
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
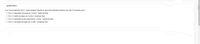
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 2
In a Cournot duopoly firm 1's best-response function is downward sloping because when firm 2 produces more:
O Firm 1's marginal cost goes up, so firm 1 produces less.
O Firm 1's total cost goes up, so firm 1 produces less.
O Firm 1's marginal revenue goes down, so firm 1 produces less.
O Firm 1's average cost goes up, so firm 1 produces less.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two duopolists are sharing a market in which they are contemplating whether to compete or to cooperate. If they cooperate and behave like a monopolist they will share the monopolist profit of $1800. If they compete each will get a profit of $800 but if one them cooperates while the other chooses to compete the one who cooperates gets $700 while the one who competes will end up with $1000. Set-up the game, explain the process and show the Nash-equilibrium reached when the game is played.arrow_forwardCompany A and Company B are competing oligopolists. Both companies are considering increasing or maintaining their prices. The payoff matrix shows the profits of the companies in millions based on their possible actions.. Company A Increase Price Company B Increase Price Maintain Price $50, $40 Maintain Price $55, $45 $35, $30 $60, $35 The government offers a $5 million subsidy to maintain current pricing. What is the expected outcome of the new payoff matrix, given the subsidy? The Nash equilibrium changes, and both companies will maintain their prices The Nash equilibrium changes, and both companies will increase their prices. The Nash equilibrium remains the same, and both companies will increase their prices Company A will increase its price, while Company B maintains its price. Company A will maintain its price, while Company B increases its pricearrow_forwardTwo firms produce a homogeneous good and compete in price. Prices can only take integer values. The demand curve is Q = 6 p, where p denotes the lower of the two prices. The lower - priced firm meets all the market demand. If the two firms post the same price p, each one gets half the market demand at that price, i. e., each gets (6p)/2. Production cost is zero.a) Show that the best response to your rival posting a price of 6 is to post the monopoly price of 3. What is the best response against a rival's price of 4? of 5?arrow_forward
- Please help with these two: 1. Consider a Duopoly model, in which two firms decide a quantity simultaneously. If they collude (setting the total quantity together), then each firm can earn (higher, or lower) profit than in the Cournot equilibrium. 2. Consider a collusion with two firms. The joint profit is maximized by setting quantity and price together. Each firm sells the agreed amount. However, believing that the other firm sells the agreed amount, there is always a temptation for the firm sell (more, or less) than the agreed amount.arrow_forwardQUESTION 13 Consider a market where two firms (1 and 2) produce differentiated goods and compete in prices. The demand for firm 1 is given by D₁(P₁, P2) = 140 - 2p1 + P2 and demand for firm 2's product is D2 (P1, P2) 140 - 2p2 + P1 Both firms have a constant marginal cost of 20. What is the Nash equilibrium price of firm 1? (Only give a full number; if necessary, round to the lower integer; no dollar sign.)arrow_forwardThe Bertrand model of oligopoly reveals that: capacity constraints are not important in determining market performance. perfectly competitive prices can arise in markets with only a few firms. changes in marginal cost do not affect prices. All of the statements associated with this question are true. QUESTION 2 If firms are in Cournot equilibrium: each firm could increase profits by unilaterally increasing output. each firm could increase profits by unilaterally decreasing output. firms could increase profits by jointly increasing output. firms could increase profits by jointly reducing output. OOOarrow_forward
- Calculate the Herfindahl index for a duopoly market where each firm has equal market. Calculate the Herfindahl index for a three-firm oligopoly market in which one firm hasa 80% market share and the other firms each have 10% market share. iii. Calculate the Herfindahl index for a 10-firm oligopoly in which each firm has equal market shares. iv. Which of the above markets is the least competitive? Justify your position.arrow_forward1. Perloff Chapter 14, Exercise 3.13 3.13 A duopoly faces an inverse market demand function of p = 120 - Q. Firm 1 has a constant marginal cost of 20. Firm 2's constant marginal cost is 40. Calculate the output of each firm, market output, and price in (a) a collusive equilibrium or (b) a Nash-Cournot equilibrium. (Hint: See Solved Problem 14.10.) Marrow_forwardIn a Cournot duopoly firm 1’s best-response function is downward sloping because when firm 2 produces more: A) Firm 1’s marginal cost goes up, so firm 1 produces less. B) Firm 1's average cost goes up, so firm 1 produces less. C) Firm 1’s marginal revenue goes down, so firm 1 produces less. D) Firm 1’s total cost goes up, so firm 1 produces less.arrow_forward
- To advertise or not to advertise Suppose that Creamland and Dairy King are the only two firms that sell ice cream. The following payoff matrix shows the profit (in millions of dollars) each company will earn depending on whether or not it advertises: Dairy King Advertise Doesn't Advertise Creamland Advertise 10, 10 18, 2 Doesn't Advertise 2, 18 11, 11 For example, the upper right cell shows that if Creamland advertises and Dairy King doesn't advertise, Creamland will make a profit of $18 million, and Dairy King will make a profit of $2 million. Assume this is a simultaneous game and that Creamland and Dairy King are both profit-maximizing firms. If Creamland decides to advertise, it will earn a profit of _________ million if Dairy King advertises and a profit of ________ million if Dairy King does not advertise. If Creamland decides not to advertise, it will earn a profit of __________ million if Dairy King advertises and a profit of _________…arrow_forwardDeviating from the collusive outcome Please check the image there is a graph Mays and McCovey are beer-brewing companies that operate in a duopoly (two-firm oligopoly). The daily marginal cost (MC) of producing a can of beer is constant and equals $0.60 per can. Assume that neither firm had any startup costs, so marginal cost equals average total cost (ATC) for each firm. Suppose that Mays and McCovey form a cartel, and the firms divide the output evenly. (Note: This is only for convenience; nothing in this model requires that the two companies must equally share the output.) Place the black point (plus symbol) on the following graph to indicate the profit-maximizing price and combined quantity of output if Mays and McCovey choose to work together. When they act as a profit-maximizing cartel, each company will produce cans $ and charge $ per can. Given this information, each firm earns a daily profit of $ , so the daily total industry…arrow_forwardsolve i and ii please.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education