
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
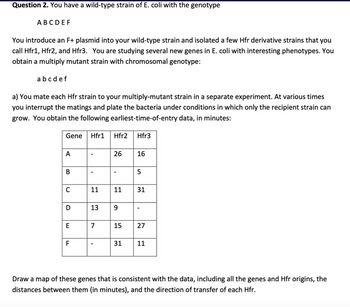
Transcribed Image Text:Question 2. You have a wild-type strain of E. coli with the genotype
A B C D EF
You introduce an F+ plasmid into your wild-type strain and isolated a few Hfr derivative strains that you
call Hfr1, Hfr2, and Hfr3. You are studying several new genes in E. coli with interesting phenotypes. You
obtain a multiply mutant strain with chromosomal genotype:
a b c d e f
a) You mate each Hfr strain to your multiply-mutant strain in a separate experiment. At various times
you interrupt the matings and plate the bacteria under conditions in which only the recipient strain can
grow. You obtain the following earliest-time-of-entry data, in minutes:
Gene Hfr1 Hfr2 Hfr3
A
B
C
D
E
F
11
13
7
I
26 16
11
9
5
31
15 27
31 11
Draw a map of these genes that is consistent with the data, including all the genes and Hfr origins, the
distances between them (in minutes), and the direction of transfer of each Hfr.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Are you a hidden heterozygote? A PCR analysis (part2) Agarose gel electrophoresis and interpretation la: Several factors (including agarose gel concentration, time and current) affect migration of DNA fragments through the agarose gel. Briefly explain how each of these factors affects DNA migration. Agarose gel concentration: Time: Voltage: 1b: Do DNA fragments move towards the positive or negative end of the gel box? Explain your answer. 1c: What is the purpose of the Tris-Acetate-EDTA (TAE) buffer that the agarose gel is prepared with and submerged in for running? What would happen if you used water to prepare and run the gel instead of TAE buffer? 1d: If the student is homozygous for the brown allele, how many bands will they see in the lanes for the blue and brown allele samples? (circle one) Brown sample: 0 Blue sample: 1 2 more than two. 1 2 more than two. le: If the student is homozygous for the blue allele, how many bands will they see in the lanes for the blue and brown allele…arrow_forwardQUESTION 5: Should PCR primers be complementary to each other? Explain the reasoning for your answer.arrow_forwardWhat is one of the end results of site-specific recombination? Diagram your answer and answer in 1-2 sentences.arrow_forward
- I’m having trouble finding which answer would be acceptable can you please help?arrow_forwardParts a-earrow_forwardA 2.0kb bacterial plasmid ‘BS1030’ is digested with the restriction endonuclease Sau3A; the plasmid map is depicted in the diagram below and the Sau3A (S) restriction sites are indicated. Which of the following DNA fragments do you expect to see on an agarose gel when you run Sau3A-digested plasmid ‘BS1030’ DNA? a. 250 bp, 450 bp, 550 bp, 1.1 kb, 1.5 kb and 2.0 kb b. 2.0kb c. 250 bp, 400 bp, 450 bp, 500 bp and 550 bp d. 100 bp, 200 bp, 250 bp, 400 bp, 500 bp and 550 bparrow_forward
- What is the final volume of the individual PCR reactions we are making?arrow_forwardTHE MOLECULAR GENETICS OF SICKLE CELL ANEMIA The following is the base sequence of DNA that codes for first eight amino acids of the B chain of hemoglobin. The B chain of hemoglobin contains a total of 147 amino acids so this is a small part of the entire gene. DNA Template Strand: TACCACGTGGACTGAGGACTCCTC 1. What is the minimum number of DNA nucleotides in this whole gene? 2. What is the sequence of bases on the strand of DNA that is complementary to the template strand? 3. What mRNA will be formed from the template strand of DNA? 4. What amino acids will this mRNA code for? 5. If the 20th base in the template strand of the DNA is changed from T to A, rewrite the new template strand below. 6. When the template strand of the DNA is changed, this is referred to as a mutation. What kind of mutation is this? 8. 7. What mRNA will be formed from the mutated template strand of DNA? What amino acids will this new mRNA from the mutated template strand code for? 9. Are these new amino acids the…arrow_forwardQuestion 13 If a recombinant plasmid (below) was obtained inserting DNA into the BamHI site, screening for the recombinant plasmid can be done by which of the following technique? A) Plate on agar plates containing tetracycline and ampicillin. (B) Plate on agar plates containing ampicillin, C) Plate the cells on agar containing ampicillin then surviving colonies are plated on another agar plates with tetracycline. D) Plate on agar plates containing tetracycline. Pal Pord- ampr EcoRI ПРИ Ano pBR322 (4363 bases) Prull BamHI Sall let" Aval -Sallarrow_forward
- Question 1: Look at the following normal and mutant DNA sequences. Normal Sequence (5'-3'): ATG AAC GTT ATC GCA Mutated Sequence (5'-3'): ATG AAT GTC ATC GCA a) What type of mutation has occurred (be specific)? b) Fill in the table for the normal and mutated sequences. Starting with the given 5'-3' sequence, input the complementary DNA, transcribed RNA from the 3'-5' DNA and translated polypeptide sequence for both. Hint: use the codon table! Normal sequence Mutant sequence DNA 5'-3' (given) DNA 3'-5' RNA Polypeptide (use 3 letter codes) c) Based on parts A and B above, what is the ultimate effect this mutation has had on the polypeptide? (1 sentence summary)arrow_forwardQuestion 2. For your senior research, you end up studying the life cycle of an animal virus whose genome consists of a single circular, double-stranded DNA molecule. Your project is to define the number and location of the origin(s) of replication and to determine whether replication proceeds in one (unidirectional) or both (bidirectional) directions away from an origin. To accomplish this, you isolate many identical strands of DNA that have already been partially replicated. You cleave each piece of DNA exactly once with a restriction enzyme. You then observe the cut pieces of DNA using an electron microscope. Below is a schematic representation of what you observe. Remember that each line represents a different piece of DNA, and not a fragment of a larger piece. Using this data, answer the following questions: A) How many origins of replication do you think the viral genome has, and why do you think this? 30: F2 #3 *** E D 80 F3 54 $ 4 F4 R LL % 5 F5 T G B) Do your data support…arrow_forwardThe region of the normal hemoglobin gene used for genetic testing for sickle cell anemia contains a restriction site such that homozygous normal individuals show two DNA fragments. If a single nucleotide change in hemoglobin destroys that restriction site, then how many DNA fragments will be visible on a gel from individuals that are homozygous mutant? What about heterozygotes?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education