
Biology 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781947172517
Author: Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
What is the correct answer?
Transcribed Image Text:CollegeBoard
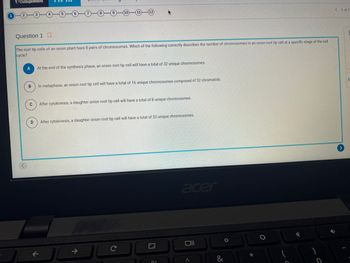
Question 1
The root tip cells of an onion plant have 8 pairs of chromosomes. Which of the following correctly describes the number of chromosomes in an onion root tip cell at a specific stage of the cell
cycle?
A
At the end of the synthesis phase, an onion root tip cell will have a total of 32 unique chromosomes.
B
In metaphase, an onion root tip cell will have a total of 16 unique chromosomes composed of 32 chromatids.
C
D
After cytokinesis, a daughter onion root tip cell will have a total of 8 unique chromosomes.
After cytokinesis, a daughter onion root tip cell will have a total of 32 unique chromosomes.
06
acer
Oll
O
*
✓
< 1 of 1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Figure 6.4 Which of the following is the correct order of events in mitosis? a. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The kinetochore becomes attached to the initotic spindle. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides. The sister chromatids separate. b. The kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. The sister chromatids separate. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides. c. The kinetochore becomes attached to metaphase plate. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The kinetochore breaks down and the sister chromatids separate. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides. d. The kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The kinetochore breaks apart and the sister chromatids separate. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides.arrow_forwardIf the M checkpoint is not cleared, what stage of mitosis will be blocked? prophase prometaphase metaphase anaphasearrow_forwardThe fusing of Golgi vesicles at the metaplhase plate of dividing plant cells forms what structure? cell plate actin ring cleavage furrow mitotic spindlearrow_forward
- Figure 28.11 depicts the eukaryotic cell cycle. Many cell types “exit� the cell cycle and don’t divide for prolonged periods, a state termedG0; some, for example neurons, never divide again. a. In what stage of the cell cycle do you suppose a cell might be when it exits the cell cycle and enters G0? b. The cell cycle is controlled by checkpoints, cyclins, and CDKs. Describe how biochemical events involving cyclins and CDKs might control passage of a dividing cell through the cell cycle.arrow_forwardWhich is not a stage of mitosis? a. prophase b. metaphase c. interphase d. anaphasearrow_forwardSeparation of the sister chromatids is a characteristic of which stage of mitosis? prometaphase metaphase anaphase telophasearrow_forward
- The cell above is a lung cell of a salamander. In which stage of mitosis is it? What are the structures visible in green and blue fluorescence?arrow_forwardIdentical copies of chromatin held together by cohesin at the centromere are called.______ histones nucleosomes chromatin sister chromatids.arrow_forwardMatch each term with its best description. __ cell plate a. lump of cells __ spindle b. made of microfilaments __ tumor c. divides plant cells __ cleavage furrow d. organize(s) the spindle __ contractile ring e. dangerous metastatic cells __ cancer f. made of microtubules __ centrosomes g. indentation __ telomere h. shortens with agearrow_forward
- The chromosomes become visible under a light microscope during which stage of mitosis? prophase prometaphase metaphase anaphasearrow_forwardMatch each stage with the events listed. _____ metaphase a. sister chromatids move apart _____ prophase b. chromosomes condense _____ telophase c. new nuclei form _____ interphase d. chromosomes aligned midway between spindle poles _____ anaphase e. G1, S, G2 _____ cytokinesis f. cytoplasmic divisionarrow_forwardAttachment of the mitotic spindle fibers to the kinetochores is a characteristic of which stage of mitosis? prophase prometaphase metaphase anaphasearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...
Biology
ISBN:9781337408332
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...
Biology
ISBN:9781305073951
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning