
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
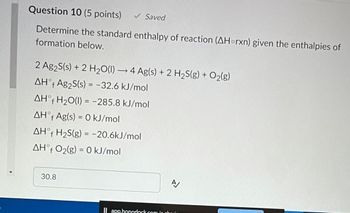
Transcribed Image Text:Question 10 (5 points) ✓ Saved
Determine the standard enthalpy of reaction (AHorxn) given the enthalpies of
formation below.
2 Ag2S(s) + 2 H₂O(1)→ 4 Ag(s) + 2 H₂S(g) + O₂(g)
AHᵒf Ag₂S(s) = -32.6 kJ/mol
AHᵒf H₂O(1) = -285.8 kJ/mol
AHᵒf Ag(s) = 0 kJ/mol
AHᵒf H₂S(g) = -20.6kJ/mol
AHᵒf O₂(g) = 0 kJ/mol
30.8
Il app.honorlock .com is aki
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the following reaction. CH3OH(g) CO(g) + 2 H2(g) H = +90.7 kJ (a) Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? endothermicexothermic (b) Calculate the amount of heat transferred when 40.0 g of CH3OH(g) are decomposed by this reaction at constant pressure.H = kJ(c) If the enthalpy change is 11.0 kJ, how many grams of hydrogen gas are produced? g(d) How many kilojoules of heat are released when 13.5 g of CO(g) reacts completely with H2(g) to form CH3OH(g) at constant pressure?H = kJ(e) Calculate E when 360.0 g of CH3OH(g) completely reacts at a constant temperature of 300 K and constant pressure of 0.95 atm. R = 8.314 J/mol*K and R = 0.08206 atm*L/mol*K kJ HopHelpCh5N1arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction. CH3OH(g) CO(g) + 2 H2(g) H = +90.7 kJ (a) Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? exothermic endothermic (b) Calculate the amount of heat transferred when 55.0 g of CH3OH(g) are decomposed by this reaction at constant pressure.H = kJ(c) If the enthalpy change is 11.0 kJ, how many grams of hydrogen gas are produced? g(d) How many kilojoules of heat are released when 12.0 g of CO(g) reacts completely with H2(g) to form CH3OH(g) at constant pressure?H = kJ(e) Calculate E when 450.0 g of CH3OH(g) completely reacts at a constant temperature of 300 K and constant pressure of 0.95 atm. R = 8.314 J/mol*K and R = 0.08206 atm*L/mol*Karrow_forwardConsider the following reaction. CH3OH(g) CO(g) + 2 H2(g) H = +90.7 kJ (a) Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? endothermicexothermic (b) Calculate the amount of heat transferred when 40.0 g of CH3OH(g) are decomposed by this reaction at constant pressure.H = kJ(c) If the enthalpy change is 11.0 kJ, how many grams of hydrogen gas are produced? g(d) How many kilojoules of heat are released when 13.5 g of CO(g) reacts completely with H2(g) to form CH3OH(g) at constant pressure?H = kJ(e) Calculate E when 360.0 g of CH3OH(g) completely reacts at a constant temperature of 300 K and constant pressure of 0.95 atm. R = 8.314 J/mol*K and R = 0.08206 atm*L/mol*K kJ HopHelpCh5N1arrow_forward
- A student runs two experiments with a constant-volume "bomb" calorimeter containing 1300. g of water (see sketch at right). thermometer stirrer First, a 6.000 g tablet of benzoic acid (C,H,C0,H) is put into the "bomb" and burned completely in an excess of water oxygen. (Benzoic acid is known to have a heat of combustion of 26.454 kJ/g.) The temperature of the water is insulation observed to rise from 13.00 °C to 40.13 °C over a time of 10.0 minutes. Next, 5.200 g of ethane (C,H) are put into the "bomb" and similarly completely burned in an excess of oxygen. This time the temperature of the water rises from 13.00 °C to 53.96 °C. chemical reaction "bomb" Use this information, and any other information you need from the ALEKS Data resource, to answer the questions below about this reaction: A "bomb" calorimeter. 2C,H,(g) + 70,(g) 4CO,(g) + 6 H,0 (g) Be sure any of your answers that are calculated from measured data are rounded to the correct number of significant digits. Note for advanced…arrow_forwardQUESTION 18 PLEASEarrow_forwardUsing the equations determine the enthalpy for the reactionarrow_forward
- A student runs two experiments with a constant-volume "bomb" calorimeter containing 1100. g of water (see sketch at right). thermometer stirrer First, a 5.500 g tablet of benzoic acid (C,H,CO, H) is put into the "bomb" and burned completely in an excess of water oxygen. (Benzoic acid is known to have a heat of combustion of 26.454 kJ/g.) The temperature of the water is observed insulation to rise from 15.00 °C to 42.56 °C over a time of 10.3 minutes. Next, 5.720 g of acetaldehyde (C2H,O} are put into the "bomb" and similarly completely burned in an excess of oxygen. This time the temperature of the water rises from 15.00 °C to 40.53 °C. chemical reaction "bomb" Use this information, and any other information you need from the ALEKS Data resource, to answer the questions below about this reaction: A "bomb" calorimeter. 2C,H,0(g) + 50, (g) 4CO, (g) + 4H,0 (g) Be sure any of your answers that are calculated from measured data are rounded to the correct number of significant digits. Note…arrow_forward5(a)arrow_forwardConsider the balanced reaction 4 A + 9 B → 8 C + 8 D and the enthalpies of formation provided in the table below. AH Compound (kJ/mol) A 170.8 231.1 D -98.4 Suppose that the AH of the overall reaction is -2,029.3 kJ/molxn. Calculate the value of the AHf of C in kJ/mol. Report your answer to three decimal places (ignore significant figures).arrow_forward
- Question 9 of 24 Determine the enthalpy of reaction for HCI(g) + NaNO2(s) → HNO2(1) + NaCI(s) 2NACI(s) + H2O(1) → 2HCI(g) + Na20(s) AH° = -507.1 kJ/mol NO(g) + NO2(g) + Na,0(s) → 2NANO2(s) AH° = -427.0 kJ/mol NO(g) + NO2(g) → N20(g) + O2(g) AH° = -43.01 kJ/mol 2HNO2(1) → N,0(g) + O2(g) + H2O(1) AH° = +34.02 kJ/mol %3D %3D %3D Tap here or pull up for additional resources @ #3 24 & 2 8.arrow_forwardUsing Enthalpies of formation provided on the exam determine the change in enthalpy (kJ/mol) for the following reaction. Do not type units into your answer. CH4(g) + 2 O2(g) ⟶⟶ CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l) Δ?=?ΔH=?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY