are released into the extracellular fluid by bone stem cells in response to environmental stimuli. The researchers also have shown that the cytokines induce these same bone stem cells to differentiate into osteoclasts. This example illustrates how a(n). signal functions in the human body. O a. autocrine b. hormone O c. paracrine O d. juxtacrine e. intracellulararrow_forward
- Question 11 The breakdown of large molecules by the enzymatic addition of water is an example of what kind of reaction? O 1. oxidation O 2. reduction O 3. condensation O 4. hydrolysis O 5. decarboxylation A Moving to another question will save this response. W AR SONY ASSIST BUtton, Onetoucharrow_forwardQUESTION 1 The Wnt signaling pathway component, Dsh, effects the action of B catenin by: O A. inhibiting the function of axin in the destruction complex O B. blocking GSK-3B from joining the destruction complex O C. stimulating ubiquitination of B catenin O D. causing its release into the cytosol from the plasma membrane complex O E. causing an increase in phophorylation of B catenin QUESTION 2 PCR can be used to identify the breakage points of mtDNA that are joined to form a mitochondrial genome with a deletion. This techni que uses: O A. two primers outside the deleted region; a long PCR extension segment. O B. one primer within the deleted region and one primer outside the deleted region; a long PCR extension segment O C. one primer within the deleted region and one primer outside the deleted region; a short PCR extension segment O D. two primers outside the deleted region; a short PCR extension segment O E. two primers within the deleted region; a short PCR extension segmentarrow_forwardQUESTION 10 In the deoxy state of HB, which of the following does not occur? O An intra-chain salt bridge between Val 98 and Tyr 145. O An intra-chain salt bridge between Histidine 146 and Aspartate 94 side chains O A peptide bond between Tyr 145 and His 146. O An inter-chain salt bridge between Histidine 146 and Lys 40arrow_forward
- QUESTION 5 In RNA, adenine pairs with bonds. with bonds and guanine pairs with with uracil, triple, thymine, double uracil, double, thymine, triple uracil, triple, cytosine, double O uracil, double, cytosine, triplearrow_forwardQuestion 9 The product of the oxidation of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is: O 2-phosphoglycerate O 1,3-biphosphoglycerate O phosphoenolpyruvate O fructose 1,6-biphosphate oxaloacetate Previcarrow_forwardQuestion 2 of 17 Fill in the blanks: is the total number of rings present in cholesterol is the total number of carbons present in cholesterol is the sphingolipid that is a major component of biological membranes is a term that refers to substances that contain hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts is the trivial name of a saturated fatty acid containing 18 carbonsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON