
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
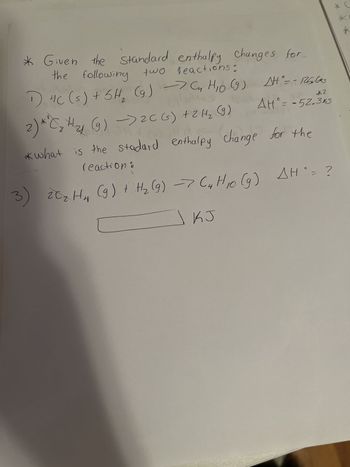
Transcribed Image Text:* Given the Changes for
the following two
Standard enthalpy
two reactions:
1) 4C (s) + 6H₂ (g) → Cn H₁0 (9) A°= -125600
tallins
*2
AH° = -52.3k5
COM
2) **C₂ H₂ (g) → 2C(s) + 2 H₂ (9)
14
*what is the stadard enthalpy change for the
reaction :
C
3) 20₂ H₁₂ (9) + H₂ (9) -> (4 H10 (9) AH`= ?
KJ
*
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Using the standard enthalpies of formation Hf0 given, determine the enthalpy of this reaction. AX2 (g) + 2Y2 (g) → AX2Y4 (g) Hf0 values AX2 (g) = - 267.4 kJ/mol Y2 (g) = 126.2 kJ/mol AX2Y2 = 324.5 kJ/mol For full credit: Round your answer to the tenths place so that there are no decimals. (EX: 12.3 = 12) Include the correct unit.arrow_forward< Question 21 of 29 O Attempt 2 When 0.376 g of sodium metal is added to an excess of hydrochloric acid, 3910 J of heat are produced. What is the enthalpy of the reaction as written? 2 Na(s) + 2 HCI(aq) 2 NaCl(aq) + H2(g) Enthalpy of reaction: 478.35 kJ Incorrectarrow_forwardGiven the two thermochemical equations below, find the enthalpy change for the reaction: N2H4 (l) + H2 (g) → 2 NH3 (g) delta H = ? Given: N2O4 (g) + 3 H2 (g) → 2 NH3 (g) + 2 O2 (g) delta H = – 100.96 kJ N2O4 (g) + 2 H2 (g) → N2H4 (l) + 2 O2 (g) delta H = + 41.47 kJ Select one: a. – 142.43 kJ b. – 59.49 kJ c. + 41.47 kJ d. + 59.49 kJ e. + 142.43 kJ f. none of these g. – 100.96 kJarrow_forward
- when 11.0 g naoh is dissolved in 100.0 g of water in a coffee-cup calorimeter, the temperature rises from 25.22c to 48.00c. what is the enthalpy change?arrow_forwardUse Hess’s law to calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction WO3(s) + 3H2(g) —> W(s) +3H2O(g) from the following data: 2W(s) + 3O2(g) —> 2 WO3(s) H=-1685.4 2H2(g) + O2(g) —> 2H2O(g) H=-477.84arrow_forwardSulfur dioxide, SO2(g), can react with oxygen to produce sulfur trioxide, SO3(g), by the reaction 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g) The standard enthalpies of formation for SO2(g) and SO3(g) are AH; [SO2(g)] = -296.8 kJ/mol AH; [SO3(g)] = -395.7 kJ/mol Calculate the amount of energy in the form of heat that is produced when a volume of 2.25 L of SO2(g) is converted to 2.25 L gas behavior. of SO3(g) according to this process at a constant pressure and temperature of 1.00 bar and 25.0 °C. Assume ideal AH= kJarrow_forward
- The enthalpy change for the oxidation of butane, C4H₁0, is measured by calorimetry. C4H10 (g) + 13/2 O2(g) → 4 CO2 (g) +5 H₂O(l) A₂H = -2877.6 kJ/mol-rxn Use this value, along with the standard enthalpies of formation of CO2(g) and H₂O(l) (-393.509 kJ/mol and -285.83 kJ/mol respectively), to calculate the enthalpy of formation of butane, C4H10, in kJ/mol. Enthalpy of formation = Submit Answer OCT 30 Try Another Version tv kJ/mol S4 I all 9 item attempts remaining Cengage Learning | Cengage Technical Support A MacBook Pro 7 ( O 04arrow_forwardMethane (CH4) burns in oxygen via the following reaction:CHa(g) + 202(g) > CO2(g) + 2H20(g) ; AH= -890 kJWhat is the enthalpy change for the combustion of 148.2 grams of methane ?arrow_forwardThe enthalpy changes, AH, for three reactions are given. H, (g) + H, O(1) AH= -286 kJ/mol Ca(s) + 2 H*(aq) Ca2+(aq) + H, (g) Ca+(aq) + H, O(1) AH = -544 kJ/mol CaO(s) + 2 H*(aq) AH = -193 kJ/mol Using Hess's law, calculate the heat of formation for CaO(s) using the reaction shown. Ca(s) + O,(g) CaO(s) AH kJ/molarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY